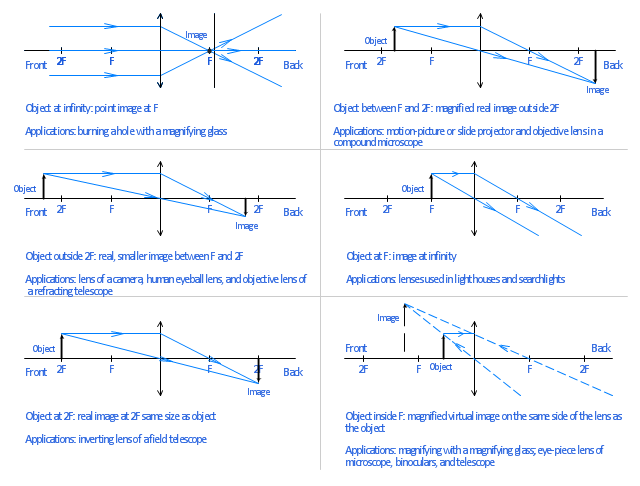
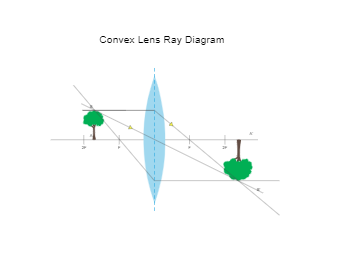
39 diverging lens ray diagram
So I'm myopic (near sighted) myself with glasses. From Ray diagram, I understand why diverging lens produce smaller images. And I also understand why myopics need diverging lenses (bc myopic eyes converge rays too soon). But I can't combine these 2 concepts together. Like why would diverging lens create smaller images even though myopics need to view things near? I just tested my glasses and if I put my glasses inches in front of me, yeah the images are smaller, but somehow clearer. But I d... Hey guys, so after hours of study/confusion (idk maybe I'm just like...physics challenged and had trouble...that happens often to me with topics)...I've boiled it down to the following. Hopefully, it can help you all solve these kinds of problems; NS Content review goes over how to draw the diagrams, etc., but I really doubt any of us will be drawing diagrams on test day. Things to be aware of that don't have to do with the 5 steps: --> Snell's Law and refraction/reflection (i.e. what ...
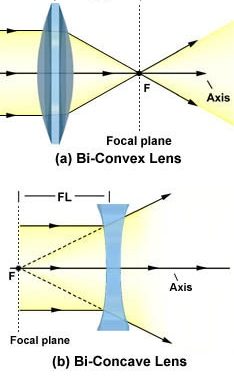
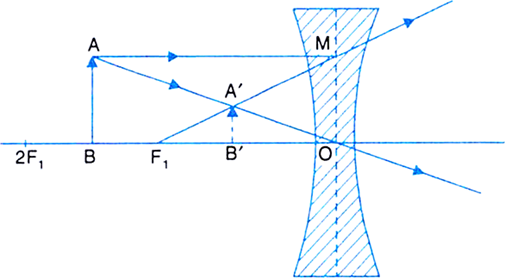
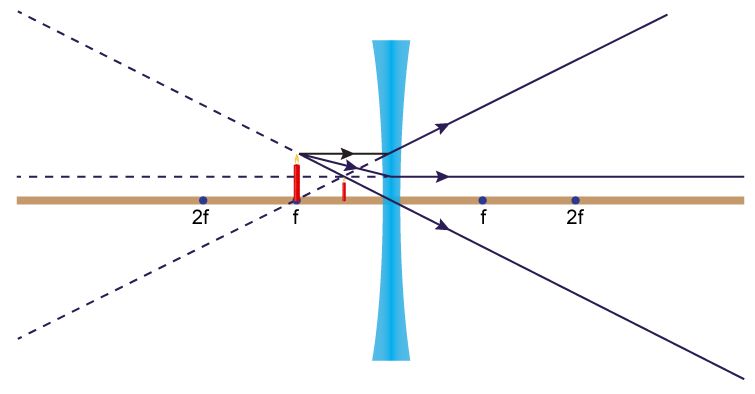
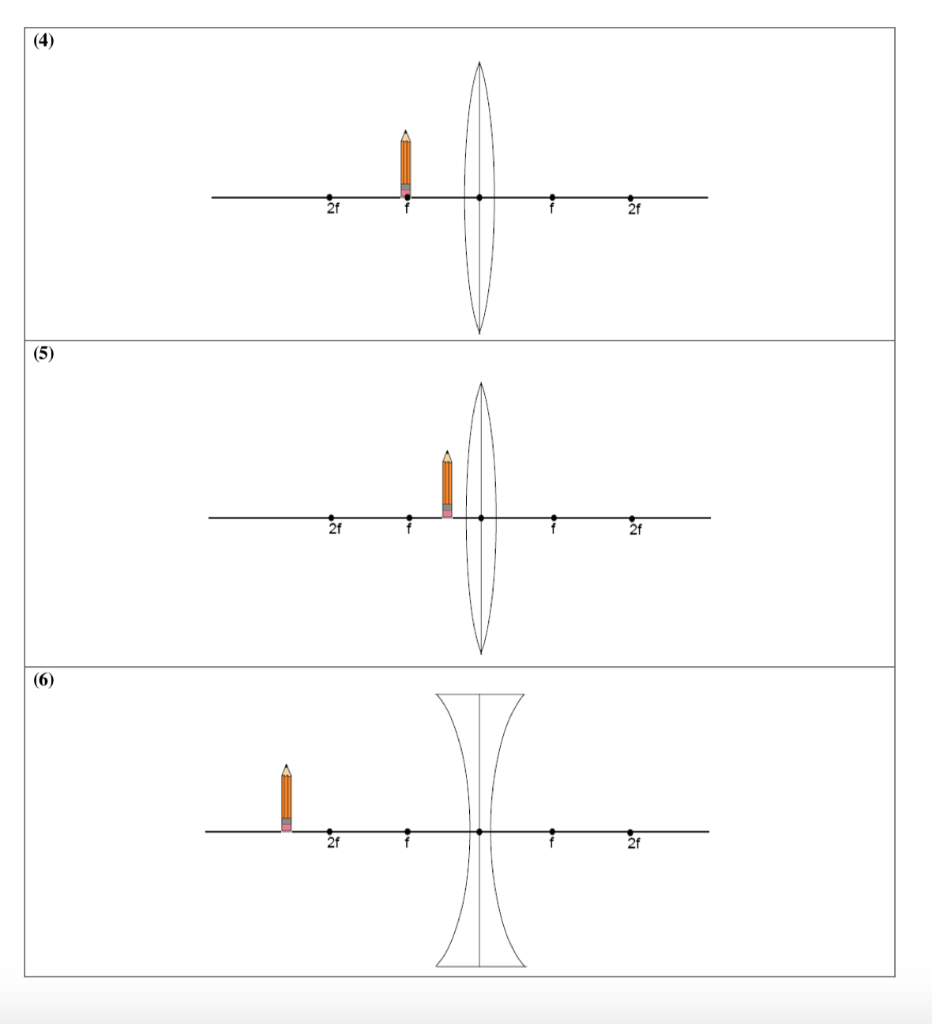
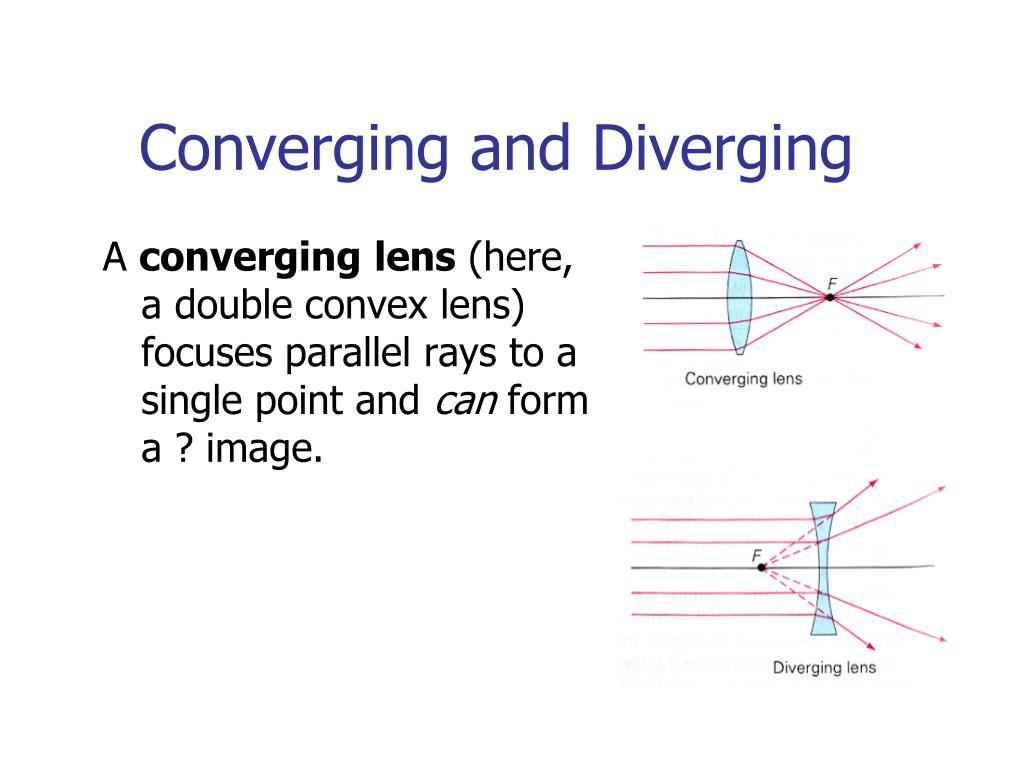
Guidelines for rays falling on the concave and convex lenses · When a ray strikes concave or convex lenses obliquely at its pole, it continues to follow its path ...
Diverging lens ray diagram
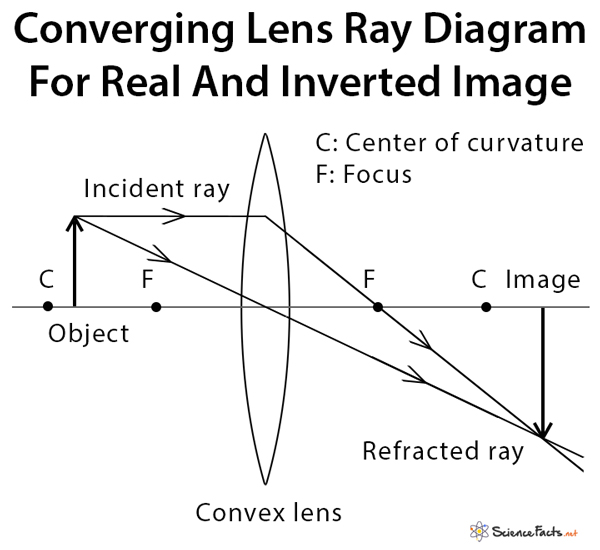
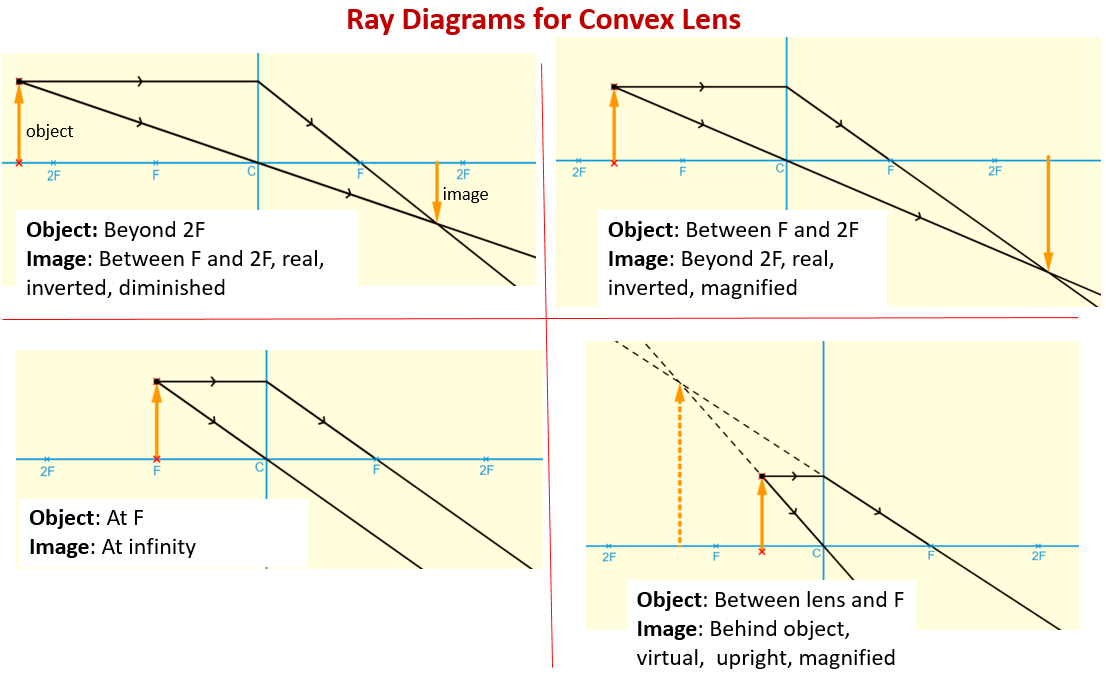
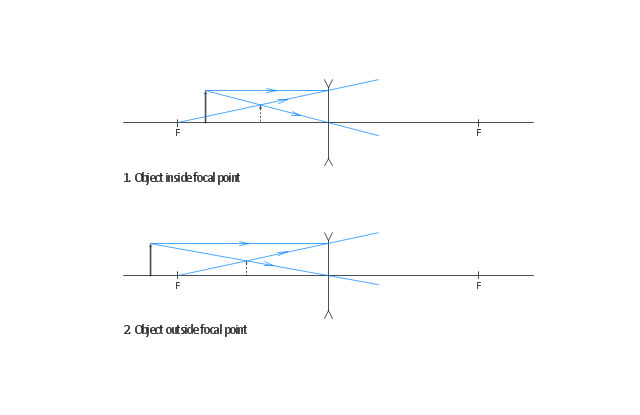
Apr 26, 2020 — For a Concave lens,There are only 2 casesThey areObject is Placed at InfinityObject is Placed between Infinity and Optical CenterCase 1 ... [https://i.imgur.com/6vJY7yh.png](https://i.imgur.com/6vJY7yh.png) Hello, is there a way to solve this problem only using a ray diagram and the thin lens equation? (1/f = 1/i \+ 1/o) I did not remember the facts that diverging lenses have negative focal lengths, and that diverging lenses create a virtual and reduced image if the object is further than the focal length. Is knowing these facts essential to finding the correct answer here? The ray diagrams for concave lenses inside and outside the focal point give similar results: an erect virtual image smaller than the object. The image is always ...
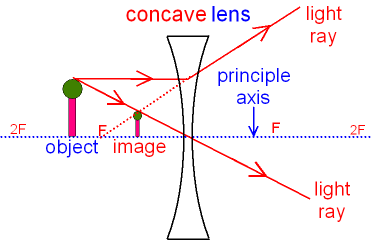
Diverging lens ray diagram. would we ever need to know how to draw ray diagrams for mirror/lens? or would it be good enough if we know the formulas,etc and that for converging lens/mirror, if object > focal length then images are real and inverted/ if object < focal length they are upright and virtual and for diverging its only upright and virtual? There are more and more reports about what are essentially contact lenses which replace displays to present an image to the user. Glasses are a less intrusive extension of this Augmented Reality concept. However, with my grasp of optics and the biology of the eye I can't understand how these could work, and here is why - see the attached diagram of the human eye I made. It is somewhat simplified: the lens is too big, the iris not considered and the corneas' effect ignored. Still, it is sufficie... A real image is formed by a converging lens. If a weak diverging lens is placed between the converging lens and the image, where is the new image ...15 pages Here you have the ray diagrams used to find the image position for a diverging lens. A diverging lens always form an upright virtual image.
Hi all. I have always been a studious guy without much artistic skills or hobbies and I am a pretty smart guy who had straight As in most of the high school and college classes. I can help you understand and excel in several topics via: 1. suggesting trusted and verified sources, books, youtube videos, links, blogs 2. private doubt solving sessions (however I would be able to do these either on weekends bcoz I work a full-time job or on weekdays after 7 PM IST (Indian Standard time) till 12 PM... The ray diagram above illustrates that the image of an object in front of a double concave lens will be located at a position behind the double concave lens. The ray diagrams for concave lenses inside and outside the focal point give similar results: an erect virtual image smaller than the object. The image is always ... [https://i.imgur.com/6vJY7yh.png](https://i.imgur.com/6vJY7yh.png) Hello, is there a way to solve this problem only using a ray diagram and the thin lens equation? (1/f = 1/i \+ 1/o) I did not remember the facts that diverging lenses have negative focal lengths, and that diverging lenses create a virtual and reduced image if the object is further than the focal length. Is knowing these facts essential to finding the correct answer here?
Apr 26, 2020 — For a Concave lens,There are only 2 casesThey areObject is Placed at InfinityObject is Placed between Infinity and Optical CenterCase 1 ...


















0 Response to "39 diverging lens ray diagram"
Post a Comment