40 free body diagram pendulum
Dr. Massa and the great Orbax discuss the conical pendulum, drawing free body diagrams and centripetal acceleration.
To begin, we first draw the free-body diagram where the forces acting on the pendulum are its weight and the reaction at the rotational joint. We also include a moment due to the friction in the joint (and the rotary potentiometer).
The force diagram on the pendulum is shown in Figure 24.4. In particular, there is an unknown pivot force and the gravitational force acts at the center of mass of the rod. Figure 24.4 Free-body force diagram on rod The torque about the pivot point P is given by P τ=r P,cm ×mg. (24.3.2)

Free body diagram pendulum
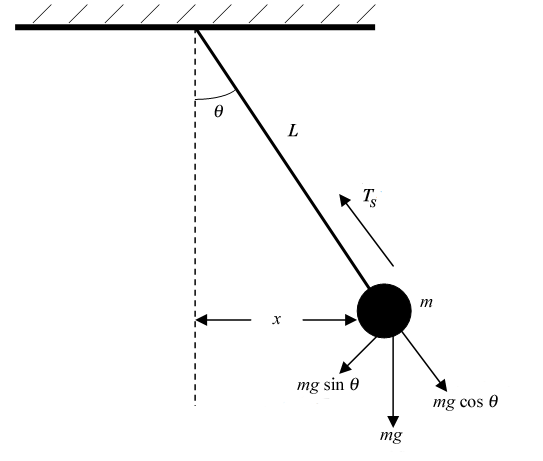
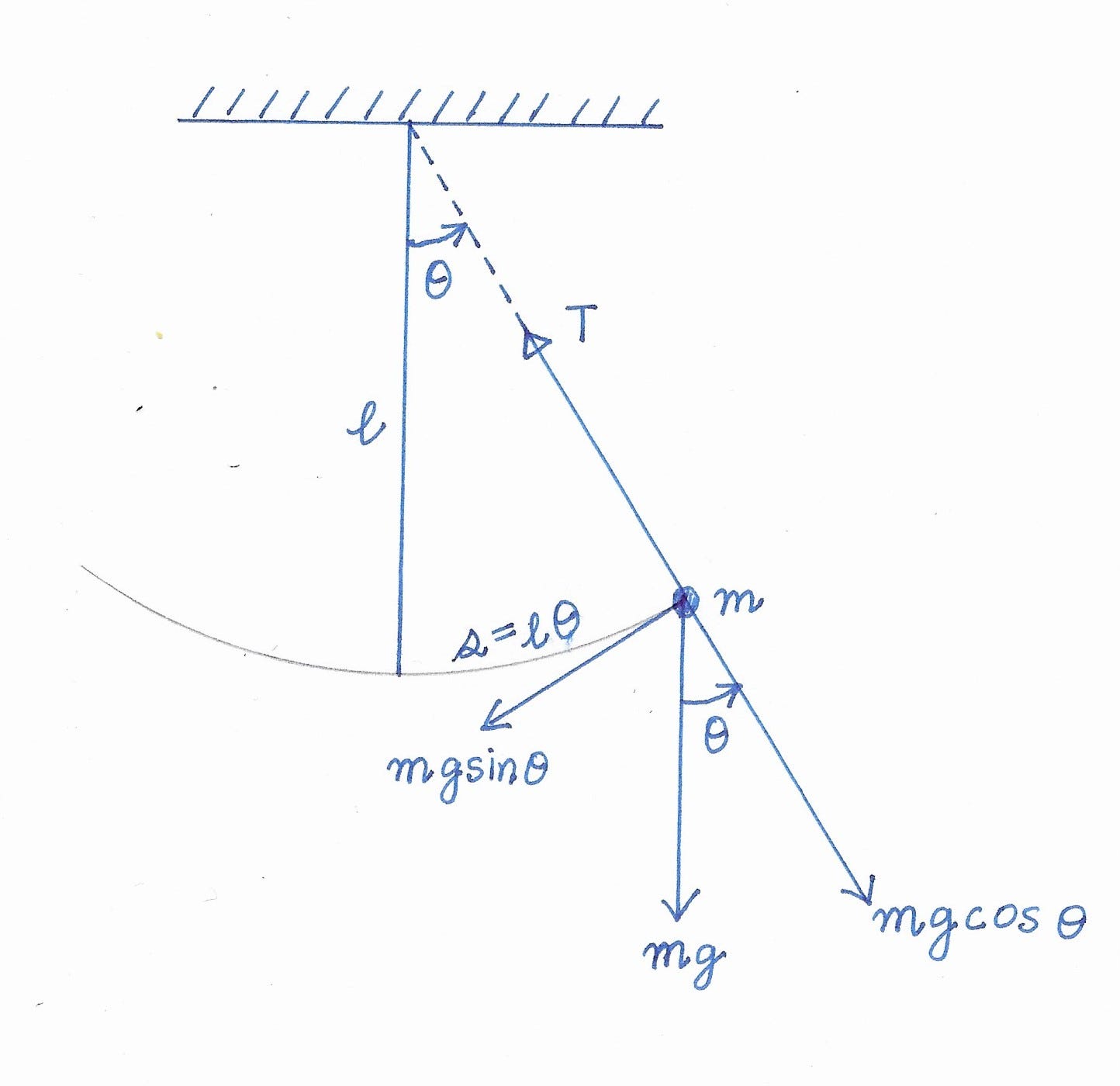
Figure 2: FBD for the pendulum Free-body-diagram of the pendulum Figure 2 shows all the forces acting on the pendulum of mass . The tension in the rope attached to the mass prevents it from flying away, and is given by . The gravitational force, , acts vertically downward and affects the motion of the pendulum. The other force is the frictional ...
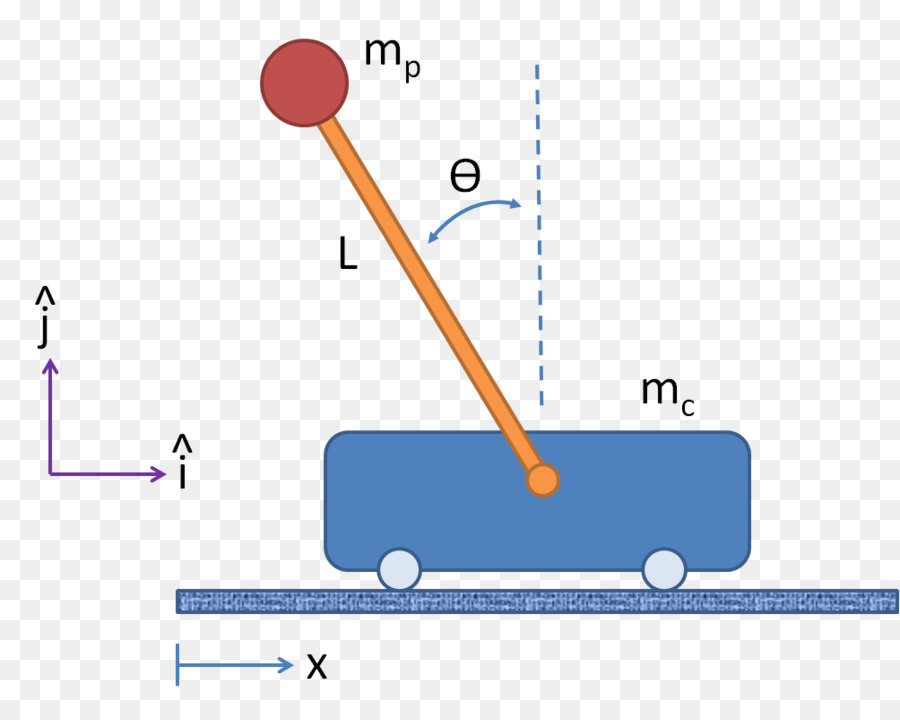
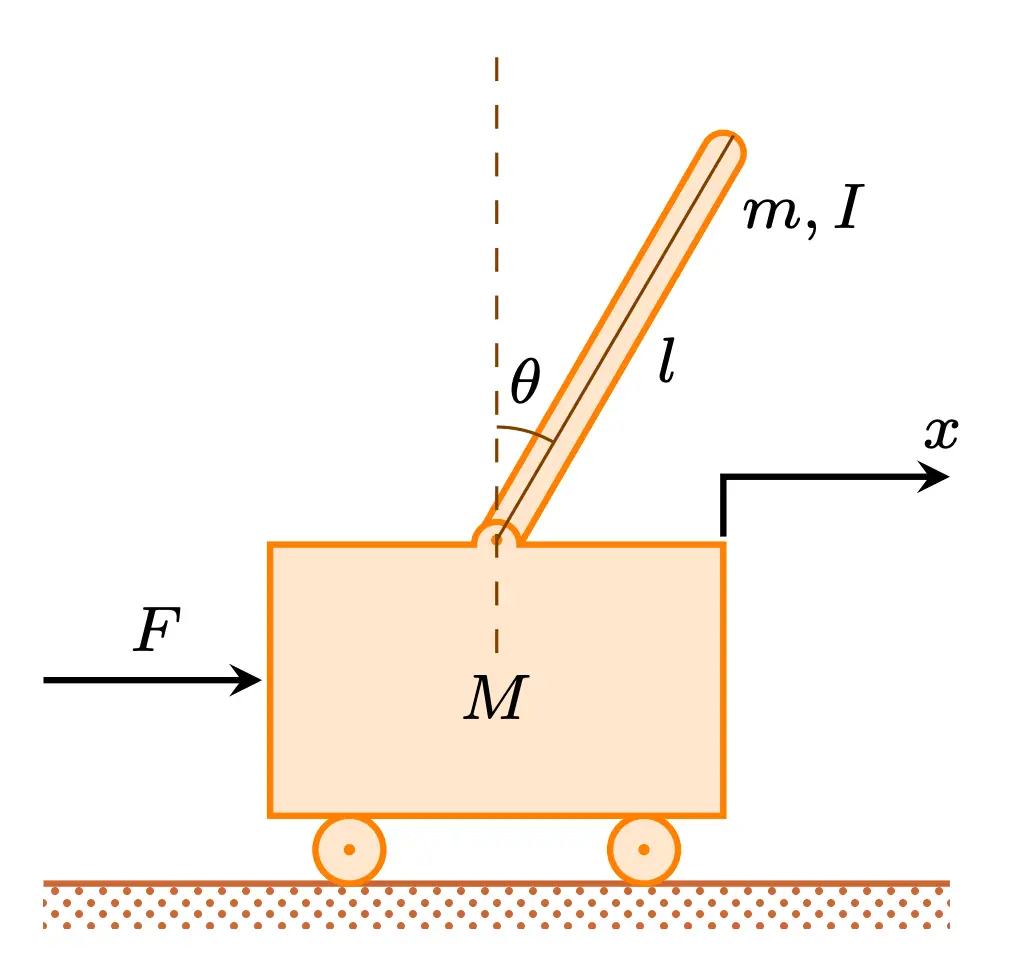
Free Body Diagram of an Inverted Pendulum in TikZ April 15, 2021 by admin In this tutorial, we will draw a free body diagram of an inverted pendulum in LaTeX using TikZ package. We will draw a cart and place a moving rod on top of it, then place the arrows to represent forces and label our elements. Table of Contents 1. Let's start by the ground
moving projectile. After the capture, the pendulum swings to a maximum opening angle of µ. Using conservation of momentum and energy, the initial velocity v of the projectile can be determine based on the opening angle µ. The center of mass of the pendulum is labeled "cm". Figure 3.2: The free-body diagram for the ballistic pendulum.
Free body diagram pendulum.
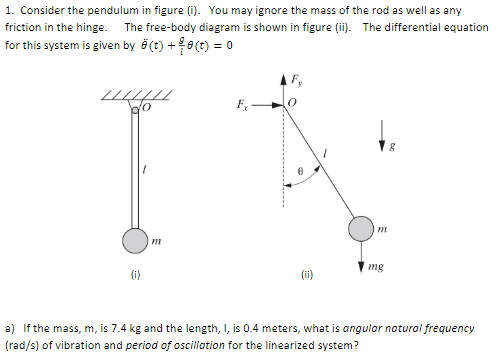
Begin by drawing the free body diagram for the upper mass and writing an expression for the net force acting on it. Define these variables: T = tension in the rod; m = mass of pendulum; g = gravitational constant; The forces on the upper pendulum mass are the tension in the upper rod T 1, the tension in the lower rod T 2, and gravity −m 1 g ...
double pendulum problem lsu free body diagrams for the forces on each mass 2 newton’s equations for the double pendulum we derive the same expressions for the first particle r. phys5 1f 10. 12 7 the simple pendulum step 1 – draw a free body diagram for the ball immediately after it is released the free body diagram is drawn in figure 12 18 ...
Aug 03, 2017 · Check here to show the free-body diagram. Purple is the true motion; orange is the comparison motion. This is a simulation of a simple pendulum (a ball attached to a massless rod). If the damping is set to zero, the pendulum moves without resistance. The larger the damping, the larger the resistive torque.
body diagram Lecture 27. THE COMPOUND PENDULUM The term "compound" is used to distinguish the present rigid-body pendulum from the "simple" pendulum of Section 3.4b, which consisted of a particle at the end of a massless string. Derive the general differential equation of motion for the pendulum of figure 5.16a and determine its ...
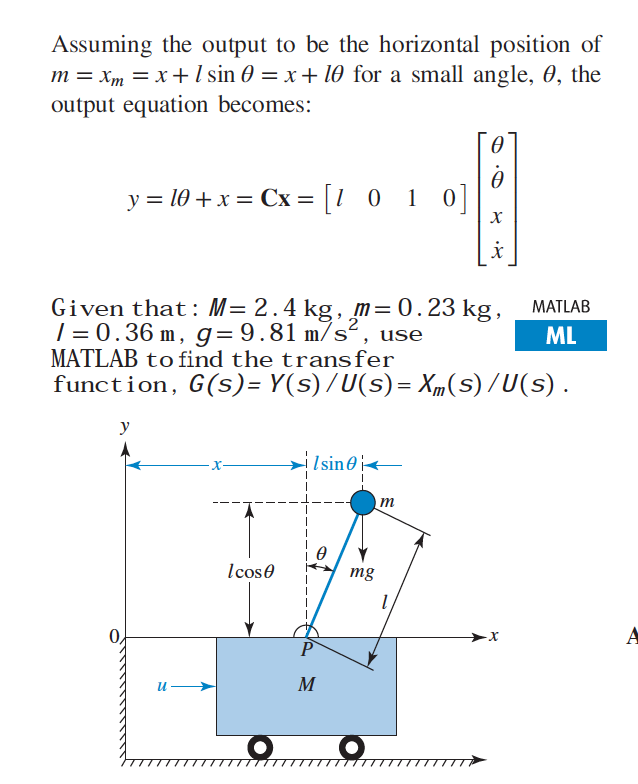
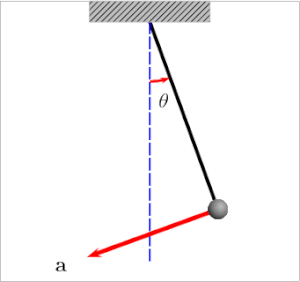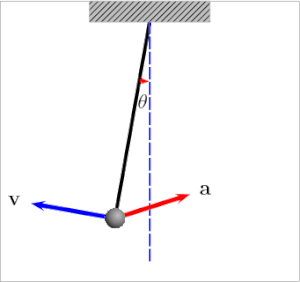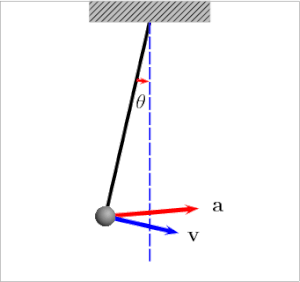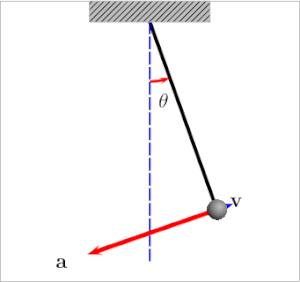
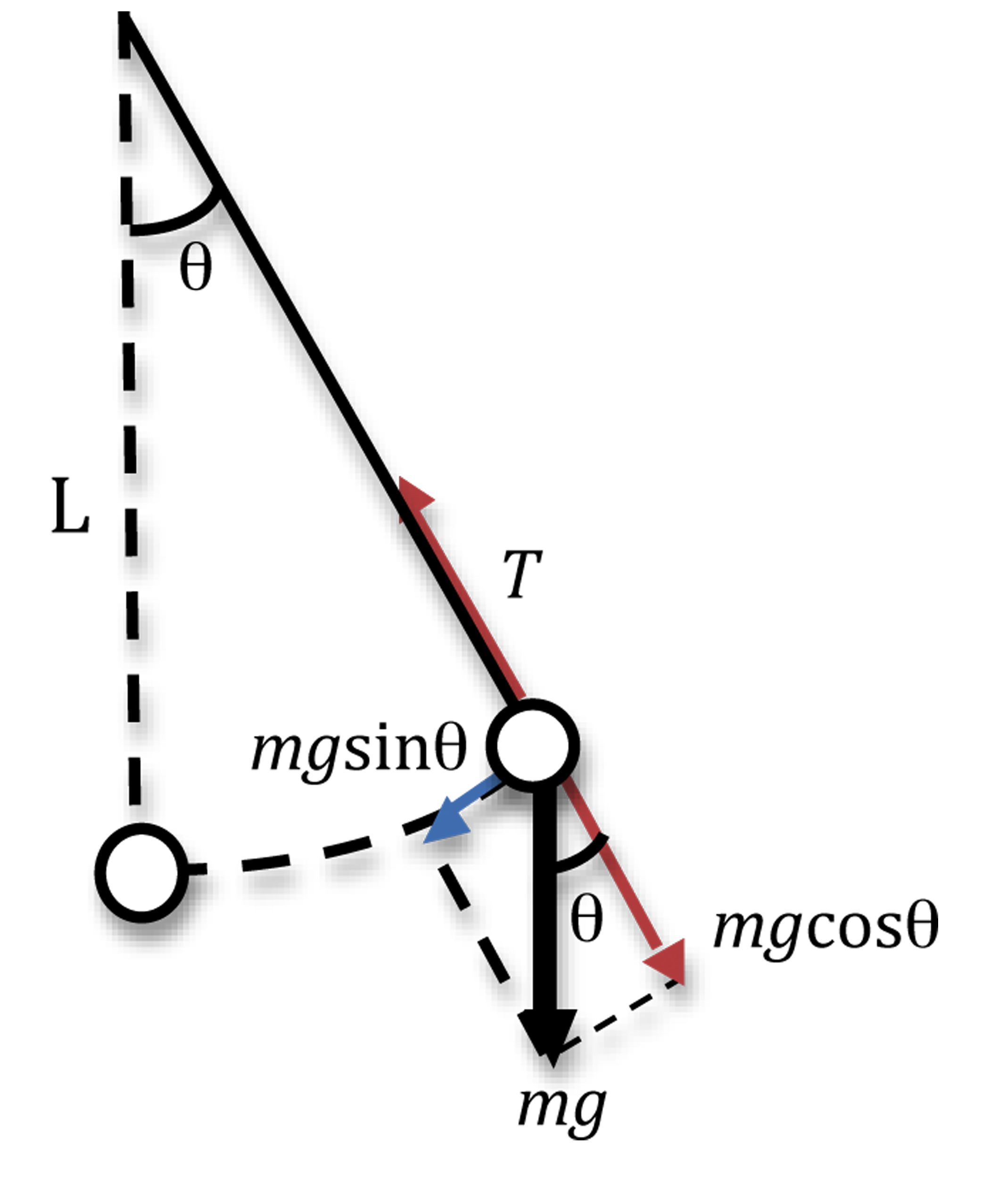
free body diagram in Fig. 6 below. Free Body Diagram Fig. 6 The free body diagram of the pendulum bob shows the gravitational force mg, the tension force T and the centripetal acceleration ac. The components of the gravitational force are also shown. Applying Newton's second law along the direction of tension force on gets T mg θ mgCos(θ)
Or, d 2 θ/dt 2 + ω 2 θ = 0. This equation represents a simple harmonic motion. Thus, the motion of a simple pendulum is a simple harmonic motion with an angular frequency, ω = (g/L) 1/2 and linear frequency, f = (1/2π) (g/L) 1/2. The time period is given by, T = 1/f = 2π (L/g) 1/2. Starting with the right-hand side, the dimension analysis ...
Free body diagram of pendulum Thread starter-EquinoX-Start date Nov 30, 2008; Nov 30, 2008 #1 -EquinoX-564 1. Homework Statement I am asked to draw a free body diagram of a pendulum and a bob with it's maximum amplitude of 30 degrees. Below is my attempt, I just forgot to say that theta is equal to
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators ...
of the inverted pendulum-cart system. In (1), F a is the force exerted on the cart by the motor. (M+ m) x+ mL p = F a (1) mL p x + 4mL2 p 3 mgL p = 0 (2) One way of doing this is by considering the free-body diagrams of the cart and the pendulum separately and writing their respective equations of motion.
Find the equation of motion of this pendulum by taking the time rate of change of the angular momentum computed with respect to the pivot. ... Be sure to include a free body diagram. Pendulum with Torsional Spring - Solution: The free body diagram depicting the torques on the body is shown below. Note the directions of the unit
Double Pendulum • The disk shown in the figure rolls without slipping on a horizontal plane. Attached to the disk through a frictionless hinge is a massless pendulum of length L that carries another disk. The disk at the bottom of the pendulum cannot rotation relative to the pendulum arm. • Draw free-body diagrams and
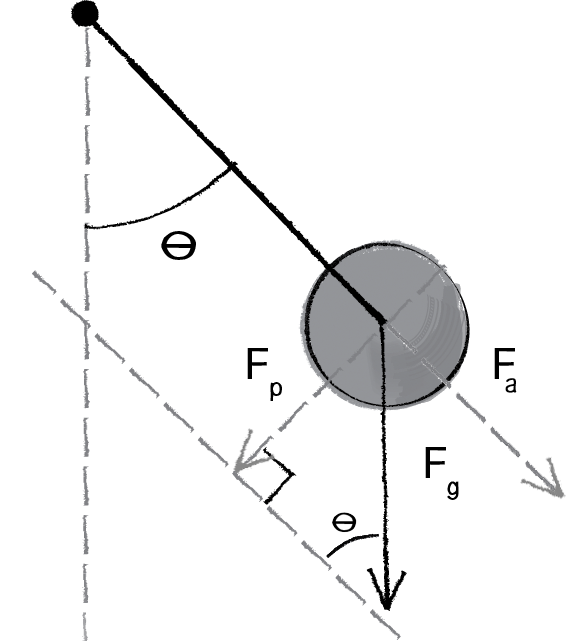
The height of the conical pendulum in terms of ω 2 and g Let's start with the derivation of θ, which begins with a free-body diagram showing the forces acting on the mass.
Dec 30, 2015 · The free body diagram depicting the torques on the body is shown below. The forces on the pendulum are the tension in the rod t and gravity. The diagram at the right shows the pendulum bob at a position to the right of its equilibrium position and midway to the point of maximum displacement. Solved 1 2 3 Draw The Free Body Diagrams For Pendulum The Simple Pendulum College Physics
Download scientific diagram | Inverted Pendulum-cart system (Free body diagram). from publication: Ant Colony based LQR and PID tuned parameters for controlling Inverted Pendulum | This paper ...
Next we draw the free body diagram for the pendulum. So we can write the net force as: F= Tcos θj− Tsin θi− mgj Using Newton's law F= maand the pendulum acceleration we found earlier, we have Tcos θj− Tsin θi− mgj= mR(θ''cos θi− θ'2sin θi+ θ''sin θj+ θ'2cos θj) Write the vector components of the above equation as separate equations.
-Rigid Body Kinematics x y z = cosθ sinθ 0 −sinθ cosθ 0 0 0 1 X Y Z i j k = cosθ sinθ 0 −sinθ cosθ 0 0 0 1 I J K . Derivation of Equations of Motion -Rigid Body Kinematics Free Body Diagram After substitutions and evaluation: Derivation of Equations of Motion-Lagrange Equations ... Spring Pendulum Dynamic System Investigation ...
Below are the free-body diagrams of the two elements of the inverted pendulum system. Summing the forces in the free-body diagram of the cart in the horizontal direction, you get the following equation of motion. (1) Note that you can also sum the forces in the vertical direction for the cart, but no useful information would be gained.
Draw free-body diagrams that conform to the assumed displacement positions and their resultant reaction forces (i.e., tension or compression). c. Apply to the free body diagrams to obtain the governing equations of motion. The matrix statement of Eqs.(3.123) is The mass matrix is diagonal, and the stiffness matrix is symmetric.
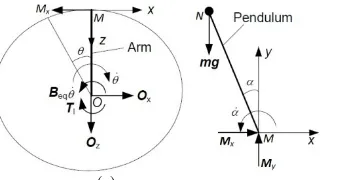
Download scientific diagram | Conical pendulum and corresponding free body diagram. from publication: The Bravais pendulum: The distinct charm of an almost forgotten experiment | In the year 1851 ...
The Simple Pendulum: Force Diagram A simple pendulum consists of a small mass suspended on an approximately massless, non-stretchable string. It is free to oscillate from side to side. The forces acting on the mass are the force of gravity and the tension in the string:
Answer to 1. Draw a free body diagram of a pendulum while in. This problem has been solved! See the answer See the answer See the answer done loading
A simple pendulum consists of a relatively massive object - known as the pendulum bob - hung by a string from a fixed support. When the bob is displaced from equilibrium and then released, it begins its back and forth vibration about its fixed equilibrium position. The motion is regular and repeating, an example of periodic motion. In this Lesson, the sinusoidal nature of pendulum motion is ...
















0 Response to "40 free body diagram pendulum"
Post a Comment