37 sodium potassium pump diagram
A diagram showing six steps of active transport in the sodium-potassium pump. Each numbered step corresponds to the text above. The net result is that the concentration of Na+ is higher outside the cell and the concentration of K+ is higher inside the cell.
How a sodium potassium pump can maintain a voltage gradient across a cell or neuron's membrane. The sodium-potassium pump goes through cycles of shape changes to help maintain a negative membrane potential. In each cycle, three sodium ions exit the cell, while two potassium ions enter the cell. These ions travel against the concentration gradient, so this process requires ATP.
5. History The sodium-potassium pump was discovered in 1957 by the Danish scientist Jens Christian Skou. He was awarded a Nobel Prize for his work in 1997. 6. Structure The Na+ - K+-ATPase can function as an α β dimer. Consists of - - a catalytic α subunit with ten trans-membrane segments (8 transmembrane α-helical segments and two large ...
Sodium potassium pump diagram
The sodium potassium pump ratio, as mentioned above, is the prime function of this protein enzyme present in the cell membrane of different animal cells. Its functions are quite important for cellular physiology and the functioning of the tissues. By studying the structure and mode of operation of this pump, many pharmacological compounds can ...
sodium-potassium pump sodium and potassium gates polarity Nerve impulse = resting potential + action potential Resting Potential: outside of the neuron is positive, the inside of the neuron (axoplasm) is negative due to the distribution of Na+, K+, and negative ions. • At rest, there is more K+ inside and more Na+ outside of the neuron.
Sodium potassium pump. Active transport review. Practice: Facilitated diffusion. Next lesson. Mechanisms of transport: tonicity and osmoregulation. Sort by: Top Voted. Uniporters, symporters and antiporters. Sodium potassium pump. Up Next. Sodium potassium pump. Biology is brought to you with support from the Amgen Foundation.
Sodium potassium pump diagram.
What is the Sodium-Potassium Pump Sodium-Potassium Pump, also known as the Na + /K + pump or Na + /K + -ATPase, is a transmembrane protein pump found in animals' cell (plasma) membrane. Its fundamental purpose is to transport sodium and potassium ions across the cell in the ratio of 3: 2.
sodium-potassium pump is a protein complex than pumps three sodium (Na+) ions out of the cells while drawing two potassium (K+) ions into the cell
The Sodium-potassium Pump: structure, function, regulation and pharmacology 972 8 934 2278 steven.karlish@weizmann.ac.il www.weizmann.ac.il Biological Chemistry Prof. Steven J.D.Karlish The Na, K-pump or Na/K-ATPase actively transports Na and K ions across mammalian cell membranes to establish and maintain the characteristic trans-
1.4 Membrane Transportation: Structure and Function of Sodium-Potassium PumpUnderstanding that:- Structure and function of sodium-potassium pumps for active ...
Na⁺/K⁺-ATPase (sodium-potassium adenosine triphosphatase, also known as the Na⁺/K⁺ pump or sodium-potassium pump) is an enzyme (an electrogenic transmembrane ATPase) found in the membrane of all animal cells. It performs several functions in cell physiology.. The Na⁺/K⁺-ATPase enzyme is active (i.e. it uses energy from ATP).For every ATP molecule that the pump uses, three ...
The sodium-potassium-ATPase, also known as the Na-K pump or the sodium pump, is the protein responsible for the ATP-dependent, coupled transport of sodium and potassium ions across the plasma membrane. The Na-K pump is found on the surface of all animal cells and is a major force in maintaining the concentration gradients of these ions across ...
The process of moving sodium and potassium ions across the cell membrance is an active transport process involving the hydrolysis of ATP to provide the necessary energy. It involves an enzyme referred to as Na + /K +-ATPase.This process is responsible for maintaining the large excessof Na + outside the cell and the large excess of K + ions on the inside. A cycle of the transport process is ...
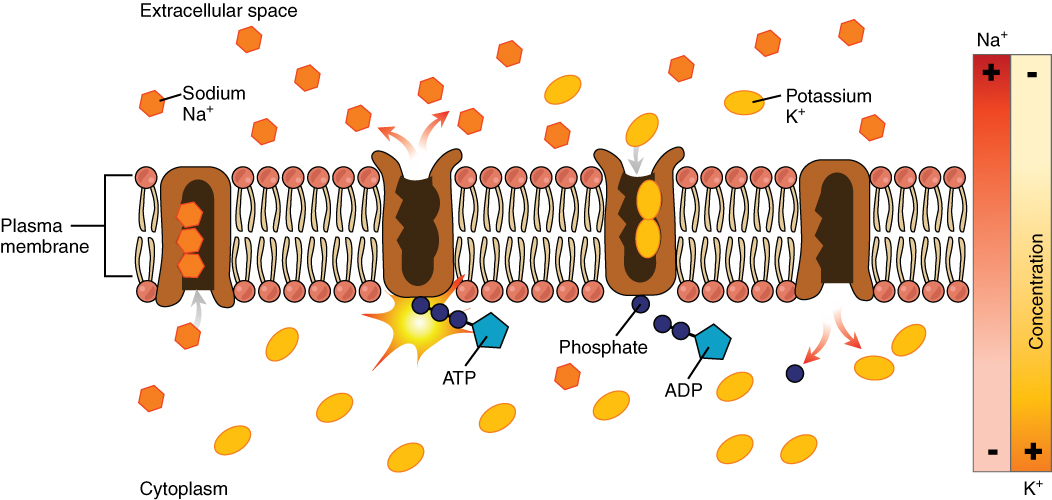
36 sodium potassium pump diagram. The sodium - potassium pump moves sodium ions out of and potassium ions into the cell. This pump is powered by ATP. For each ATP that is broken down, 3 sodium ions move out and 2 potassium ions move in. In more detail: Sodium ions bind to the pump and a phosphate group from ATP attaches to the pump, causing it ...
Mar 5, 2021 — The sodium-potassium pump system moves sodium and potassium ions against large concentration gradients. It moves two potassium ions into the ...The Sodium-Potassium Pump · The Electrochemical Gradient
The sodium-potassium pump system moves sodium and potassium ions against large concentration gradients. It moves two potassium ions into the cell where potassium levels are high, and pumps three sodium ions out of the cell and into the extracellular fluid. As is shown in the figure above, three sodium ions bind with the protein pump inside the ...
Sodium-potassium pump - also known as the Na+/K+ pump or Na+/K+-ATPase, this is a protein pump found in the cell membrane of neurons (and other animal ...Nov 20, 2019 · Uploaded by Neuroscientifically Challenged
The sodium-potassium pump moves sodium ions out of and potassium ions into the cell. This pump is powered by ATP. For each ATP that is broken down, 3 sodium ions move out and 2 potassium ions move in. In more detail: Sodium ions bind to the pump and a phosphate group from ATP attaches to the pump, causing it to change its shape.
The sodium-potassium pump actively transports Na+ out of the cell while actively transporting a K+. The result is a concentration gradient or stockpile of ions that have the ability to do work in (nerve impulse propagation, muscle contraction, and stockpiling nutrients in root cells). Bulk Transport using Vesicles 11.
The sodium-potassium pump uses active transport to move molecules from a high concentration to a low concentration. The sodium-potassium pump moves sodium ions out of and potassium ions into the cell. This pump is powered by ATP. For each ATP that is broken down, 3 sodium ions move out and 2 potassium ions move in.
Sodium-potassium pump (diagram) The concentration gradient will later contribute to generating an action potential, because of one of the laws of physics.By concentration gradient definition, every element modifies its concentration gradient to seek equilibrium.For example, ions will diffuse from a place of higher concentration to a place of lower concentration until the concentration of the ...
The Na+ K+ pump is an electrogenic transmembrane ATPase first discovered in 1957 and situated in the outer plasma membrane of the cells; on the cytosolic side.[1][2] The Na+ K+ ATPase pumps 3 Na+ out of the cell and 2K+ that into the cell, for every single ATP consumed. The plasma membrane is a lipid bilayer that arranged asymmetrically, containing cholesterol, phospholipids, glycolipids ...
One of the most important pumps in animal cells is the sodium-potassium pump (Na +-K + ATPase), which maintains the electrochemical gradient (and the correct concentrations of Na + and K +) in living cells.The sodium-potassium pump moves K + into the cell while moving Na + out at the same time, at a ratio of three Na + for every two K + ions moved in. The Na +-K + ATPase exists in two forms ...
The sodium potassium pump (NaK pump) is vital to numerous bodily processes, such as nerve cell signaling, heart contractions, and kidney functions. The NaK pump is a specialized type of transport ...
The sodium potassium pump is the mechanism responsible for maintaining this electrical gradient, doing so by pumping two potassium ions into the cell and pumping out three sodium ions, ultimately leading to the interior of the nerve cell being slightly more negative than the exterior.
channel and the sodium-potassium pump in the diagram. Table 1. Average Ion Concentrations Inside and Outside of Mammalian Neurons . Ion Intracellular Concentration (mM) Extracellular Concentration (mM) Potassium (K+) 140 5 Sodium (Na+) 15 150 Chloride (Cl-) 10 120 Large anions (A-), such as
The Sodium (Na+) - Potassium (K+) Pump BIG IDEAS: +Uses energy supplied by the cell in the form of ATP to +transport Na out of the cell and K into the cell + Both Na+ and K are moved against the concentration gradient (from low to high) Creates an electrical gradient across the membrane (outside of the cell is + while the inside off the cell is -)
During depolarization, which of the following statements about voltage-gated ion channels is TRUE. Na+ gates open before K+ gates. Depolarization occurs because. more Na+ diffuse into the cell than K+ diffuse out of it. The sodium-potassium pump is involved in establishing the resting membrane potential. TRUE.
sodium-potassium pump, in cellular physiology, a protein that has been identified in many cells that maintains the internal concentration of potassium ions [K +] higher than that in the surrounding medium (blood, body fluid, water) and maintains the internal concentration of sodium ions [Na +] lower than that of the surrounding medium.
The sodium-potassium (Na +-K+) pump is an example of P-type ATPase pump that moves three Na+ions out and two K+ions into the cell for each ATP hydrolyzed. The action of Na +-K+pump maintains a resting membrane potential of -30 mV to -70 mV in mammalian cells. (The potential is negative on the inside of the membrane.)
The sodium and potassium gradients across the plasma membrane are used by animal cells for numerous processes, and the range of demands requires that the responsible ion pump, the Na,K-ATPase, can be fine-tuned to the different cellular needs. Therefore, several isoforms are expressed of each of the three subunits that make a Na,K-ATPase, the alpha, beta and FXYD subunits.


0 Response to "37 sodium potassium pump diagram"
Post a Comment