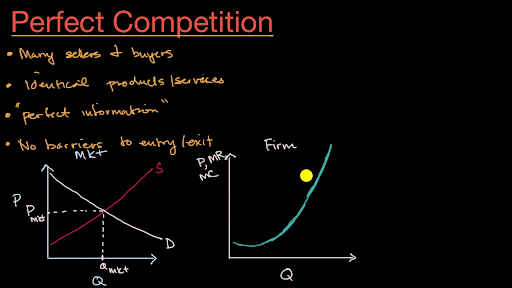
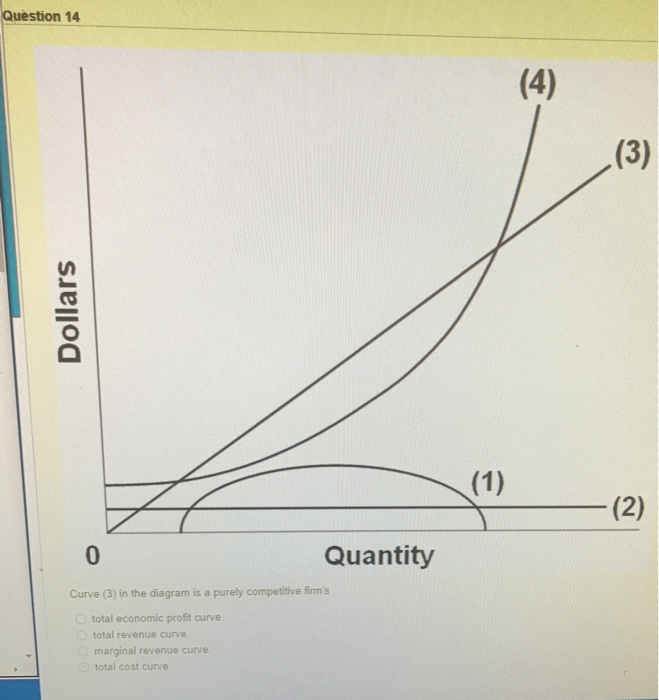
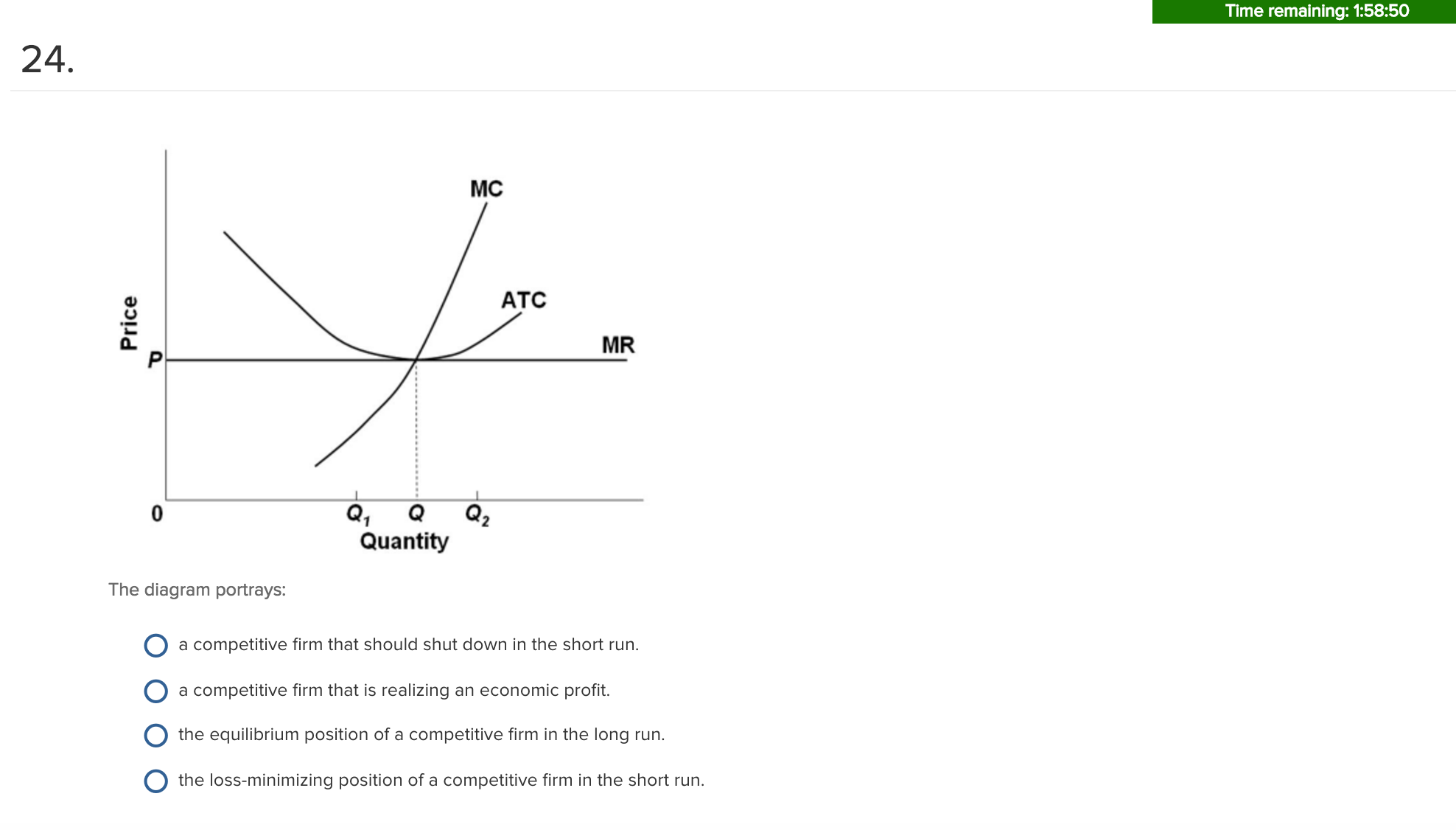
37 curve (2) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's
2. Assume the price of a product sold by a purely competitive firm is $5. ... Using the diagram above, in order to maximize profits, this firm would produce ... Curve (2) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's: marginal revenue curve. A purely competitive seller should produce (rather than shut down) in the short run:
Curve (2) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's. Multiple Choice A. marginal revenue curve. Correct B. total economic profit curve.

Curve (2) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's
2. In which of the following industry structures is the entry of new firms the most difficult? ... The marginal revenue curve of a purely competitive firm:. 2. Economists use the term imperfect competition to describe: . ... The marginal revenue curve of a purely competitive firm:. 2. Assume for a competitive firm that MC = AVC at $12, MC = ATC at $20, ... Refer to the above diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. Curve C ...
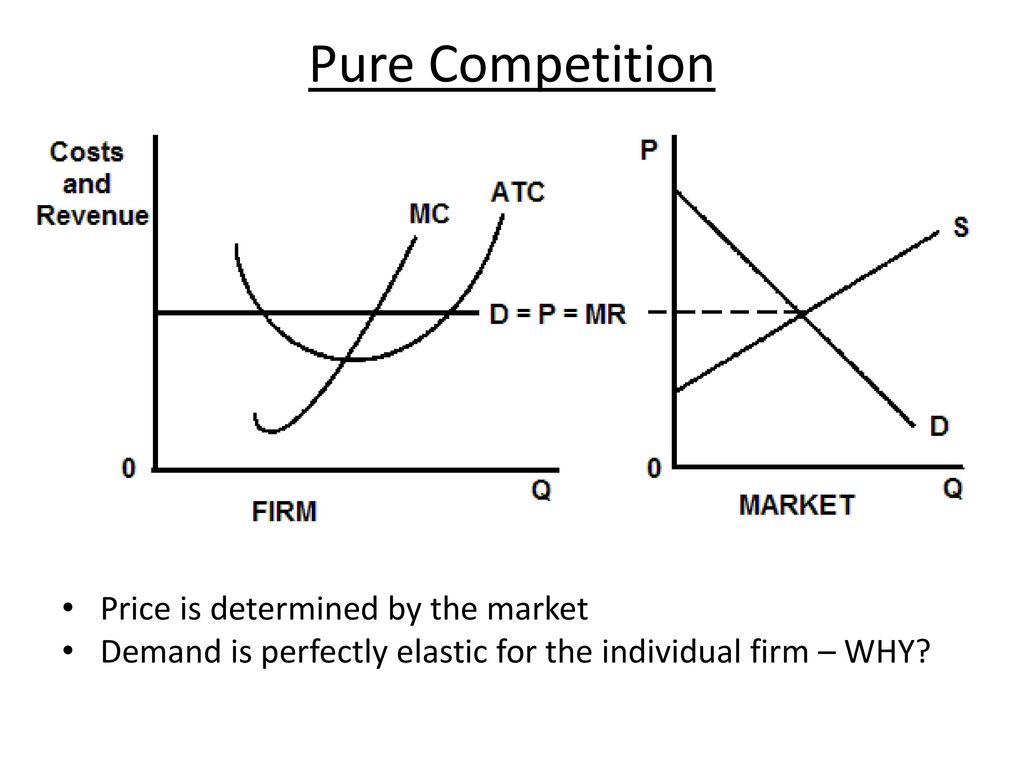
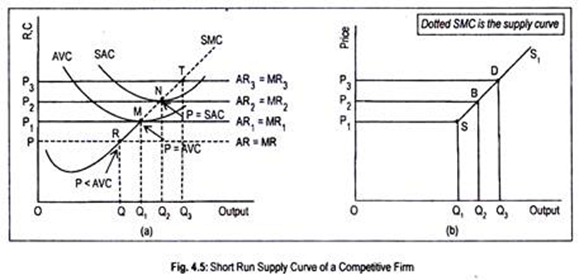
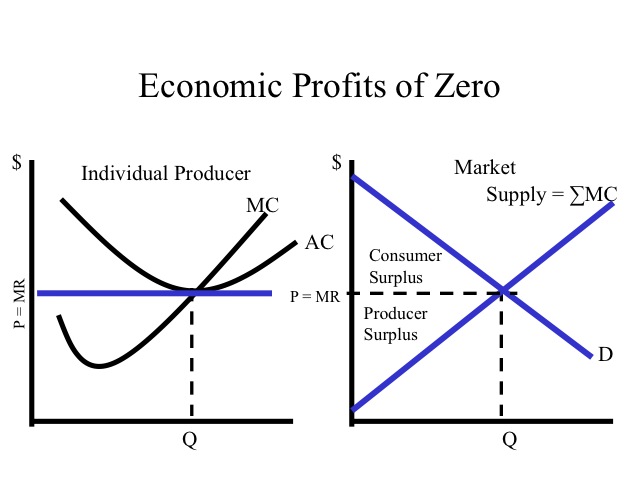
Curve (2) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's. Pure Competition in the Short Run Learn with flashcards, games, and more — for free. ... Curve (2) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's:. Rating: 5 · 1 review Curve (1) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's. total economic profit curve. Curve (2) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's. marginal revenue curve. Refer to the diagram. Other things equal, an increase of product price would be shown as ... Each purely competitive firm's demand curve is perfectly _____ at the equilibrium price. 38. Curve (2) in the above diagram is a purely competitive firm's: A. total cost curve.B. total revenue curve. C. marginal revenue curve.D. total economic profit curve. Answer: CTopic: Profit maximization in the short run Learning Objective: 11-03: Convey how purely competitive firms maximize profits or minimize losses in the short run. Curve (1) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's: total economic profit curve. Refer to the diagram for a purely competitive producer. The firm's short-run supply curve is: the bcd segment and above on the MC curve. In the short run, a purely competitive seller will shut down if product price: is less than AVC.
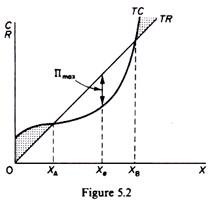
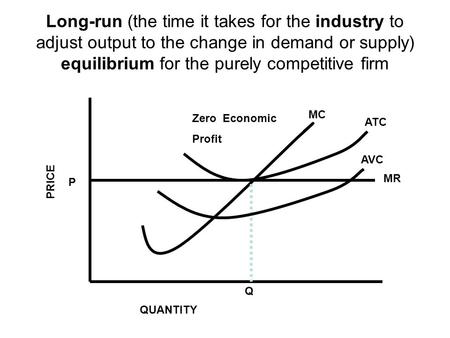
The combinations of products M and N indicated by points 1, 2, and 5 are such that: ... Curve (1) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's:. Technological advance improves productivity in a purely competitive industry. This change will result in a shift A. down of the individual firm's MC curve, causing the market supply curve to shift to the left. B. down of the individual firm's MC curve, causing the market supply curve to shift to the right. 100% (2 ratings) A). Marginal Revenue Curv …. View the full answer. Transcribed image text: O pure competition. O oligopoly. Question 16 0 Quantity Curve (2) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's: O marginal revenue curve. O total revenue curve. O total economic profit curve. O total cost curve. Refer to the diagram showing the average total cost curve for a purely competitive firm. At the long-run equilibrium level of output, this firm's total cost: a. is $10. b. is $40. c. is $400. d. cannot be determined from the information provided.
Curve 2 in the above diagram is a purely competitive firms 45. A total cost curve. Key points for pure competition in the long run. Convey how purely competitive firms maximize profits or minimize losses in the short run. Quantity curve 4 in the diagram is a purely competitive firms. For a purely competitive firm. Curve (2) in the above diagram is a purely competitive firm's: A. total cost curve.B. total revenue curve.C. marginal revenue curve.D. total economic profit curve. 15. Curve (3) in the above diagram is a purely competitive firm's: A. total cost curve.B. total revenue curve.C. marginal revenue curve.D. total economic profit curve. If a firm in a purely competitive industry is confronted with an equilibrium price of $5, its marginal revenue: a. may be either greater or less than $5 b. will also be $5 c. will be less than $5 d. will be greater than $5. b. will also be $5. Curve (3) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm’s: a. total cost curve b. total revenue curve 2. Assume for a competitive firm that MC = AVC at $12, MC = ATC at $20, ... Refer to the above diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. Curve C ...

Section 4 Profit Maximization Using A Purely Competitive Firm S Cost And Revenue Curves Inflate Your Mind
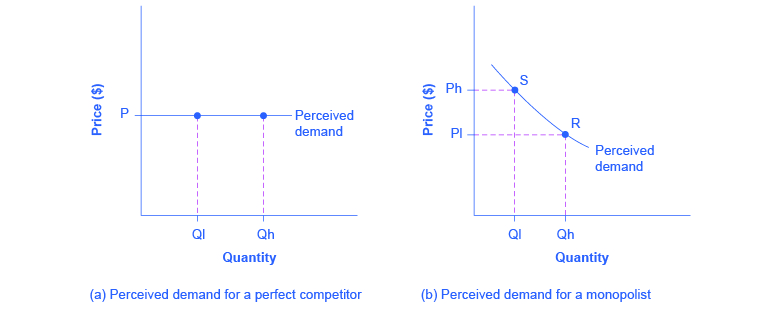
2. Economists use the term imperfect competition to describe: . ... The marginal revenue curve of a purely competitive firm:.
2. In which of the following industry structures is the entry of new firms the most difficult? ... The marginal revenue curve of a purely competitive firm:.

Use The Below Diagram Containing A Competitive Firm S Short Run Average And Marginal Cost Curves Recall That An Individual Competitive Firm Has No Control Over The Price Of Its Product Study Com

















0 Response to "37 curve (2) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's"
Post a Comment