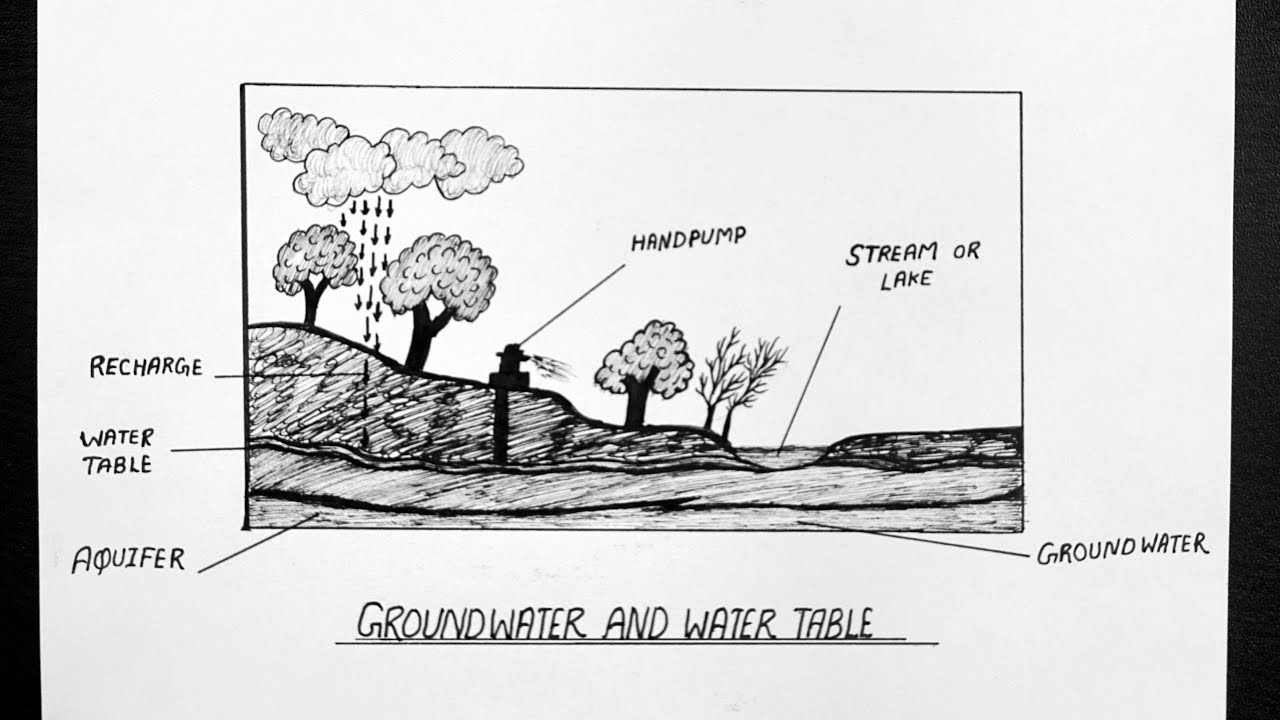
40 sources of groundwater diagram
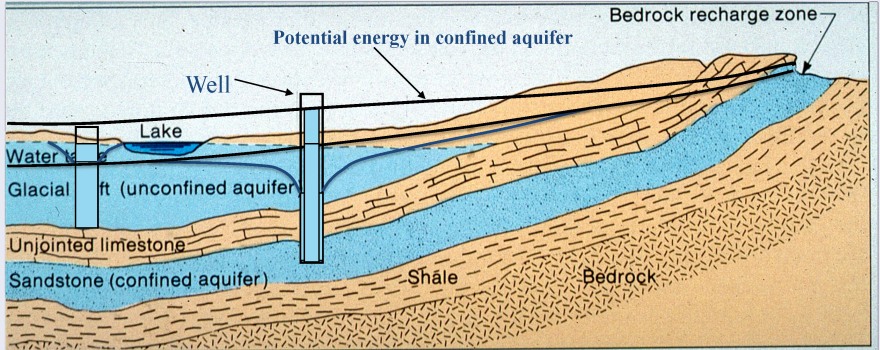
Groundwater in aquifers between layers of poorly permeable rock, such as clay or shale, may be confined under pressure. If such a confined aquifer is tapped by a well, water will rise above the top of the aquifer and may even flow from the well onto the land surface. This diagram shows a groundwater contaminant plume in red. The source of the contamination has been removed but if the plume is not dealt with, it will eventually enter the stream and threaten the health of wildlife. Pumping the contaminant from well B for treatment will not be sufficient to prevent some of the contamination from making it to ...
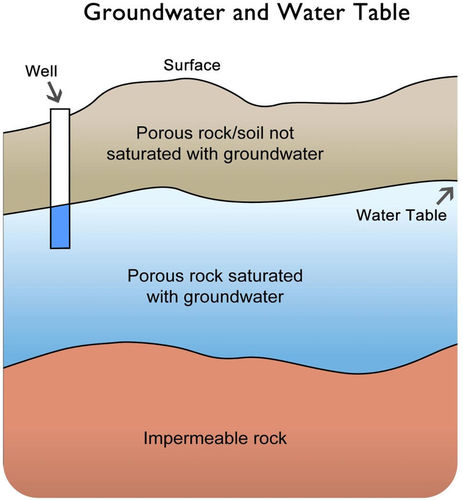
Groundwater: Origin, Sources and Other Details (with diagram) Article shared by : ADVERTISEMENTS: Water existing in the voids of the geological stratum below the surface of the earth is called groundwater. Groundwater is found in pores and fissures of rocks. It is regulated by the quantum and speed of rains, extent of vaporization at the time ...
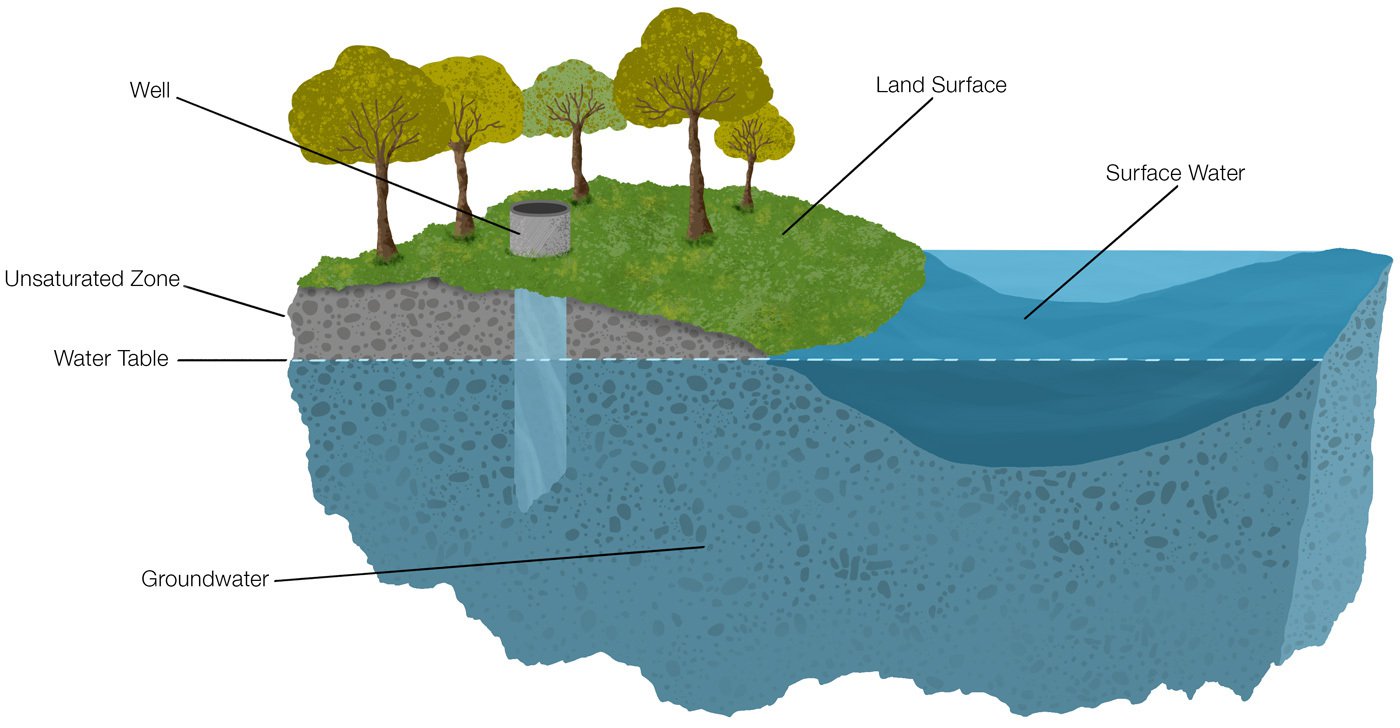
Sources of groundwater diagram
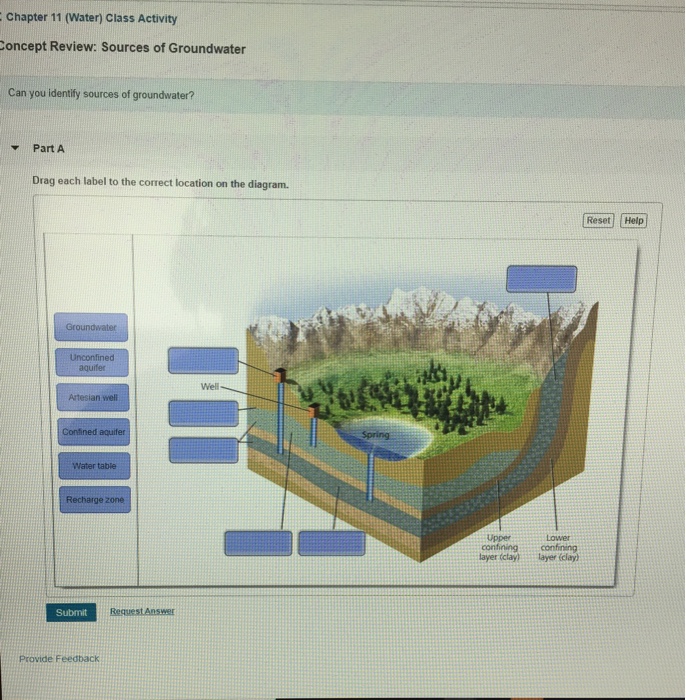
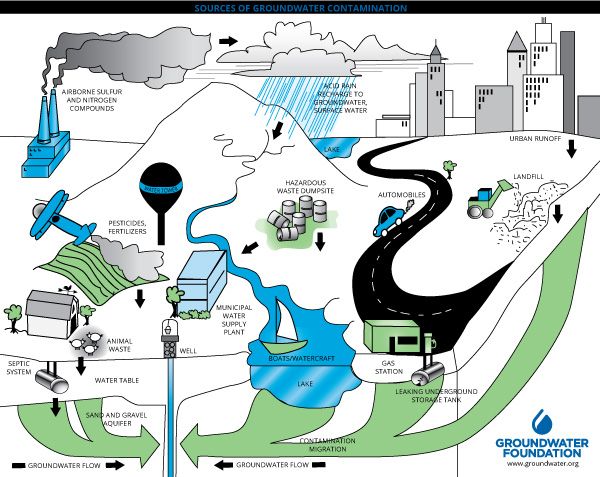
Transcribed Image Textfrom this Question. Chapter 11 (Water) Class Activity oncept Review: Sources of Groundwater Can you identify sources of groundwater? Part A Drag each label to the correct location on the diagram. Reset Help Groundwater aquifer Well Artesian well Confined aquifer Spring Water table Recharge zone Upper confiningconfining ... V = K * i. (where V is the velocity of the groundwater flow, K is the hydraulic conductivity, and i is the hydraulic gradient). We can apply this equation to the scenario in Figure 14.5. If we assume that the permeability is 0.00001 m/s we get: V = 0.00001 * 0.08 = 0.0000008 m/s. That is equivalent to 0.000048 m/min, 0.0029 m/hour or 0.069 m/day. groundwater, called a plume, can form (Diagram 3). A combination of moving groundwater and a continuous source of contamination can, therefore, pollute very large volumes and areas of groundwater. Some plumes at Superfund sites are several miles long. More than 88 percent of current Superfund sites have some groundwater contamination.
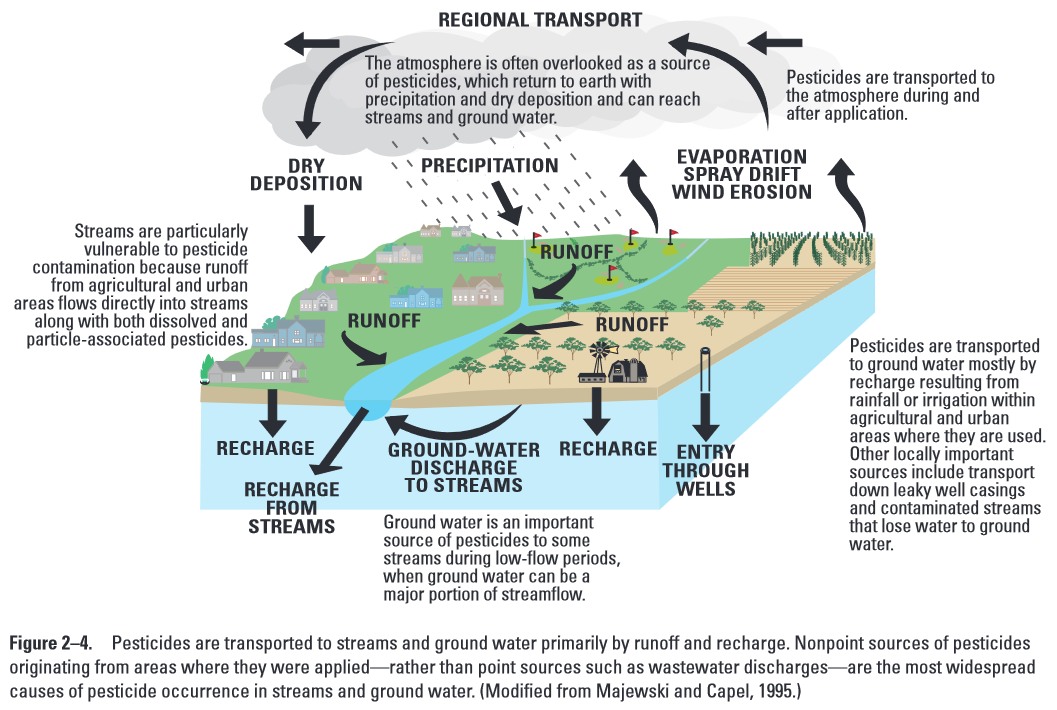
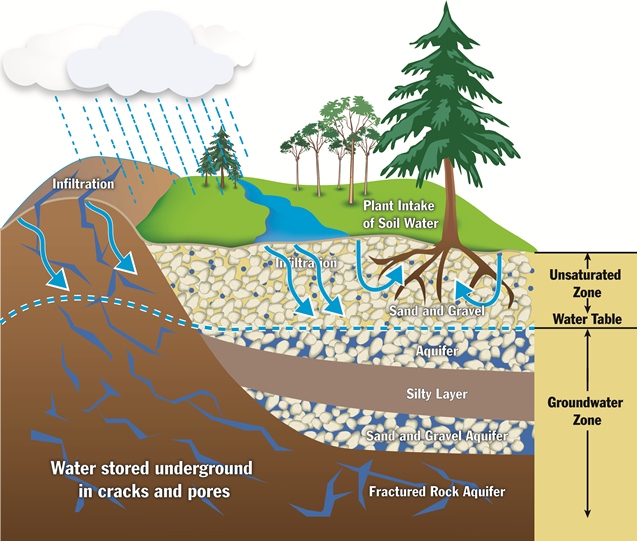
Sources of groundwater diagram. Groundwater sources have their origins in the water cycle and are held in aquifers beneath the ground surface. Groundwater slowly moves underground, generally at a downward angle (because of gravity), and may eventually seep into streams, lakes, and oceans. Here is a simplified diagram showing how the ground is saturated below the water table (the purple area). The amount of water that is available to enter groundwater in a region is influenced by the local climate, the slope of the land, the type of rock found at the surface, the vegetation cover, land use in the area, and water retention, which is the amount of water that remains in the ground. More water goes into the ground where there is a lot of ... In both (c) and (d), diffuse groundwater (GW) flows through the soil matrix and macropores are important flowpaths in addition to tile drainage discharge.
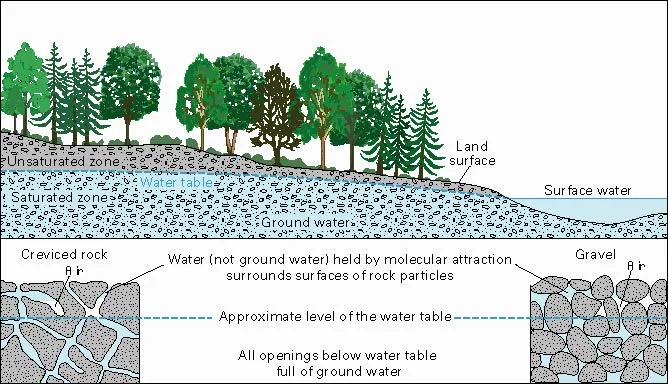
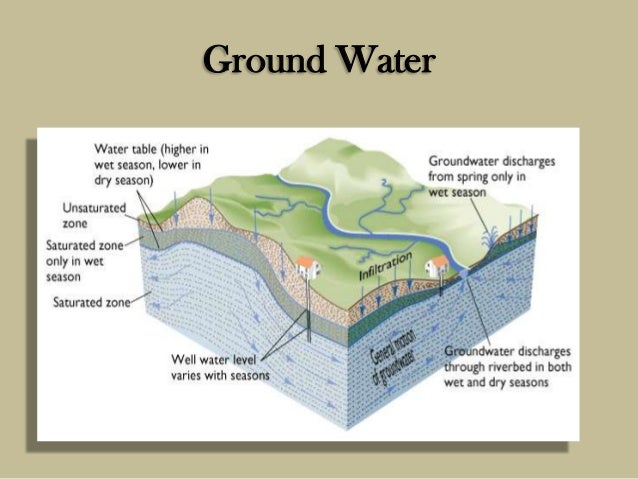
In the diagram, you can see how the ground below the water table is saturated with water (the saturated zone). Aquifers are replenished by the seepage of ... Groundwater well diagram showing both urban and rural communities. Image provided by USGS. Basic Groundwater diagram showing an ocean, river, wetland, recharge and discharge arrows. ... Black and white image of potential sources of groundwater pollution. Image provided by USGS. 601 Dempsey Road Westerville OH 43081 Toll Free 1-800-858-4844 ... by TC Winter · Cited by 1815 — oceans, as depicted in this diagram of a conceptual landscape. ... hyporheic zone and ground water from distant sources. Unsaturated zone. Saturated zone.87 pages Nitrate in groundwater generally originates from nitrate sources on the land surface, in the soil zone, or in shallow subsoil zones where nitrogen-rich wastes are buried (Figure 9.17). In some situations that enters the groundwater system originates as ; in wastes or fertilizers applied to the land surface.
groundwater, called a plume, can form (Diagram 3). A combination of moving groundwater and a continuous source of contamination can, therefore, pollute very large volumes and areas of groundwater. Some plumes at Superfund sites are several miles long. More than 88 percent of current Superfund sites have some groundwater contamination. V = K * i. (where V is the velocity of the groundwater flow, K is the hydraulic conductivity, and i is the hydraulic gradient). We can apply this equation to the scenario in Figure 14.5. If we assume that the permeability is 0.00001 m/s we get: V = 0.00001 * 0.08 = 0.0000008 m/s. That is equivalent to 0.000048 m/min, 0.0029 m/hour or 0.069 m/day. Transcribed Image Textfrom this Question. Chapter 11 (Water) Class Activity oncept Review: Sources of Groundwater Can you identify sources of groundwater? Part A Drag each label to the correct location on the diagram. Reset Help Groundwater aquifer Well Artesian well Confined aquifer Spring Water table Recharge zone Upper confiningconfining ...
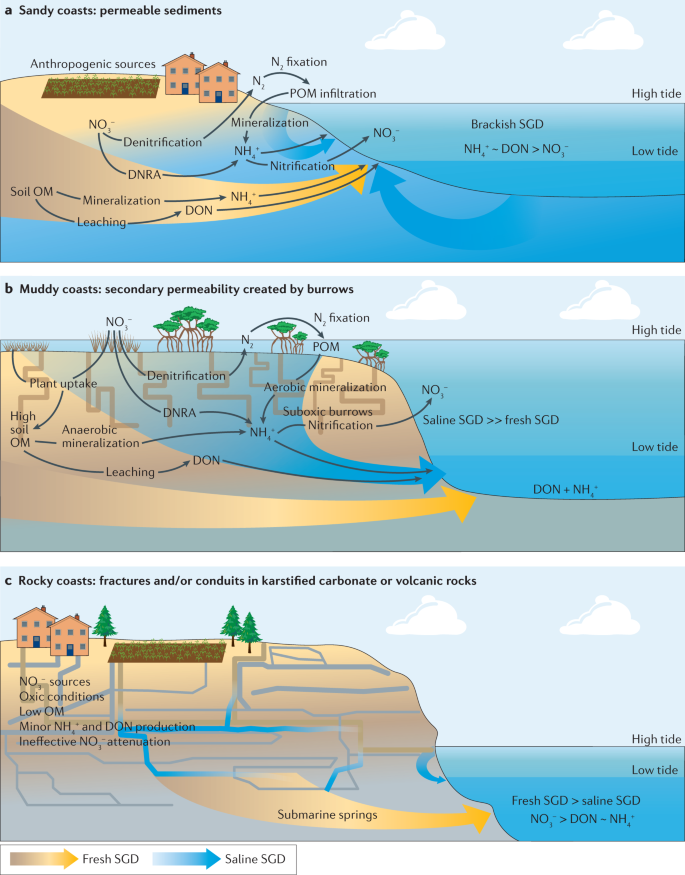
Submarine Groundwater Discharge Impacts On Coastal Nutrient Biogeochemistry Nature Reviews Earth Environment

Fluency Focus Academy Ielts Ielts Writing Task 1 The Diagram Shows Nitrogen Sources And Concentration Levels In The Groundwater Of A Coastal City
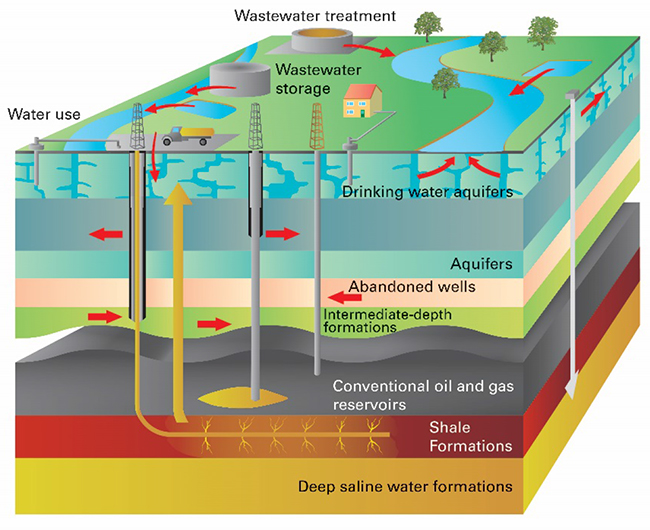
Assessing Potential Groundwater Contamination In The Pursuit Of New Energy Sources British Geological Survey

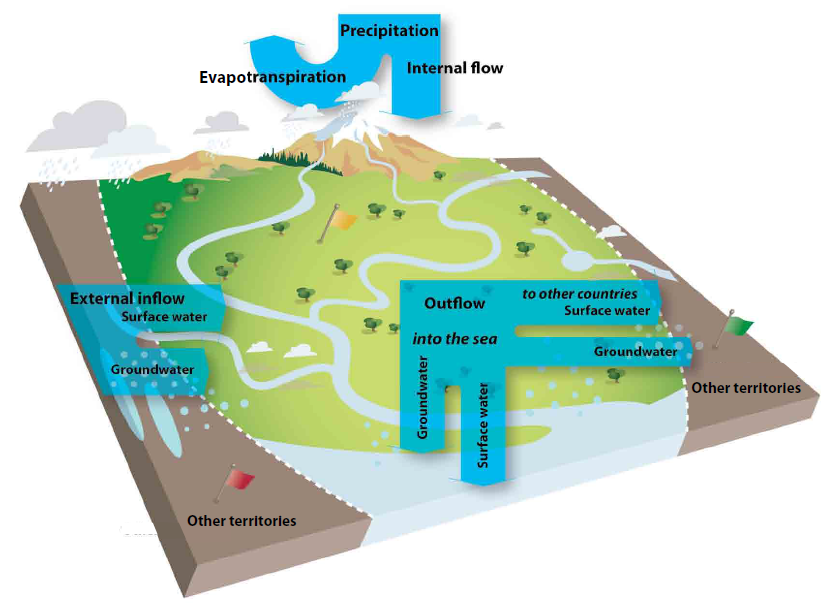

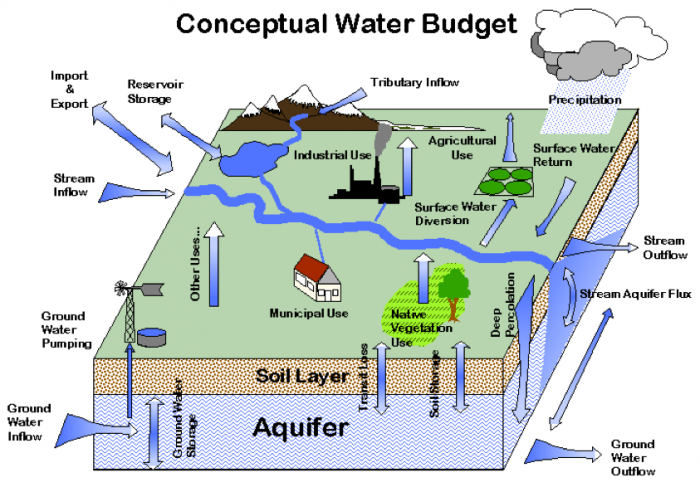
















0 Response to "40 sources of groundwater diagram"
Post a Comment