36 ray diagram for blind spot
The Blind Spot One of the most dramatic experiments to perform is the demonstration of the blind spot. The blind spot is the area on the retina without receptors that respond to light. Therefore an image that falls on this region will NOT be seen. It is in this region that the optic nerve exits the eye on its way to the brain.
The Blind Spot. There is something kind of funky about the setup here. The photoreceptors are at the back of the retina, the ganglion cells are at the front, and the ganglion cell axons make up the optic nerve that goes out through a hole at the back. ... Diagram of flow and blockage. Glaucoma is a disease caused by a blockage of the flow ...
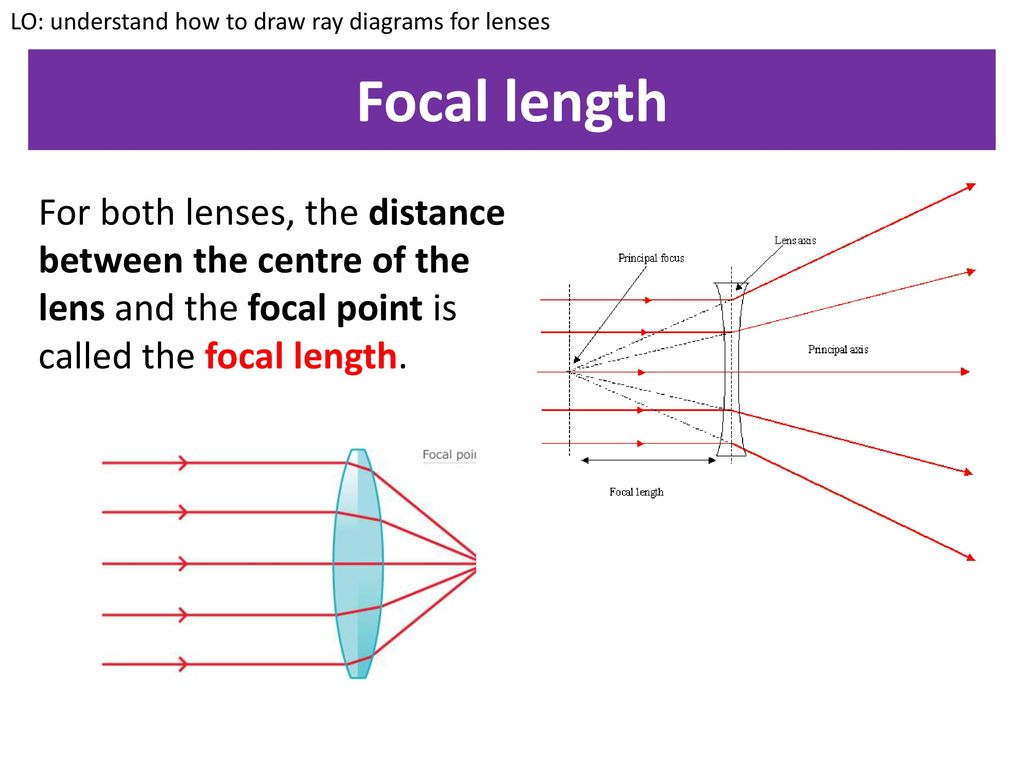
Principle 3: Any ray of light that passed through a focal point on the same side as the object will refract upon contacting the lens and become parallel to the principal axis on the other side. While there are three principles for predicting image quality through a convex lens, only two principals can apply to an object while drawing a ray diagram.
Ray diagram for blind spot
ray diagrams to show the image formation in case of defective eye and corrected eye. Ans : [CBSE 2012] Causes of Myopia a. Excessive curvature of cornea b. Elongation of eye ball. 42. (a) What is the least distance of distinct vision for the normal eye? (b) Does the above distance increase or decrease for long sighted eye? Give reason for your ...
US20100049393A1 US12/196,042 US19604208A US2010049393A1 US 20100049393 A1 US20100049393 A1 US 20100049393A1 US 19604208 A US19604208 A US 19604208A US 2010049393 A1 US2010049393 A1 US 2010049393A1 Authority US United States Prior art keywords vehicle driver blind spot dangerous change Prior art date 2008-08-21 Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion.
Describe with a ray diagram how this defect of vision can be corrected by using spectacles. Answer: Hypermetropia (Long-sightedness): A person can see distant objects distinctly but cannot see nearby objects so clearly in this case, the image is formed behind the retina.
Ray diagram for blind spot.
Two convenient and commonly used rules of reflection for concave mirrors are: (1) Any incident ray traveling parallel to the principal axis on the way to the mirror will pass through the focal point upon reflection. (2) Any incident ray passing through the focal point on the way to the mirror will travel parallel to the principal axis upon reflection.
Four statements are written below which are the general rules for drawing ray diagrams in case of lenses. Select the incorrect statements: (I) A ray of light from the object, parallel to the principal axis, after refraction from a concave lens, passes through the principal focus on the other side of the lens. ... This eliminates blind spots and ...
Question 8: The diagram given below represents the cross-section of the human eye: (i) Name the parts labeled 1—12. (ii) What is the function of the part marked '10'? (iii) What would happen if part '5' is damaged or cut ? Answer: (i) 1. Sclerotic 2. Choroid 3. Retina 4. Yellow spot or fovea 5. Optic nerve 6. Blind spot 7. Lens 8 ...
Finding Your Blind Spot: 2018/02/28 - 18:58 : Constructing Ray Diagrams - Concave Lens: 2018/02/28 - 03:05 : Convex Lens - how to construct a ray diagram to locate the image: 2018/02/28 - 03:09 : Cathode Ray Tube: 2018/02/15 - 01:29 : CRT Oscilloscope: 2018/04/17 - 04:47 : Bending Light Through A Prism #1: 2018/02/04 - 03:50
the retina through the optic disc (blind spot). Figure 2.8 Photomicrograph of the retina . Eyes That Capture Light Rods and cones are so named because of their respective shapes. Figure 2.9 Rod and cone . Eyes That Capture Light The distribution of rods and cones is not
(d) on the blind spot. Answer: (c) in front of the retina. Question 8. The eye defect 'presbyopia' can be corrected by: (a) convex lens (b) concave lens (c) convex mirror (d) Bi focal lenses Answer: (d) Bi focal lenses. Question 9. Which of the following lens would you prefer to use while reading small letters found in a dictionary?
Temporary blindness and blind spots (particularly in the center of the visual field) are symptoms associated with an ocular migraine. In most cases, only one eye is affected. An ocular migraine blind spot may start small and grow in size. One episode can last up to an hour.
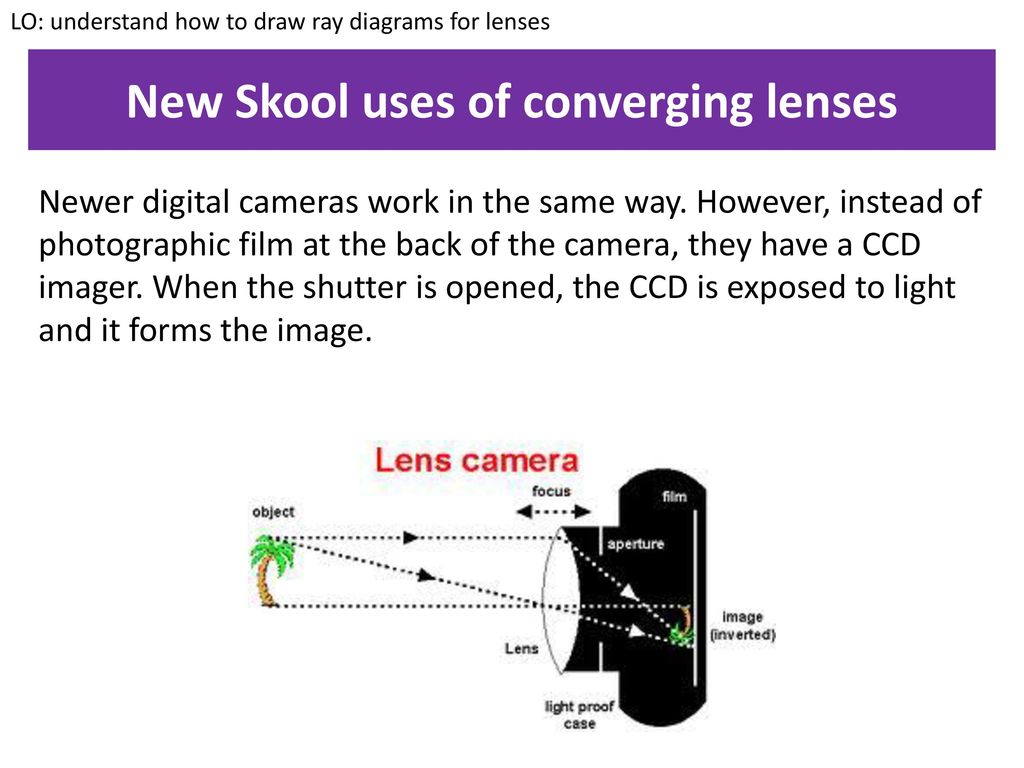
RAY DIAGRAM OF A CONCAVE OR DIVERGING LENS. ... It contains the optic disk, or blind spot, which is the junction of nerve fibers passing to the brain. It is the counterpart of the film in a camera. The film stores the photographic chemical record of data.
Spot compression or a "spot view" is a mammographic technique utilized to try and spread out the breast parenchyma in an effort to decrease overlap. For a spot compression view, the technologist uses a smaller paddle which thereby provides more focal and locally intense compression. Spot compression views are useful in the workup of focal ...
Every human eye has something called a blind spot. This natural blind spot is the place in the retina — the light-sensitive inner lining at the back of your eye — that doesn't have any cells that respond to light. The blind spot sits in the part of your retina where the optic nerve exits the eye.. Why do you have blind spots? Blind spots are a normal part of your vision.
The natural blind spot (scotoma) is due to lack of receptors (rods or cones) where the optic nerve and blood vessels leave the eye. There can also be artificial blind spots when something blocks light from reaching the photoreceptors, or when there is local adaptation of the retina as just after seeing a bright light.
Convex Mirror is a curved mirror where the reflective surface bulges out towards the light source. This bulging out surface reflect light outwards and are not used to focus light. These mirrors form a virtual image as the focal point (F) and the centre of curvature (2F) are imaginary points in the mirror that cannot be reached.
3) on a ray diagram how can you tell if an image is in focus? When you are looking at the image itself, how can you determine if it's in focus? 4) what is the blind spot in your eye caused by? Question: 1) why under very low light conditions are you unable to see color? 3) on a ray diagram how can you tell if an image is in focus?
To make a ray diagram, first, draw the mirror in the middle of the page and then draw a horizontal axis right through the center of the mirror. Carefully measure the focal length, and mark this on ...
Refraction And Light Ray Formation And Drainage Of Aqueous Humor Iris Structure Of Retina Retinal Ganglion Cell Diagram of blind spot Definition The blind spot is found in the sensory organ of humans, these are present in the eyes of human beings. These are found on the retina usually on the optic disk.
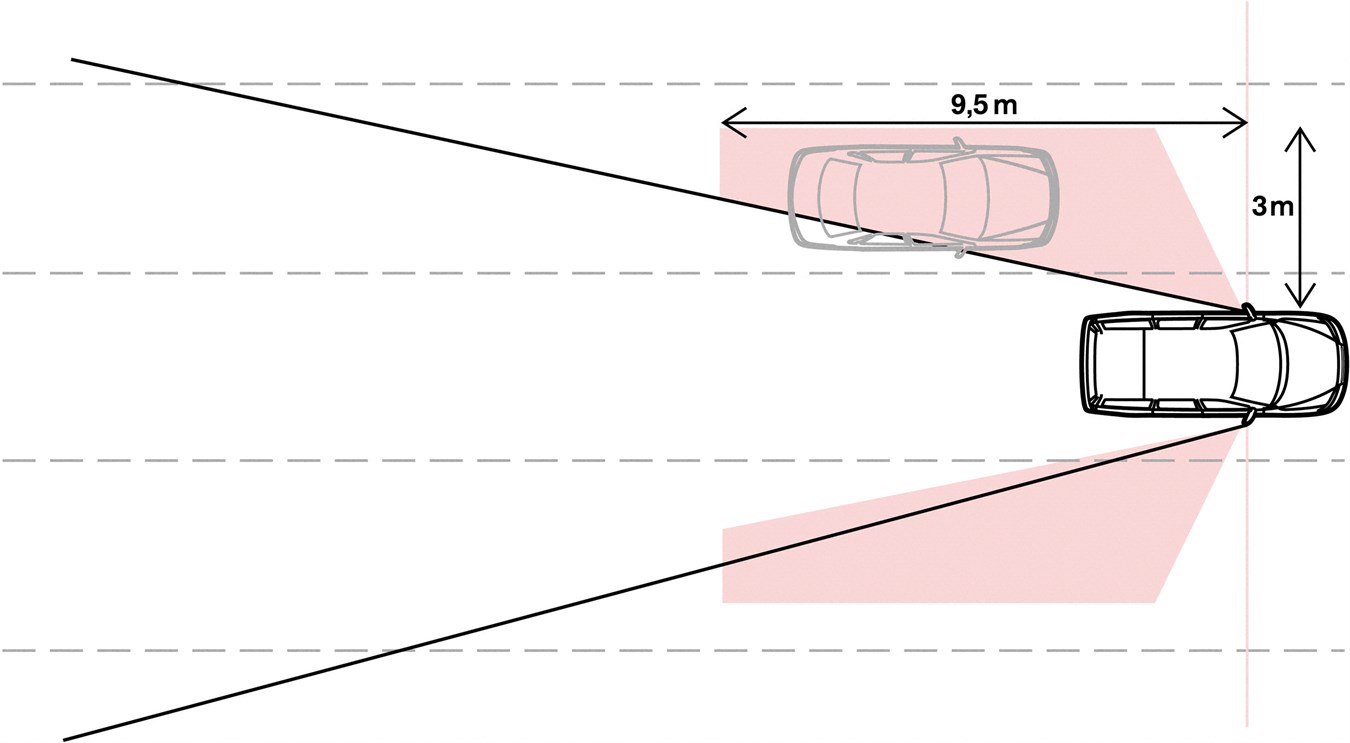
A blind spot in a vehicle is an area around the vehicle that cannot be directly seen by the driver while at the controls, under existing circumstances. In transport, driver visibility is the maximum distance at which the driver of a vehicle can see and identify prominent objects around the vehicle. Visibility is primarily determined by weather conditions (see visibility) and by a vehicle's design.
Driver's Side Mirror with No Blind Spot In 2012 a mathematician at Drexel University, Andrew Hicks, invented a curved side mirror for cars that greatly increases the field-of-view to eliminate blind spots (see photo above). His mirror has a field-of-view of about 45 degrees, compared with 14-17 degrees for flat driver's side mirrors.
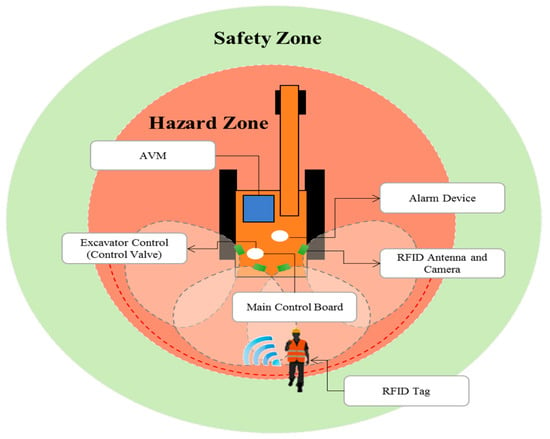
mated blind spot measurement tool, a ray-tracing algorithm, grid representation of the vehicle, and the development of an auto-mated blind spot measurement tool. The results show the visibility of personnel on the ground from the vehicle operator's perspective. Fig. 2 shows blind spot results of a dozer when using the GT method.
Blind spot: Where the optic nerve leaves the retina so lacks receptor cells. Pupil: Small window at the centre of the iris through which light enters the eye. The retina.
The ray diagram in Figure 2 shows image formation by the cornea and lens of the eye. The rays bend according to the refractive indices provided in Table 1. The cornea provides about two-thirds of the power of the eye, owing to the fact that speed of light changes considerably while traveling from air into cornea.
Equipment blind spots are dynamic! By overlaying a 3D point cloud from a laser scan of a construction forklift with information from an automated real-time h...
The ray diagram in Figure 16.33 shows image formation by the cornea and lens of the eye. The rays bend according to the refractive indices provided in Table 16.4 . The cornea provides about two-thirds of the magnification of the eye because the speed of light changes considerably while traveling from air into the cornea.
Blind Spot: Rotate the eye model so that part of the image falls on the blind spot. What happens to the portion of the image that falls on the blind ... Indicate on the ray diagram (back of data sheet) to show how squinting improves poor vision. (If you are nearsighted, try the following exercise. Make a small hole with your fist and

























0 Response to "36 ray diagram for blind spot"
Post a Comment