41 this diagram would represent the enthalpy change in which of the following
This diagram would represent the enthalpy changes in which of the following? - 9007542 bmisses bmisses 03/03/2018 Chemistry College answered This diagram would represent the enthalpy changes in which of the following? boiling liquid hot pack cold pack melting solid ... The concentrations of _____ change by the smallest amount throughout the ... How to Draw & Label Enthalpy Diagrams - Quiz & Worksheet. Choose an answer and hit 'next'. You will receive your score and answers at the end. Glucose + Oxygen goes to carbon dioxide and water ...
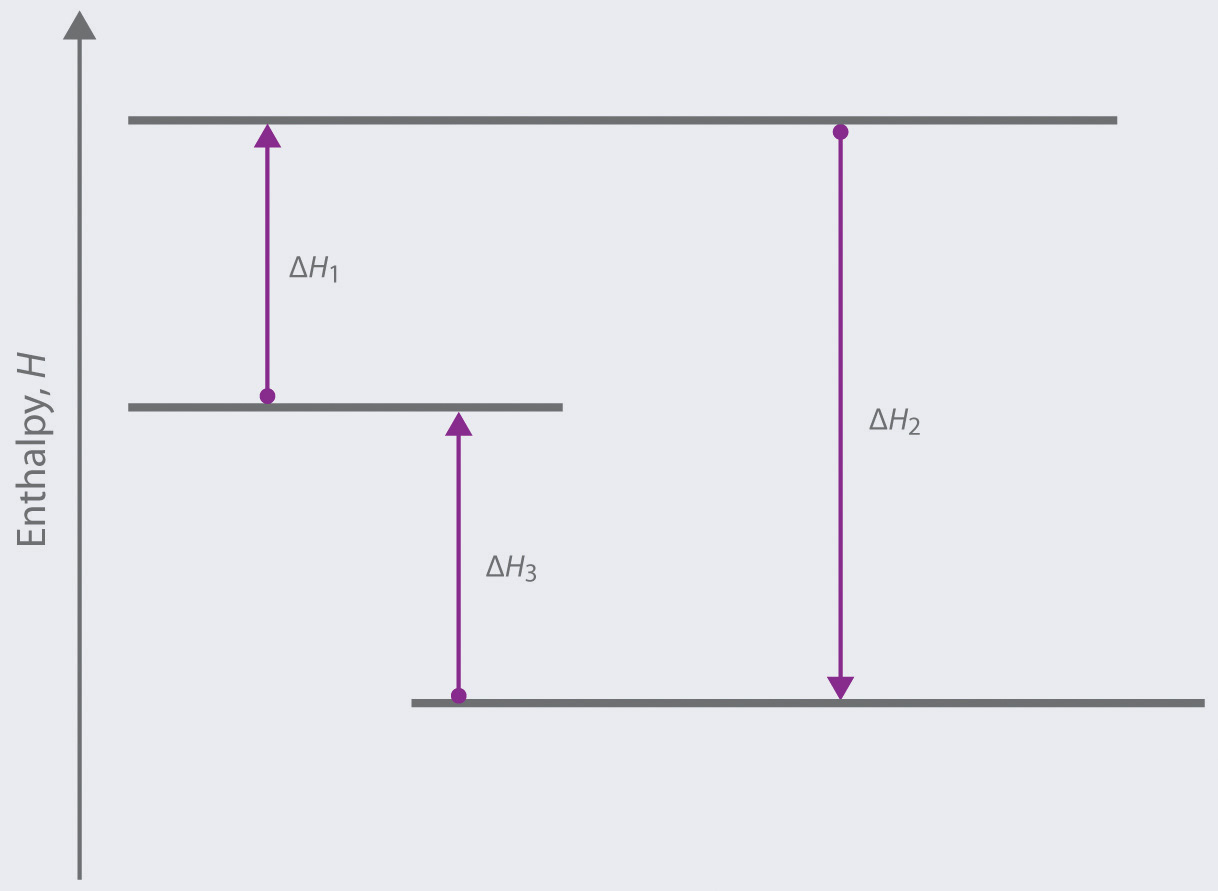
60 MHR Chemistry 12 Solutions Manual 978 --07-106042-4 Using Hess's Law to Determine Enthalpy Change (Student textbook page 316) 41. Nitrogen dioxide, NO 2(g), is an emission resulting from the burning of gasoline in an automobile engine that contributes to the formation of smog and acid rain.
This diagram would represent the enthalpy change in which of the following
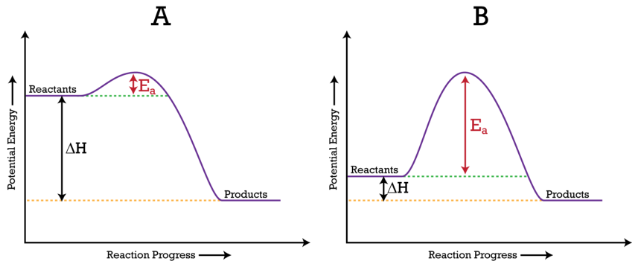
How to draw the potential energy diagram for this reaction? Chemistry. 2 Answers. Truong-Son N. Apr 9, 2018. Since heat is released for. C3H8(g) + 5O2(g) → 3CO2(g) +4H2O(g) + 2219.9 kJ, we say that ΔH ∘ C = − 2219.9 kJ/mol propane. We approximate that this is the change in potential energy for the reactants going to the products. Determine the activation energy and the enthalpy change for the reaction. b. Draw a labelled potential energy diagram for the reaction, indicating the relative energies of the reactants, products, and activated complex. What Is Required? You need to determine the activation energy, E a, and the enthalpy change, ΔH r, for the reaction. The standard enthalpy of reaction, Ho, is the sum of the enthalpy of the products minus the sum of the enthalpy of the reactants. H o = prod n fHo- react n fHo Hess's Law Hess's Law: The heat change in any reaction is the same whether the reaction takes place in one step or several steps, i.e.the overall energy change of a
This diagram would represent the enthalpy change in which of the following. 3. The enthalpy change for the following reaction: H 2 (g) + I 2 (g) 2HI(g) is -9 kJmol-1 Use this information and the values in the above table to calculate the bond dissociation energy for the H-I bond. 4. Explain why using bond dissociation energies only give you an approximate value for the overall energy change Measuring enthalpy changes For the following reaction: 2H_2 (g) + O_2 (g) to 2H_2O (g) Delta H = -483.6 kJ Draw the enthalpy diagram, and label the activation energy. From a molecular viewpoint, where does the energy ... The spontaneity of a reaction depends both on the enthalpy change, ΔH, and entropy change, ΔS. Reactions that release energy produce more stable products, and the universe tends toward disorder. Thus, an exothermic reaction with a positive entropy change will always be spontaneous. Mathematically, this relationship can be represented as The changes in energy during a reaction (Explanation): it is called an ENERGY diagram, so it shows the different energy levels during a reaction for a reason.
the system changes during the process, how is the change in internal energy related to the change in enthalpy? [Sec-tions 5.2 and 5.3] 350 K 290 K 5.9 In the accompanying cylinder diagram a chemical process occurs at constant temperature and pressure. Is the a sign of w indicated by this change positive or negative? a) Draw an enthalpy level diagram for a neutralization reaction. i) Indicate on your diagram the enthalpy change of the reaction and deduce its sign. ii) Compare the relative stabilities and strengths of the bonds of the reactants and products. [4] iii) Define the term standard enthalpy change of a reaction. [1] 13. 1.18 DETERMINE the change in the enthalpy of a fluid as it passes through a system component, given the state of the fluid at the inlet and outlet of the component and either steam tables or a Mollier diagram. Standard Enthalpy of Combustion (∆H c °) The enthalpy change when one mole of a substance is completely burned in oxygen Not one mole of product! Problem 13 Write the equations to represent the standard enthalpy of combustion for: C 5 H 12(l) CO (g) H 2(g) Al (s)
The pressure-enthalpy chart, as shown in Fig. 2, displays all the pertinent properties for a given refrigerant (in this example R22). The bubble to the left is the portion of the diagram where the refrigerant is in the saturated condition. The blue line on the left of the bubble represents the 100% saturated liquid line, Which combination is correct for the standard enthalpy change of neutralization? 35. When four moles of aluminium and four moles of iron combine with oxygen to form their oxides, the enthalpy changes are -3338 kJ and -1644 kJ respectively. What is the enthalpy change, in kJ, for the reduction of one mole of iron(III) oxide by aluminium? Q. CO (g) + 2 H 2(g) ↔ CH 3 OH (g) K = 2.2 x10 4 at 298 K. A stoichiometric mixture of CO (g) and H 2(g) was allowed to react in two different rigid containers at a constant temperature of 298 K. The reaction is represented by the equation above. Diagram 1 represents the uncatalyzed reaction and diagram 2 represents the catalyzed reaction one hour after the reactants were mixed. The diagram shows the distribution of energy for the molecules in a sample of gas at a given temperature, T1 (a) In the diagram . E. a. represents the . activation energy . for a reaction. Define this term. (b) On the diagram above draw another curve to show the energy distribution for the same gas at a higher temperature. Label the curve T. 2. (c)
Will mark as brainliest. this diagram would represent the enthalpy changes in which of the following... Questions in other subjects: Mathematics, 26.09.2019 22:20
"Heat change when 1 mole of gaseous atom is formed from its element at standard states" is the definition for _____. answer choices standard enthalpy of formation
This diagram would represent the enthalpy change in which of the following? liquid water freezing A 10 g gold coin is heated from 25°C to 50°C (CAu is 0.13 J/g-°C).
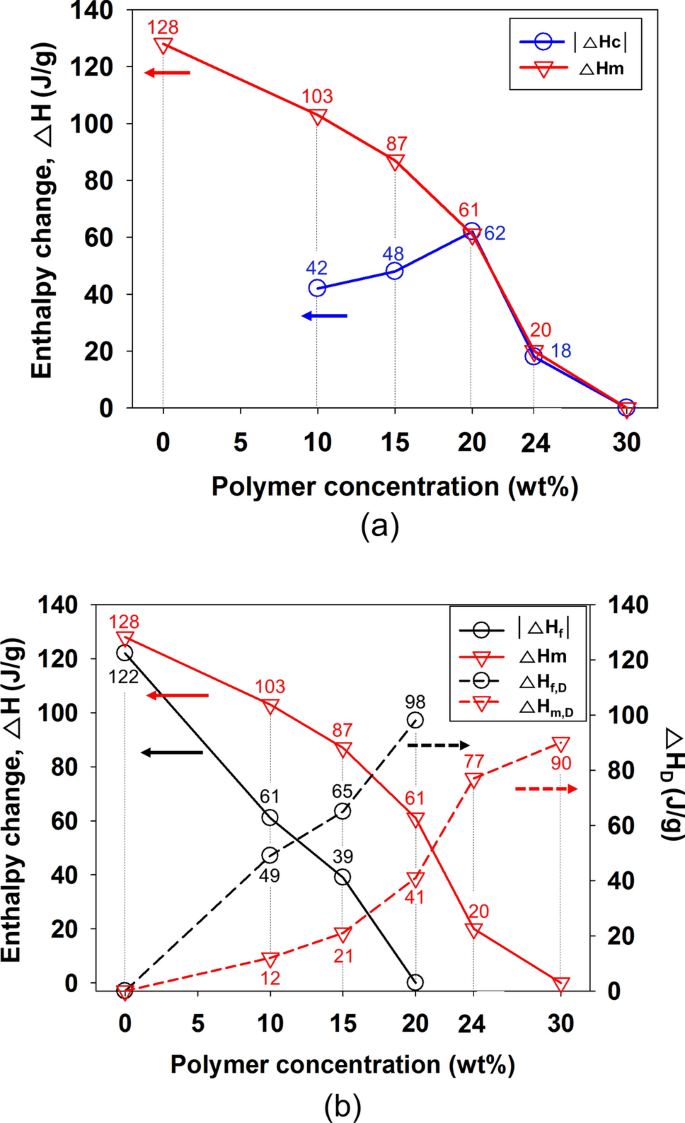
Novel Behavior In A Polymer Solution The Disappearance Of The Melting Temperature Tm And Enthalpy Change Dhm Of The Solvent Scientific Reports
Knowing the enthalpy changes of formation of compounds enables you to calculate the enthalpy changes in a whole host of reactions and, again, we will explore that in a bit more detail on another page. And one final comment about enthalpy changes of formation: The standard enthalpy change of formation of an element in its standard state is zero.
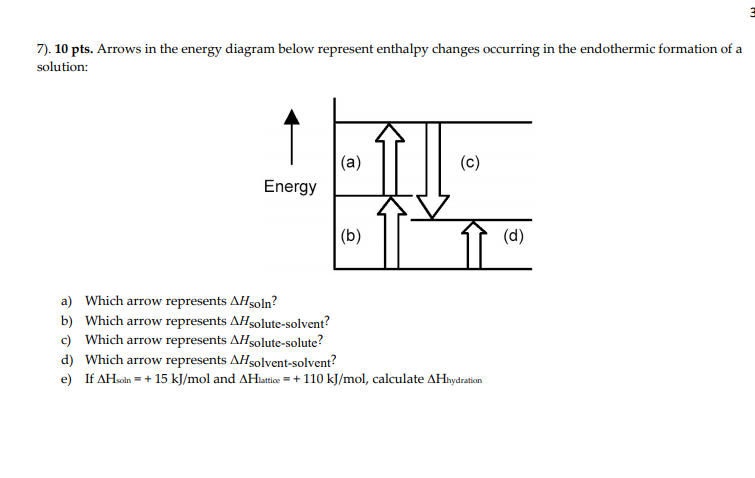
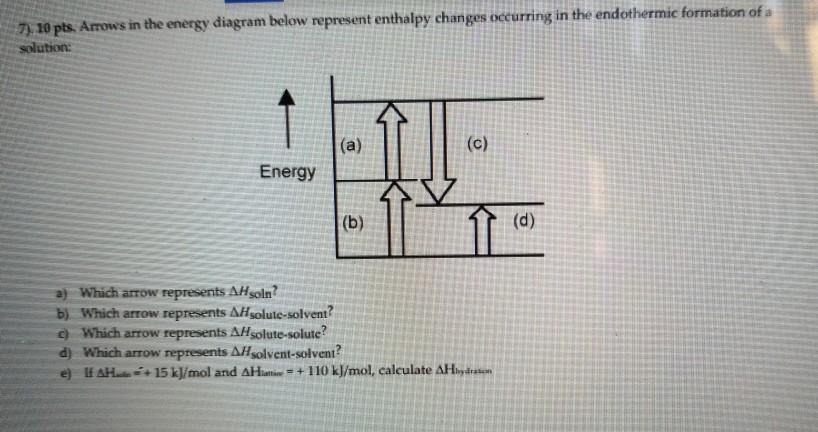
Chemistry. Chemistry questions and answers. Arrows in the energy diagram below represent enthalpy changes occurring in the formation of a solution: | (a) (c) Energy (b) (d) Which arrow represents Asoln? O A arrow (a) OB, arrow (b) O Carrow (d) D. arrow (c) Question: Arrows in the energy diagram below represent enthalpy changes occurring in the ...
This diagram would represent the enthalpy changes in which of the following. H for the reaction can be calculated from the h of the following reactions. The boiling liquid and melting solid are just phase changes. The diagram represents the potential energy changes when a cold pack is activated.

This Diagram Would Represent The Enthalpy Changes In Which Of The Following Boiling Liquid Hot Brainly Com
Represent the potential energy/enthalpy change in the following processes graphically. (a) Throwing a stone from the ground to roof. (b) 1/2 H 2 (g) + 1/2 Cl 2 (g) ⇄ HCl(g) Δ r H Θ = -92.32 kJ mol -1 . In which of the processes potential energy/enthalpy change is contributing factor to the spontaneity?
The enthalpy level diagram can now be constructed. In this case, the red dotted line is obtained by subtracting the small blue dotted line from the longer blue dotted line. That is, the enthalpy of 4 - 2 = -463 - (-124) = -339 kJ. Therefore the standard enthalpy of formation, ΔH f, of phosphorus(III) chloride = -339 kJ
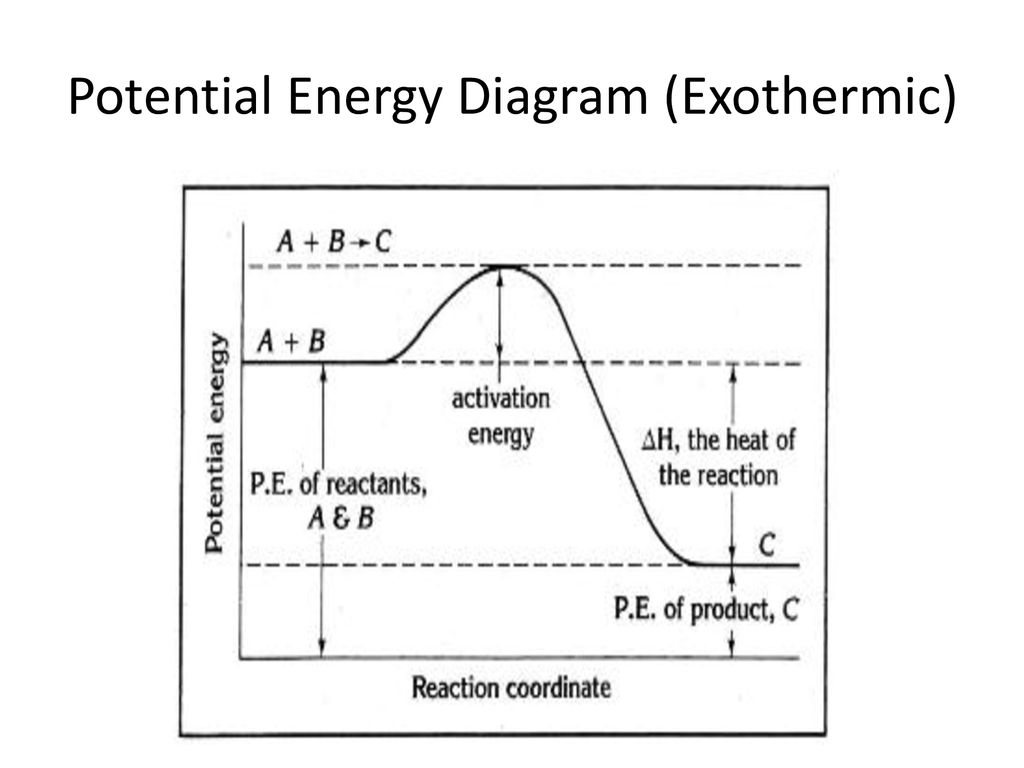
The diagram below represents a potential energy diagram of a chemical reaction. The graph below represents the potential energy changes that occur in a chemiCal reaction. (a) (b) (c) Reacäon Coordinate AccordinŒ to the graph, is energy absorbed or released durincr the action? Which lettere interv represents the AH of the reaction?

Consider The Following Enthalpy Diagram And Enthalpies Of Intermediate And Overall Chemical Brainly Com
The combustion of benzene ( l) gives C O 2 ( g) and H 2 O ( l) . Given that heat of combustion of benzene at constant volume is − 3263.9 k J m o l − 1 at 25 ∘ C ; heat of combustion (in k J m o l − 1 ) of benzene at constant pressure will be - ( R = 8.314 J K − 1 m o l − 1) 2. For which of the following reactions, Δ H is equal to ...
(ii) Suggest why this enthalpy change cannot be measured directly. [1] b)( Enthalpy changes of combustion can often be measured directly. The equation for the reaction which represents the enthalpy change of combustion (∆Hc)fthanol o e is as follows. C 2H5OH(I) + 3O 2(g) 2CO 2(g) + 3H 2O(I)

Which Of The Following Phase Diagrams Represents How A Catalyst Is Able To Change The Rate Of A Brainly Com
The standard enthalpy of reaction, Ho, is the sum of the enthalpy of the products minus the sum of the enthalpy of the reactants. H o = prod n fHo- react n fHo Hess's Law Hess's Law: The heat change in any reaction is the same whether the reaction takes place in one step or several steps, i.e.the overall energy change of a
Determine the activation energy and the enthalpy change for the reaction. b. Draw a labelled potential energy diagram for the reaction, indicating the relative energies of the reactants, products, and activated complex. What Is Required? You need to determine the activation energy, E a, and the enthalpy change, ΔH r, for the reaction.

Will Mark As Brainliest This Diagram Would Represent The Enthalpy Changes In Which Of The Brainly Com
How to draw the potential energy diagram for this reaction? Chemistry. 2 Answers. Truong-Son N. Apr 9, 2018. Since heat is released for. C3H8(g) + 5O2(g) → 3CO2(g) +4H2O(g) + 2219.9 kJ, we say that ΔH ∘ C = − 2219.9 kJ/mol propane. We approximate that this is the change in potential energy for the reactants going to the products.









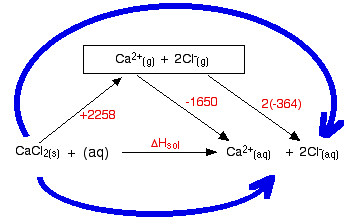

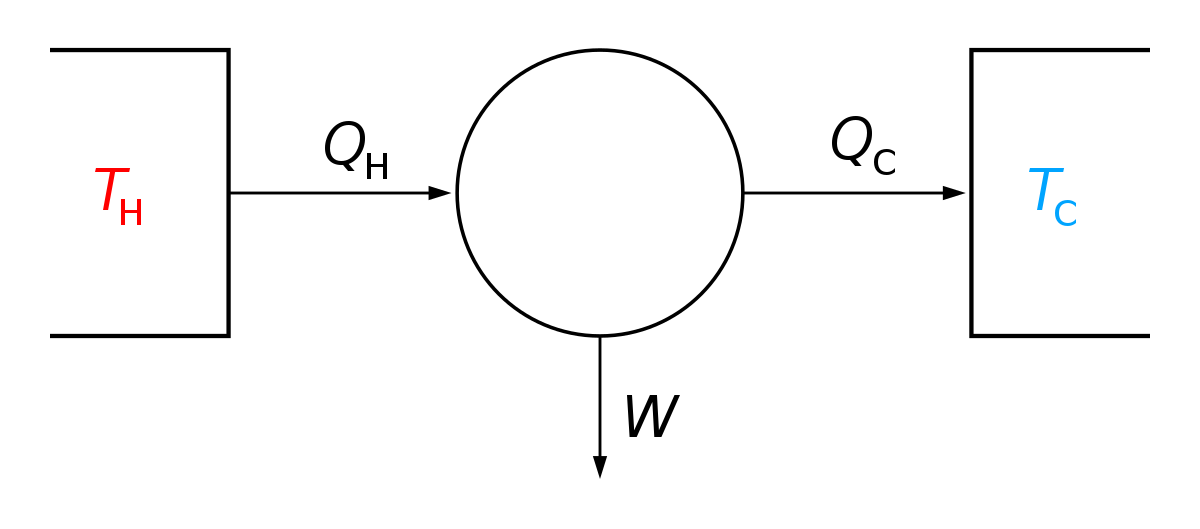


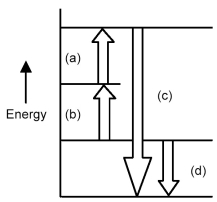
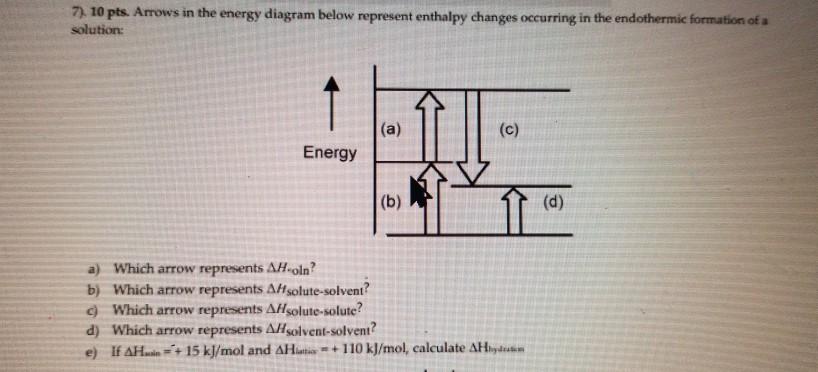


0 Response to "41 this diagram would represent the enthalpy change in which of the following"
Post a Comment