37 in the diagram to the right, moving from point a to point b is called a
In the second diagram, the two ends of the train moving to the right, are shown by parallel lines. The flash of light is given off at a point exactly halfway between the two ends of the train, and again form two 45° lines, expressing the constancy of the speed of light. This figure is called the Argand diagram, and the plane of the figure is called the Argand plane or the complex plane.The location of the point in the Argand plane can also be specified using polar coordinates. We use the symbol r for the distance from the origin to the point, and the symbol ϕ for the angle in radians between the positive real axis and the line segment from the …
pulled to the right? a) Left, b) Right, c) Not enough information given. Problem 1 Solution: This problem is most easily done by computing the velocity of a point by means of a translating and rotating reference frame attached to the moving body. Refer to the diagram provided with the problem statement. O xyz is an inertial non-moving reference ...
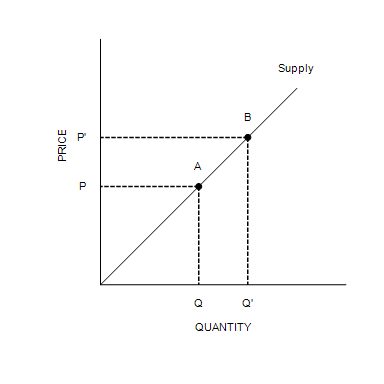
In the diagram to the right, moving from point a to point b is called a
the information and diagram shown. Two waves, Aand B, travel in the same direction in the same medium at the same time. On the grid, draw the resultant wave produced by the superposition of waves Aand B. 45. What is the amplitude of the resultant wave? 46. The diagram shows two pulses, Aand B, moving to the right along a uniform rope. 2.The diagram below shows two points, A and B, on a wave train. A)1.0 B)1.5 C)3.0 D)0.75 ... 11.Which diagram best represents the motion of the particle at position C as the wave moves to the right? A)light, only B)sound, only C)both light and sound ... 22.A single vibratory disturbance moving through a medium is called A)nodes B)antinodes C)a ... The point of intersection of all three curves is labeled B in Figure 2. At the pressure and temperature represented by this point, all three phases of water coexist in equilibrium. This temperature-pressure data pair is called the triple point. At pressures lower than the triple point, water cannot exist as a liquid, regardless of the temperature.
In the diagram to the right, moving from point a to point b is called a. In the diagram to the right, moving from Point A to point b is called a _____ the AD curve movement along; shift in Indicate which of the following is an explanation for the productivity slowdown of 1973-1994 0, as we move from left to right through the point of load application. In summary: Distributed loads Shear force slope (dV/dx) = -q V B - V A = Area of load intensity diagram between A and B Moment slope (dM/dx) = V M B - M A = Area of shear force diagram between A and B Concentrated loads Shear force slope (dV/dx) = 0 At load application ... A)left B)right C)ceiling D)floor 7.A box is pushed toward the right across a classroom floor. The force of friction on the box is directed toward the A)1 B)2 C)3 D)4 8.The diagram below represents a box shown sliding down an inclined plane. Toward which point will the force of friction on the box be directed? 1 Answer to 1. A single disturbance that moves from point to point through a medium is called a ___. a. period b. periodic wave c. wavelength d. pulse 2. If the particles of the medium are vibrating to and fro in the same direction of energy transport, then the wave is a ____ wave. a. longitudinal b. sound c....
The number of waves passing a point in a unit of time is called A. frequency B. wavelength C. amplitude D. period ... Aand B, moving to the right along a uniform rope. Compared to pulse A, pulse Bhas A. a slower speed and more energy ... In the accompanying diagram, the distance between points A and B on a wave is 5.0 meters. B) vibrate left and right C) vibrate into and out of the page D) remain stationary 47.The diagram below represents two waves of equal amplitude and frequency approaching point P as they move through the same medium. As the two waves pass through each other, the medium at point P will A) A and C B) A and D right hand rule. •Point thumb in direction of current •The fingers will curl in the direction of the ... the moving particle, and B is the magnetic field vector. Right hand rule for force due to a ... F = q v B = q v By the right hand rule the force points towards the wire. Same problem using vector analysis I = ... In the diagram to the right, moving from point A to point B is called a the AD curve. Moving from point A to point C is referred to as a the AD curve. Aggregate Demand Curve (AD) a B A с Price level AD AD2 Real GDP, Y (trillions of $) Question: In the diagram to the right, moving from point A to point B is called a the AD curve. Moving from ...
Position to right of origin, position(x) is positive Position to left of origin, position(x) is negative ... a.Can you show more than one object moving on a motion diagram? b.Look at the motion diagram below. ... • A motion diagram should specify the starting point • If the object stands still, indicate it with a single dot: Step 1 - Sketch a motion diagram for an object that is moving at a constant velocity. An object with constant velocity travels the same distance in the same direction in each time interval. The motion diagram in Figure 2.9 shows equally spaced images along a straight line. The numbers correspond to times, so this object is moving to the right with In the diagram to the right, a mass suspended at the end of an elastic spring undergoes SHM between point A and B. Use this diagram for questions 8 and 9. 8. At which location of the mass the system has the maximum kinetic energy? A. Only point A B. Only point B C. Only point 0 D. Point A and B E. The kinetic energy remains constant 9. field, as shown in the diagram (not to scale). The field is into the page on the diagram. (a) Where is the electron (b) What is the direction qB mv r=? Good to discuss A uniform magnetic field is directed into the page. A charged particle, moving in the plane of the page, follows a clockwise spiral of decreasing radius as shown. A reasonable ...
The object accelerates uniformly from point A to point B in 4 seconds, attaining a maximum speed of 10 meters per second at point B. The object then moves up the incline. [Neglect friction.] 7. The kinetic energy of the object at point B is 1) 1,000 J 2) 500 J 3) 100 J 4) 50 J 8. What distance did the object travel in moving from point A to ...
Rectangular Grid Walk. Grid walking describes a class of problems in which one counts the number of paths across a given grid, subject to certain restrictions. Most commonly, the restriction is that the only valid moves are those that approach the goal; in fact, this is so common that the term "grid-walking problems" almost invariably contains ...
point A, goes to point B and describes an arc of half of the circle. Which of ... The relationship between the position and time of a moving object is shown on the graph. Use this graph for questions 11 and 12. ... shown in the diagram to the right. Use this diagram to answer questions 28 through 30. 28. What is the x-component of vector D?
11.The diagram below represents the wave fronts produced by a point source moving to the right in a uniform medium. Observers are located at points A and B. Compared to the wave frequency and wavelength observed at point A, the wave observed at point B has a
The diagram below shows a transverse wave moving toward the left along a rope. Wave Velocity At the instant shown, point P on the rope is moving toward the (I) bottom of the page (3) left of the page (4) right of the page (2) top of the page 20. The diagram below shows a pulse moving to the right in a rope A is a point on the rope.
162 BLOCK DIAGRAM ALGEBRA AND TRANSFER FUNCTIONS OF SYSTEMS [CHAP. 7 We do not apply Step 3 at this time, but go directly to Step 4, moving takeoff point 1 beyond block G2 + G,: We may now rearrange summing points I and 2 and combine the cascade blocks in the forward loop using Transformation 6, then Transformation 1: Step 3: Finally, we apply Transformation 5 to remove l/(G2 + G,) from the ...
The diagram is representing a model of two spacetime events, event A and event B. Two observers in two inertial reference frames pass each other in the origin. At that point is event A - the green ball. The user inputs the time and distance for event B - the red ball - …
of time. The wave is travelling to the right. On the diagram (a) mark a point on the water surface whose motion is exactly 180o out of phase with the motion at X. Label this point A, (1) (b) draw an arrow at point Y to show the direction in which the water at Y is moving at the instant shown, (1)
Right Angle Straight Angle Acute Triangle Right Triangle Obtuse Triangle ... an image formed by moving every point on the preimage the same distance in the same direction pre-image image . ... preimage about a point called the center of rotation pre-image image .
When two forces act on a point particle, the resulting force, the resultant (also called the net force), can be determined by following the parallelogram rule of vector addition: the addition of two vectors represented by sides of a parallelogram, gives an equivalent resultant vector that is equal in magnitude and direction to the transversal of the parallelogram.
Business. Economics. Economics questions and answers. In the diagram to the right, mowing from point A to point B is called a the AD curve Moving from point A to point C b referred to as a the AD curve.
B) one of the two points. C) the midpoint of the line connecting the two points. D) None of the above. 2. When the direction of velocities of two points on a body are perpendicular to each other, the IC is located at A) infinity. B) one of the two points. C) the midpoint of the line connecting the two points. D) None of the above.
12.11.2018 · Diagram of Production Possibility Frontier. Moving from Point A to B will lead to an increase in services (21-27). But, the opportunity cost is that output of goods falls from 22 to 18. At point D, the economy is inefficient. At point D, we can increase both goods and services without any opportunity cost. Pareto efficiency is any point on the ...
Point A is called the base point in this analysis. It generally has a ... Write the equation vB = vA + vB/A and by using the kinematic diagram, underneath each term represent the vectors ... Plan: Notice that the downward motion of C causes B to move to the right. Also, CB and AB both rotate counterclockwise.
1. Roughly sketch the phase diagram, using units of atmosphere and Kelvin. Answer. 1-solid, 2-liquid, 3-gas, 4-supercritical fluid, point O-triple point, C-critical point -78.5 °C (The phase of dry ice changes from solid to gas at -78.5 °C) 2. Rank the states with respect to increasing density and increasing energy.
the supports as the bar deflects under the loads. The beam is shown in Fig. 5.1 (b). Overhanging Beam The beam freely supported at any two points and having one or both ends projected beyond these supports is called an overhanging beam. Fig. 5.1 (c). Fixed Beams A beam, whose both ends are fixed or built-in walls, is known as fixed beam.
In the diagram to the right, moving from point A to point B is called a the AD curve. Moving from point A to point C is referred to as a the AD curve. movement along; shift in. Indicate which of the following would cause a shift in the aggregate demand curve from point A to point C. (Mark all that apply.)
The point of intersection of all three curves is labeled B in Figure 2. At the pressure and temperature represented by this point, all three phases of water coexist in equilibrium. This temperature-pressure data pair is called the triple point. At pressures lower than the triple point, water cannot exist as a liquid, regardless of the temperature.
2.The diagram below shows two points, A and B, on a wave train. A)1.0 B)1.5 C)3.0 D)0.75 ... 11.Which diagram best represents the motion of the particle at position C as the wave moves to the right? A)light, only B)sound, only C)both light and sound ... 22.A single vibratory disturbance moving through a medium is called A)nodes B)antinodes C)a ...
the information and diagram shown. Two waves, Aand B, travel in the same direction in the same medium at the same time. On the grid, draw the resultant wave produced by the superposition of waves Aand B. 45. What is the amplitude of the resultant wave? 46. The diagram shows two pulses, Aand B, moving to the right along a uniform rope.








0 Response to "37 in the diagram to the right, moving from point a to point b is called a"
Post a Comment