38 the diagram below shows a 4.0 kilogram object accelerating at 10 meters
Mean distance from Pluto (km) 19,596 Sidereal orbit period (days) 6.3872 Sidereal rotation period (days) 6.3872 Orbital inclination to Pluto (deg) 0.00005 Orbital eccentricity 0.0 Equatorial radius (km) 606 Mass (10 21 kg) 1.586 Mean density (kg/m 3) 1700 Surface gravity (m/s 2) 0.29 Escape velocity (km/s) 0.59 Bond albedo 0.25 Apparent visual ... An object that falls through a vacuum is subjected to only one external force, the gravitational force, expressed as the weight of the object. An object that is moving only because of the action of gravity is said to be free falling and its motion is described by Newton's second law of motion. With algebra we can solve for the acceleration of a free falling object.
Two objects with mass 3.5 kg are placed at 4.0 m from each other. Calculate the gravitational force between the objects. ... The diagram shows object A on the surface of the earth and object B at height h from the earth. R is the radius of earth, r is the ... the value of gravitational acceleration of object A. ketinggian 345 km dari permukaan ...
The diagram below shows a 4.0 kilogram object accelerating at 10 meters
Phase 4: The Flight. During this phase, the athlete can't impact the velocity of his center of gravity any further. The height of the jump has been predetermined by the build up of speed before and during takeoff. The only force that is now acting upon the athlete is the gravity that is pulling the jumper back down. what is the acceleration of a plane moving at 45 m/s and come to the rest in 10 s? A snowmobile has an initial velocity of +4.4 m/s.If it accelerates at the rate of +0.34 m/s2 for 4.2 s, what is the final velocity?31. A particular type of fundamental particle decays by. transforming into an electron e- and a positron e+. Suppose the. 4. Ask any question and get an answer from our subject experts in as little as 2 hours.
The diagram below shows a 4.0 kilogram object accelerating at 10 meters. For T₂, its free-body diagram shows us it is only responsible for the mass of m₂, we can say that T₂ = a * m₂. With that said, T₂ = (2.4 m/s²) * (2 kg) = 4.8 N. On the other hand, T₁ is the tension force that pulls both the weight of m₁ and m₂. Acceleration is the rate of change of an objects speed; in other words, it's how fast velocity changes. According to Newton's second law, acceleration is directly proportional to the summation of all forces that act on an object and inversely proportional to its mass.It's all common sense - if several different forces are pushing an object, you need to work out what they add up to (they may be ... To help compare different orders of magnitude, this section lists lengths between 10 −3 m and 10 −2 m (1 mm and 1 cm). 1.0 mm - 1/1,000 of a metre. 1.0 mm - 0.03937 inches or 5/127 (exactly) 1.0 mm - side of square of area 1 mm². 1.0 mm - diameter of a pinhead. 1.5 mm - length of average flea. This tool estimates the potential energy on the basis of three values. These are: The mass of the object. Gravitational acceleration, which on Earth amounts to 9,81 m/s². The height of the object. Then the calculator will give you the result in joules. As with all of our calculators, this potential energy calculator does not have to be ...
(a) The diagram shows a velocity-time graph for a vehicle. The vehicle, moving at 4.0 m s-1 begins to accelerate at time = 0. What is the vehicle's acceleration at time = 3.0 s? (b) A ball rolls off a platform of height 1.8m at a horizontal speed of 15ms-1. How far off the edge of the platform does it land. Acceleration Formula. The following formula is used to calculate the acceleration of an object. Acceleration = (Final Velocity - Initial Velocity) / Time. In Si units, acceleration is displayed as meters per second square (m/s^2), velocity is measure in meters per second (m/s), and time is measured in seconds (s). The diagram below represents velocity vs. time graph for a straight line motion of a car. The car starts from x = 0 m at time t = 0 s. Find the position of the car at t = 14 s. Achieving Excellence · School Messenger Quick Tip allows you to submit anonymous tips to our school district. Send a Message Find Out More
In other words, it causes the object to accelerate. Like any other force, gravity makes falling objects accelerate—but only up to a point. If you jump out of a plane, your body ought to speed up by 10 meters per second (32ft per second) every single second you're falling. January 14, 2018 - John Bowne High School official website to high school in Flushing, NY The diagram below shows a 4.0 kilogram object accelerating at 10 meters. 3. The diagram below shows a horizontal 12-newton force being applied to two blocks, A and B, initially at rest on a horizontal, frictionless surface. Block A has a mass of 1.0 kilogram and block B has a mass of 2.0 kilograms. A) 6.0 m/s2 B) 2.0 m/s2 C) 3.0 m/s2 D)4.0 m/s2 The magnitude of the acceleration of block B is 4 ... 43. The diagram below shows a 4.0-kilogram object accelerating at 10. meters per second2 on a rough horizontal surface. What is the magnitude of the frictional force Ff acting on the object? A. 5.0N B. 10.N C. 20.N D. 40.N 44. In the diagram below, scaled vectors represent the momentum of each ...
4.1.3 Calculate the magnitude of the velocity she will reach after 4,0 s. (3) 4.2 A system of two objects, an elevator and a counterweight, suspended by a pulley and light cable is shown in the diagram below. The mass of the elevator with four people inside is mE = 1 150 kg and its mass is 850 kg when empty.
A toy racing car moves with constant speed around the circle shown below. When it is at point A its coordinates are x = 0, y = 3 m and its velocity is (6 m/s)ˆi. When it is at point B its velocity and acceleration are: Physics. A particle starts from xi = 10 m at t0 = 0 and moves with the velocity graph shown in the graph below.
Three objects are connected on an inclined table as shown in the diagram below. The objects have masses 8.0 kg, 4.0 kg and 2.0 kg as shown, and the pulleys are frictionless. The tabletop is rough, with a coefficient of kinetic friction of 0.47, and makes an angle of 20.0° with the horizontal. a.free body diagram b. Determ
An object that is falling through the atmosphere is subjected to two external forces. The first force is the gravitational force, expressed as the weight of the object, and the second force is the aerodynamic drag of the object. The weight equation defines the weight W to be equal to the mass m of the object times the gravitational acceleration g:
12.The diagram below shows a 4.0-kilogram object accelerating at 10. meters per second2 on a rough horizontal surface. What is the magnitude of the frictional force Ff acting on the object? A)downward with decreasing speed B)downward at constant speed C)upward with decreasing speed D)upward ...
Answer: 3 📌📌📌 question How much force is needed to accelerate a 1000-kg car at a rate of 3 m/s2? a 1003 N b 0.003 N c 3000 N d 333.3 N - the answers to estudyassistant.com
1. The diagram below shows a 4.0-kilogram object accelerating at 10. meters per second2 on a rough horizontal surface. What is the magnitude of the frictional force Ff acting on the object? A. 5.0N B. 10.N C. 20.N D. 40.N 2. What is the magnitude of the force needed to keep a 60.-newton rubber ...
The table below shows the relative humidity for a location at different times within a 9 hour period, explain whether this is telling you about the lo … cation's weather or climate. Relative Humidity Time Percentage 7:00 a.m. 47% 10:00 a.m. 52% 1:00 p.m. 53% 4:00 p.m. 61%
80 feet. The answer, which surprises nearly everyone, is (d) 80 feet (on dry, level pavement and neglecting driver reaction distance). This is because the energy of a moving car is proportional to its mass times the square of its velocity, based on the kinetic energy equation from physics: Where: = Kinetic energy, joules.
Calculate the acceleration of the car. Solution: Initial velocity, u = 24ms -1. Final velocity, v = 0 ms -1. Time taken, t = 4 s. Example 3. Time-velocity graph of a body is shown in the figure. Find its acceleration in m/s 2. Solution: As it is clear from the figure, At t = 0 s, v = 20 m/s.
The diagram below shows an 8.0-kilogram cart moving to the right at 4.0 meters per second about to make a head-on collision with a 4.0-kilogram cart moving to the left at 6.0 meters per second. After the collision, the 4.0-kilogram cart moves to the right at 3.0 meters per second.
A ball of mass 2 kg 2 \text{ kg} 2 kg is placed in front of a spring having constant 20 N/m 20 \text{ N/m} 2 0 N/m and compression 20 m 20 \text{ m} 2 0 m at a height of 100 m 100 \text{ m} 1 0 0 m above the ground. Now, the spring is released, giving the ball a horizontal velocity.
If the final velocity is less than the initial velocity, the acceleration will be negative, meaning that the object slowed down. Now let's breakdown the acceleration equation step-by-step in a real example. How to Calculate Acceleration: Step-by-Step Breakdown. Now we'll breakdown the acceleration formula step-by-step using a real example.
Start studying Forces Topic 2 question/concept matching. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.

As Respresented In The Diagram Below A Constant 15 Newton Force F Is Applied To A 2 5 Kilogram Brainly Com
The diagram below shows two forces applied to a 2.0-kilogram block on a frictionless, horizontal surface. F = 8.0 N 2.0 kg F2 = 3.0 N Frictionless Surface What is the acceleration of the block? A 4.0 m/s2 to the left B.O 2.5 m/s2 to the right C.O 2.5 m/s2 to the left D. 1.5 m/s2 to the right
Question-8 :- (Friction HC Verma Exercise) In a children-park an inclined plane is constructed with an angle of incline 45° in the middle part (in the following figure). Find the acceleration of boy sliding on it if the friction coefficient between the cloth of the boy and the incline is 0.6 and g = 19 m/s 2.
Answer: 3 📌📌📌 question The diagram below shows a 4.0-kilogram object accelerating at 10. meters per second on a rough horizontal surface. Acceleration = 10. m/s2 Frictional force = F1 Applied force = 50. N. m = 4.0 kg (Not drawn to - the answers to estudyassistant.com
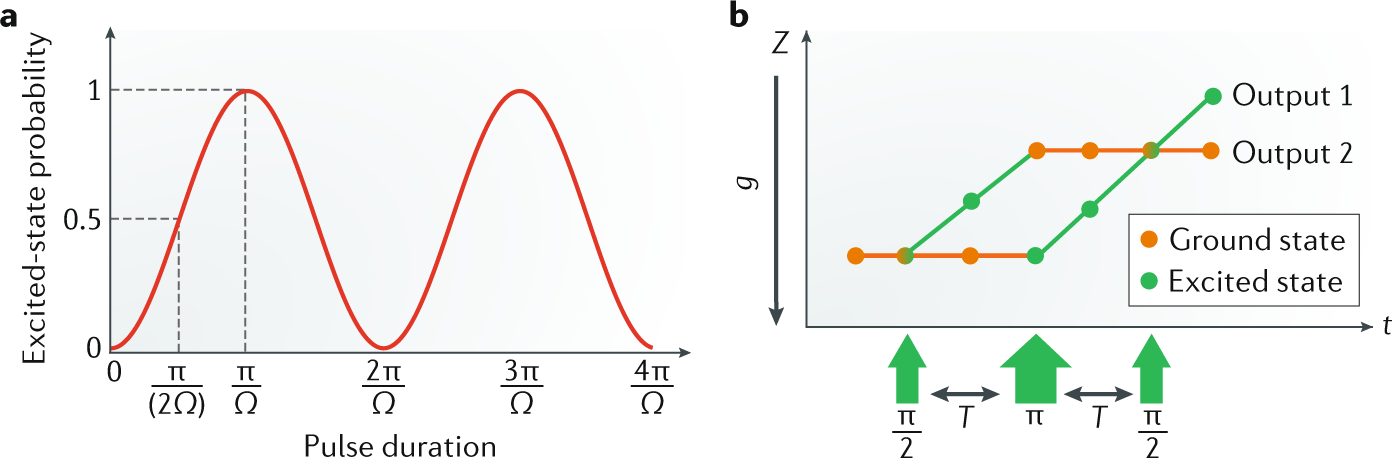
Taking Atom Interferometric Quantum Sensors From The Laboratory To Real World Applications Nature Reviews Physics
4.The diagram below shows a 4.0-kilogram object accelerating at 10. meters per second2 on a rough horizontal surface. What is the magnitude of the frictional force Ff acting on the object? A)is greater than the force of static friction B)is less than the force of static friction C)increases ...
NC)20. ND)40. N 30.The diagram below shows a 4.0-kilogram object accelerating at 10. meters per second2 on a rough horizontal surface. What is the magnitude of the frictional force Ff acting on the object? A)A B)B C)C D)D 31.The diagram below represents a block sliding down an incline.
Let's just make it simple: To achieve an artificial gravity of 0.5 g, you'll need a radius of 450 meters and a spacecraft-to-counterweight distance of twice that (900 meters). Just for fun, the ...

Rules 1 Everyone Must Attempt To Answer Each Question 2 Show Your Work On A Separate Sheet Of Paper 3 Keep Track Of Your Points 4 Winners Receive Prize Ppt Download
38 The diagram below shows a 4.0-kilogram object accelerating at 10. meters per second 2 on a rough horizontal surface. What is the magnitude of the frictional force F f acting on the object? (1) 5.0 N
B) 4.5 × 104 kg•m/s, west C) 4.5 × 106 kg•m, east D) 4.5 × 106 kg•m, west 27.What is the momentum of a 1.5 × 103-kilogram car as it travels at 30. meters per second due east for 60. seconds? A) 64 kg B) 20 kg C) 12 kg D)4.0 kg 28.An object traveling at 4.0 meters per second has a ...
105. The diagram below shows a 4.0-kilogram object accelerating at 10. meters per second2 on a rough horizontal surface. Acceleration = 10. m/s2 Frictional force = Ff m = 4.0 kg (Not drawn to scale) Applied force = 50. N 5ctO* What is the magnitude of the frictional force "acting on the object?
7.) The diagram below shows a 4.0-kilogram object accelerating at 10. meters per second 2 on a rough horizontal surface. What is the magnitude of the frictional force F f acting on the object? (1) 5.0 N (2) 20. N (3) 10. N (4) 40. N
🔴 Answer: 3 🔴 on a question The diagram below shows a 4.0-kilogram object accelerating at 10. meters per second on a rough horizontal surface. Acceleration = 10. m/s2 Frictional force = F1 Applied force = 50 - the answers to ihomeworkhelpers.com
The diagram below shows a mass m, which is rotated in a vertical circle. ... Figure 6 shows an object of mass 2.0 kg whirled in a vertical circle of radius 0.7m at a uniform speed of 50ms-1; ... A body moving in a circular path at constant speed is said to be accelerating. b) Figure 10 below shows a bucket filled with water moving round in a ...
Diagram 1 shows the angle of bank, the radius of the curve, and how high the object is from the flat surface. ... Objects accelerating centripetally are moving in a curved path, ... A 780-kilogram ...
meter per second. If the speed of the cart is doubled, the inertia of the cart is 6. 7. 8. When the index card is quickly pulled away from the glass in a horizontal direction, the disk falls straight down into the glass. This action is a result of the disk's A) inertia C) shape B) charge D) ...
in this solution, we have to find the value of frictional force An Exhibition of Block Off Mosque 10 Kg. So first of all I am growing the dialogue for execution. So we have you in here block of martin K. G. And it is connected with this spring through a pulley and there is another block connected ...
v is the linear velocity of the stone = 4.0 m/s and r is the radius of curvature = 0.8 m So F = (1.5)(4.0^2)/0.8 = 19.2 N. Question: An electrically driven crane rises a load of mass 238 kg from the ground, accelerating it from rest to a speed of v = 0.8 m/s over a distance of h =5 m. Friction resistance to motion is Ff = 113 N.
Ask any question and get an answer from our subject experts in as little as 2 hours.
what is the acceleration of a plane moving at 45 m/s and come to the rest in 10 s? A snowmobile has an initial velocity of +4.4 m/s.If it accelerates at the rate of +0.34 m/s2 for 4.2 s, what is the final velocity?31. A particular type of fundamental particle decays by. transforming into an electron e- and a positron e+. Suppose the. 4.
Phase 4: The Flight. During this phase, the athlete can't impact the velocity of his center of gravity any further. The height of the jump has been predetermined by the build up of speed before and during takeoff. The only force that is now acting upon the athlete is the gravity that is pulling the jumper back down.









0 Response to "38 the diagram below shows a 4.0 kilogram object accelerating at 10 meters"
Post a Comment