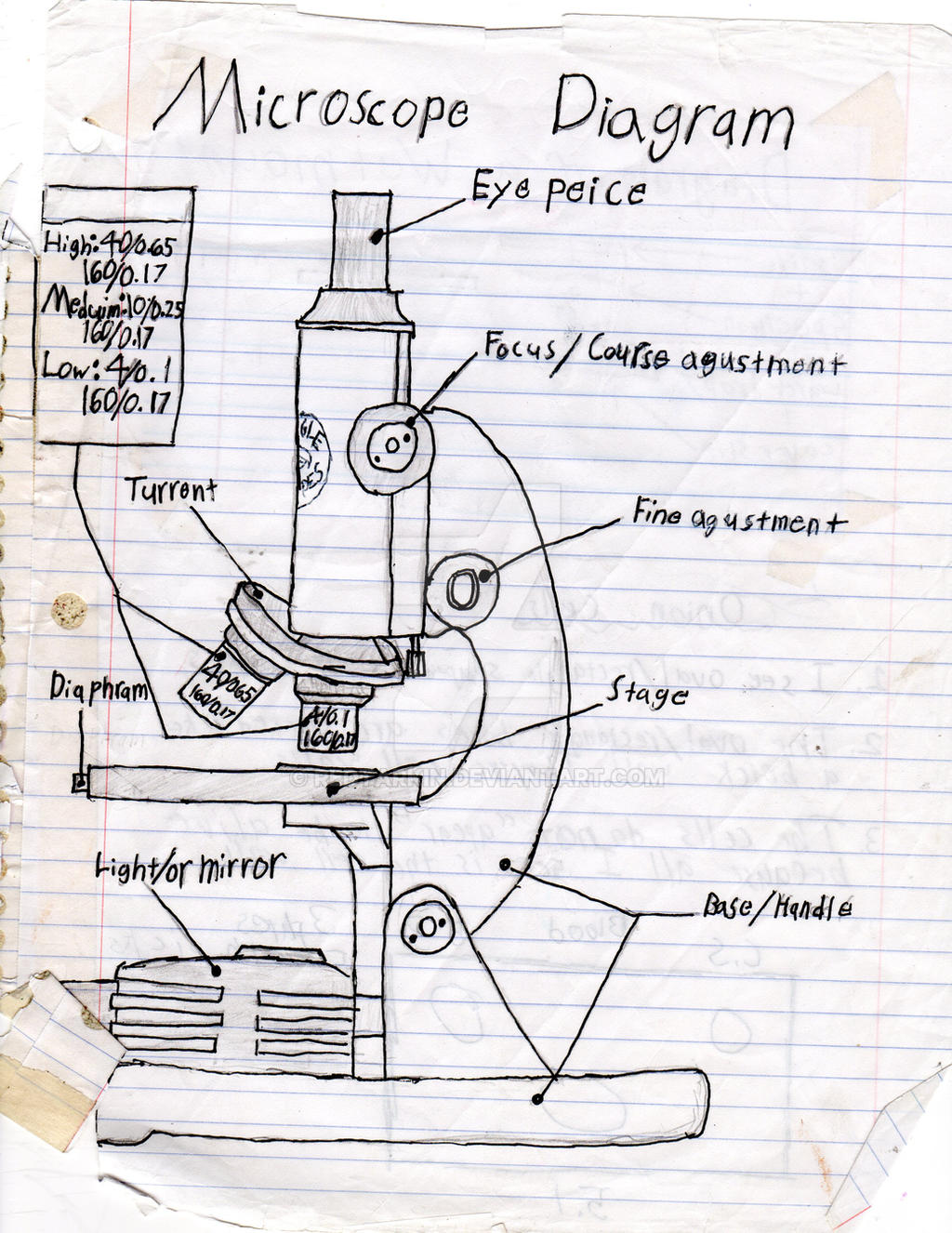
41 diagram of the microscope
All microscopes share features in common. In this interactive, you can label the different parts of a microscope. Use this with the Microscope parts activity to help students identify and label the main parts of a microscope and then describe their functions.. Drag and drop the text labels onto the microscope diagram. If you want to redo an answer, click on the box and the answer will go back ...
Having been constructed in the 16th Century, Microscopes have revolutionalized science with their ability to magnify small objects such as microbial cells, producing images with definitive structures that are identifiable and characterizable. So, what are microscopes? Microscope Definition- Microscopes are instruments that are used in science laboratories, to visualize very minute objects such as cells, microorganisms, giving a contrasting image, that is magnified. Microscopes are made up of lenses for magnification, each with its own magnification powers. Depending on the type of lens, it will magnify the specimen according to its focal strength. Their ability to function is because they have been constructed with special components that enable them to achieve high magnification levels. they can view very small specimens and distinguish their structural differences, for example, the view of animal and plant cells, viewing of microscopic bacterial cells. Microscopes are generally ma...
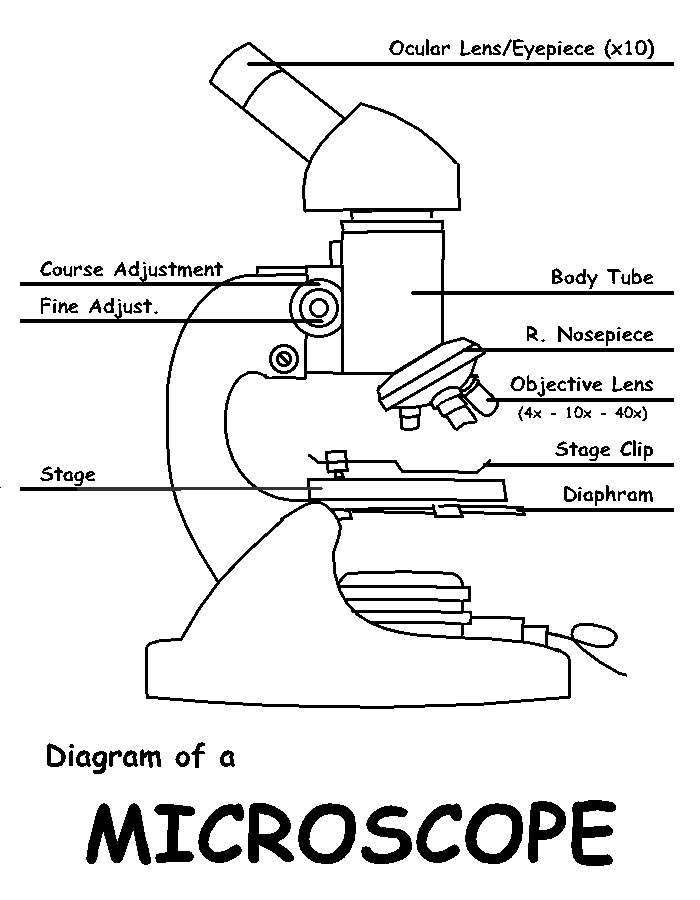
Using the terms listed below, label the microscope diagram. arm - this attaches the eyepiece and body tube to the base. base - this supports the microscope. body tube - the tube that supports the eyepiece. coarse focus adjustment - a knob that makes large adjustments to the focus. diaphragm - an adjustable opening under the stage, allowing ...
Diagram of the microscope
A microscope is an instrument used to see objects that are too small to be seen by the naked eye. We have an article covering the history, types, and evolution of all kinds of microscopes. If you are interested in this topic, please click the link above. [In this figure] The name "microscope" came from two words - "micro" and "scope".
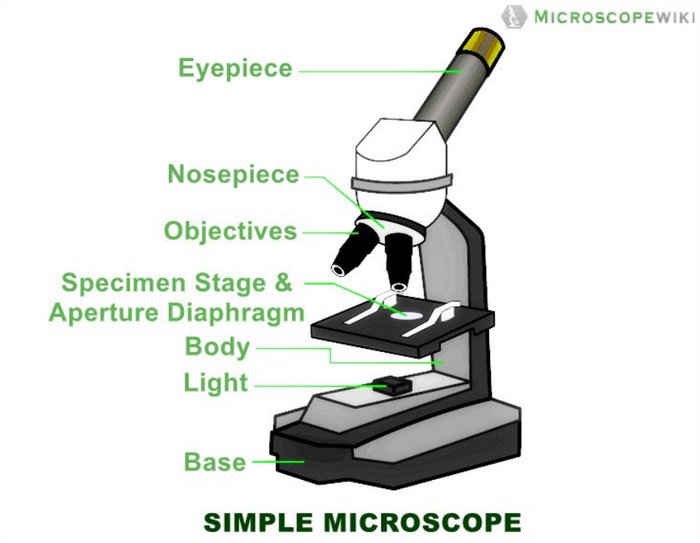
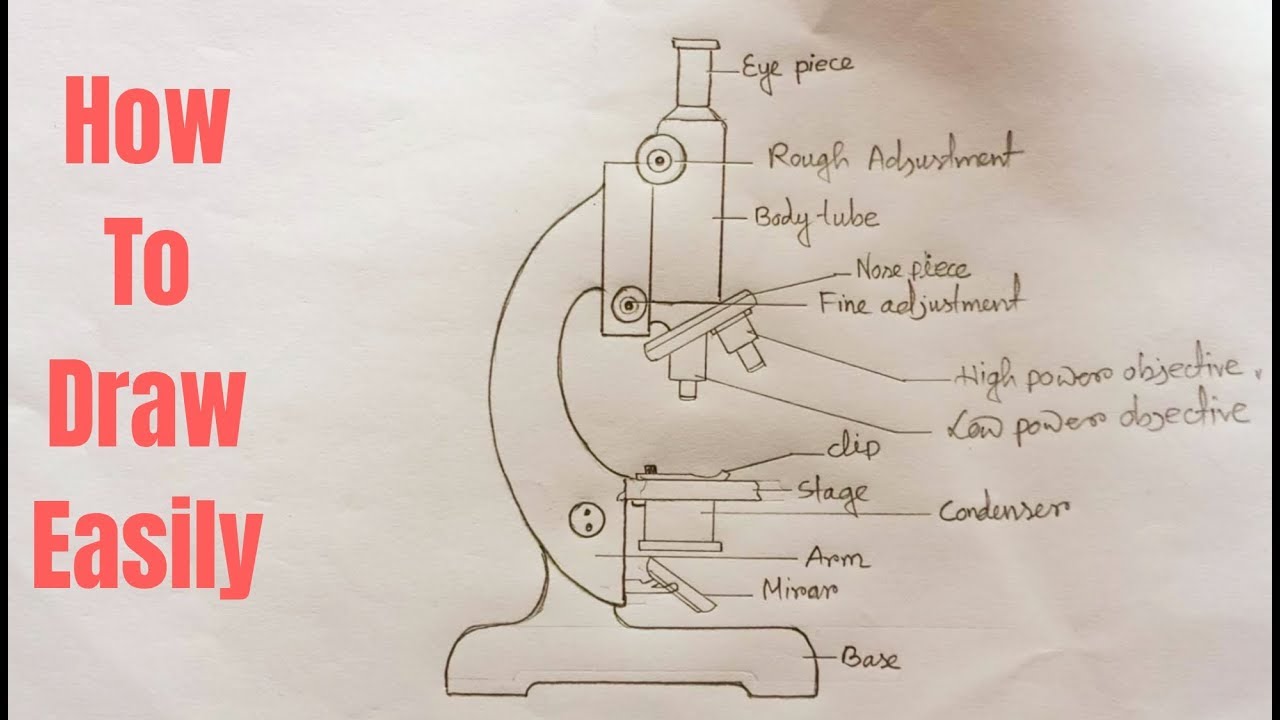
B. NOSEPIECE microscope when carried Holds the HIGH- and LOW- power objective LENSES; can be rotated to change MAGNIFICATION. Power = 10 x 4 = 40 Power = 10 x 10 = 100 Power = 10 x 40 = 400 What happens as the power of magnification increases? Name _____ Compound Light Microscope ...
ADVERTISEMENTS: In this article we will discuss about the design of transmission electron microscope, explained with the help of a diagram. In TEM a finely focused beam of electrons from an electron gun is passed through a specially prepared ultra thin section of the specimen. The beam is focused on a small area of the […]
Diagram of the microscope.
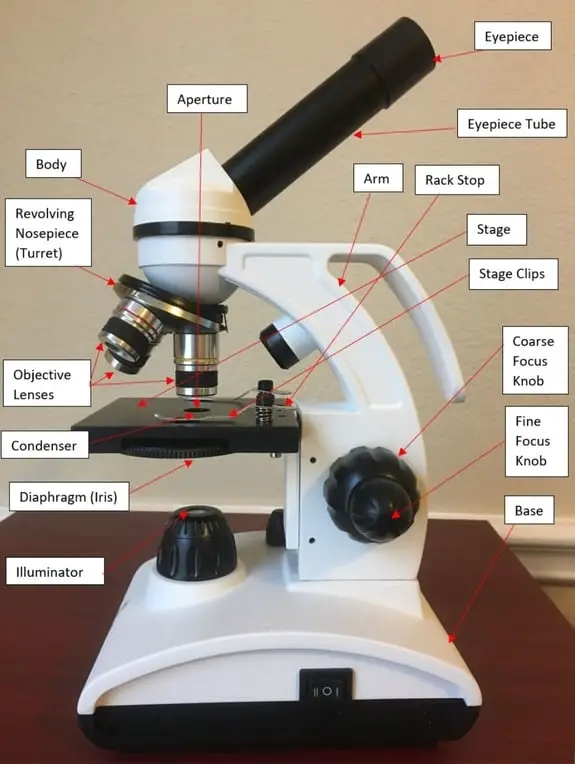
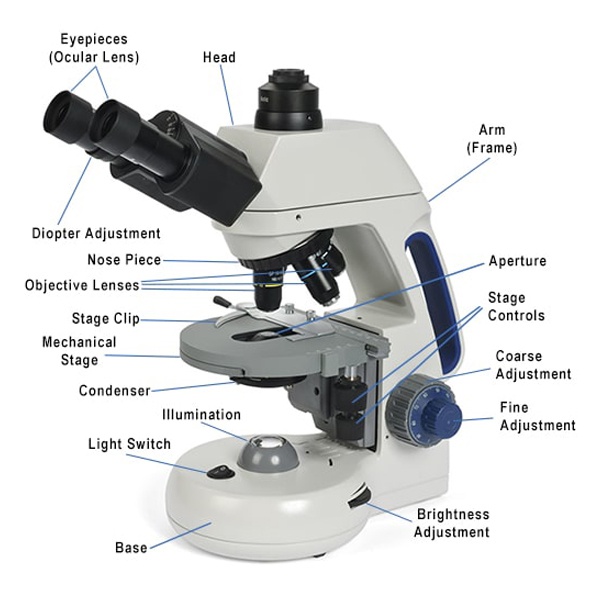
Aperture. Illuminator. Condenser. Diaphragm. Parts of a Compound Microscope. Video: Parts of a compound Microscope with Diagram Explained. As a side note, the microscope used in this post is a great entry level or beginner microscope if you are trying to get someone interested in microscopes, microbiology, or science in general.
Labeling the Parts of the Microscope. This activity has been designed for use in homes and schools. Each microscope layout (both blank and the version with answers) are available as PDF downloads. You can view a more in-depth review of each part of the microscope here.
A Study of the Microscope and its Functions With a Labeled Diagram To better understand the structure and function of a microscope, we need to take a look at the labeled microscope diagrams of the compound and electron microscope. These diagrams clearly explain the functioning of the microscopes along with their respective parts.
Compound microscope is a type of optical microscope that is used for obtaining a high-resolution image. There are more than two lenses in a compound microscope. Learn about the working principle, parts and uses of a compound microscope along with a labeled diagram here.
1. It is noted first that which objective lens is in use on the microscope. 2. Stage micrometer is positioned in such a way that it is in the field of view. 3. The eyepiece is rotated so that the two scales, the eyepiece or ocular scale and the stage micrometer scale, are parallel. 4.
The lenses in a microscope make items appear smaller. How many parts of a microscope can you identify? Can you show the arm, stage, eyepiece, head, objective lens, illuminator, nosepiece, and stage clips? Where is the safest place to hold or carry a microscope? Which part of the microscope holds the specimen slide in place? Why do we use ...
Image 2: The body tube part of a microscope is where the ray of light is bent to allow the object being viewed to enlarge by the scope. Picture Source: slideplayer.com 3. Turret/Nose piece. It is the revolving part of the microscope. It allows the use of different types of objective lenses by simply rotating the top part of the turret.
Compound microscope - It comes with more than one lens and provides better magnification than the simple microscope. A compound microscope is also called a bright field microscope. It can provide magnification by up to 1,000 times. Stereo microscope/dissecting microscope - It can magnify objects by up to 300 times. It is used to visualize ...
Compound microscope Diagram of a compound microscope A compound microscope uses a lens close to the object being viewed to collect light (called the objective lens) which focuses a real image of the object inside the microscope (image 1).
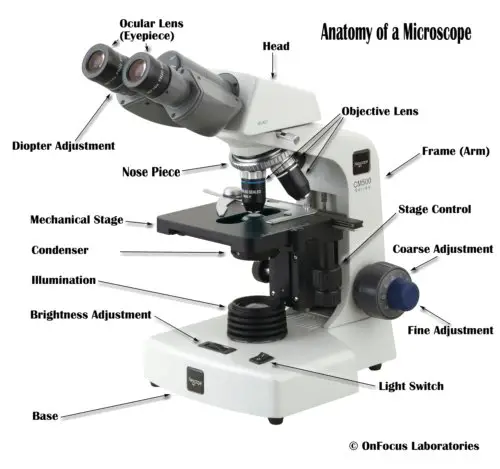
Parts of a Compound Microscope Each part of the compound microscope serves its own unique function, with each being important to the function of the scope as a whole. The individual parts of a compound microscope can vary heavily depending on the configuration & applications that the scope is being used for. Common compound microscope parts include: Compound Microscope Definitions for ...
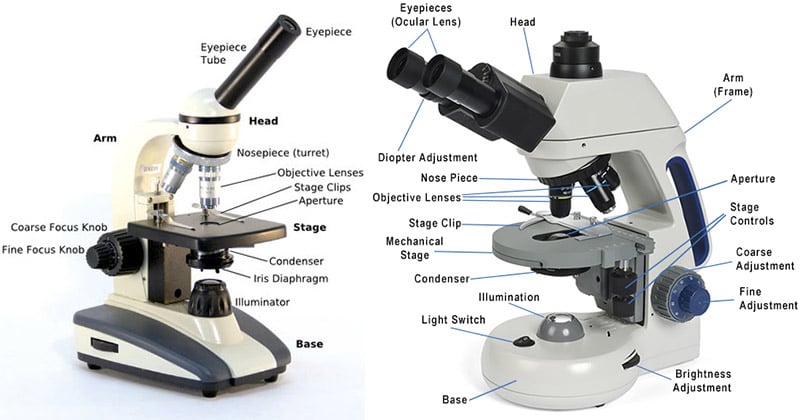
The compound microscope uses two lenses to magnify the specimen: the eyepiece and an objective lens. In most microscopes, there is a choice of objectives to use.
the year 1590. The compound microscope uses lenses and light to enlarge the image and is also called an optical or light microscope (vs./ an electron microscope) . The simplest optical microscope is the magnifying glass and is good to about ten times (10X) magnification. The
microscope's ability to magnify as of its ability to distinguish detail. Merely magnifying an object, without increasing the amount of detail seen, is of little value to the observer. The ability to distinguish detail is called resolution or resolvin g power , and depends on the wavelength of light used and on a value called the numerical ...
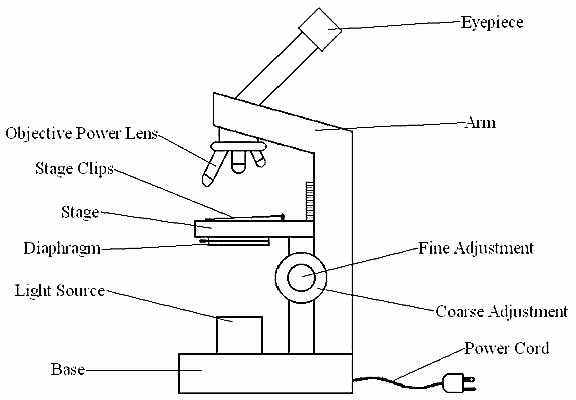
Base: A microscope is typically composed of a head or body and a base. The base is the support mechanism. Binocular Microscope: A microscope with a head that has two eyepiece lenses. Nowadays, binocular is typically used to refer to compound or high-power microscopes where the two eyepieces view through a single objective lens.
Advantages of Darkfield Microscope. Dark-field microscopy is a very simple yet effective technique. It is well suited for uses involving live and unstained biological samples, such as a smear from a tissue culture or individual, water-borne, single-celled organisms.
Microscope Parts and Functions Microscope One or more lenses that makes an enlarged image of an object. 8/7/2018 2 •Simple •Compound •Stereoscopic •Electron Simple Microscope •Similar to a magnifying glass and has only one lens. 8/7/2018 3 Compound Microscope
Science Quiz / Parts of a Microscope Random Science or Biology Quiz Can you pick the correct part of the microscope when given the part's name? by MacHater Plays Quiz Updated Mar 18, 2020 . Rate 5 stars Rate 4 stars Rate 3 stars Rate 2 stars Rate 1 star . Add to Playlist ...
(A) Mechanical Parts of a Compound Microscope. 1. Foot or base. It is a U-shaped structure and supports the entire weight of the compound microscope. 2. Pillar. It is a vertical projection. This stands by resting on the base and supports the stage. 3. Arm. The entire microscope is handled by a strong and curved structure known as the arm. 4. Stage
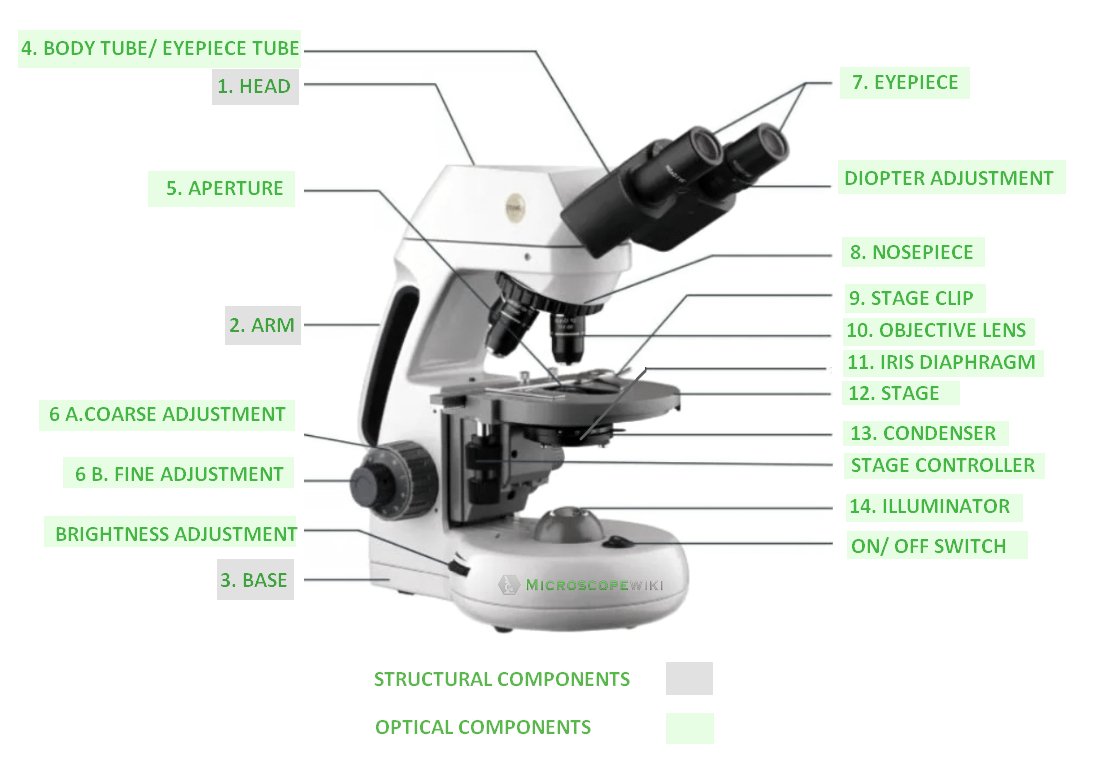
Parts of a Microscope and their Functions. The microscope comprises three main structural components: the head, the base, and the arm. HEAD: Also known as the body, the microscope's head houses the optical components in the upper portion. BASE- It serves as a support for microscopes. Illuminators for microscopic work are also included.
Microscope Parts and Functions With Labeled Diagram and Functions How does a Compound Microscope Work?. Before exploring microscope parts and functions, you should probably understand that the compound light microscope is more complicated than just a microscope with more than one lens.. First, the purpose of a microscope is to magnify a small object or to magnify the fine details of a larger ...
Apr 09, 2017 · A microscope is an instrument widely to magnify and resolve the image of an object that is otherwise invisible to naked eye. For resolving the details of objects, which otherwise cannot be achieved by naked eye, a microscope is used. The first diagram can be seen in the following image.
Dec 24, 2021 · Microscope Parts, Function, & Labeled Diagram. A microscope is a laboratory instrument used to examine very small or micro-objects such as cells and microorganisms that are not able seen by the naked eye. The study of investing in micro-objects using a microscope is known as microscopy. To examine these small objects with high magnification ...
Microscope, instrument that produces enlarged images of small objects, allowing the observer an exceedingly close view of minute structures at a scale convenient for examination and analysis. It may provide a dynamic image (as with optical instruments) or one that is static (as with scanning electron microscopes).
Aug 12, 2017 · These key microscope parts are illustrated and explained in the diagrams of microscope below. The compound microscope has two systems of lenses for greater magnification. The first set of lenses are the oculars, or eyepieces, that the viewer looks into; the second set of lenses are the objectives, the lenses closest to the object (specimen).
























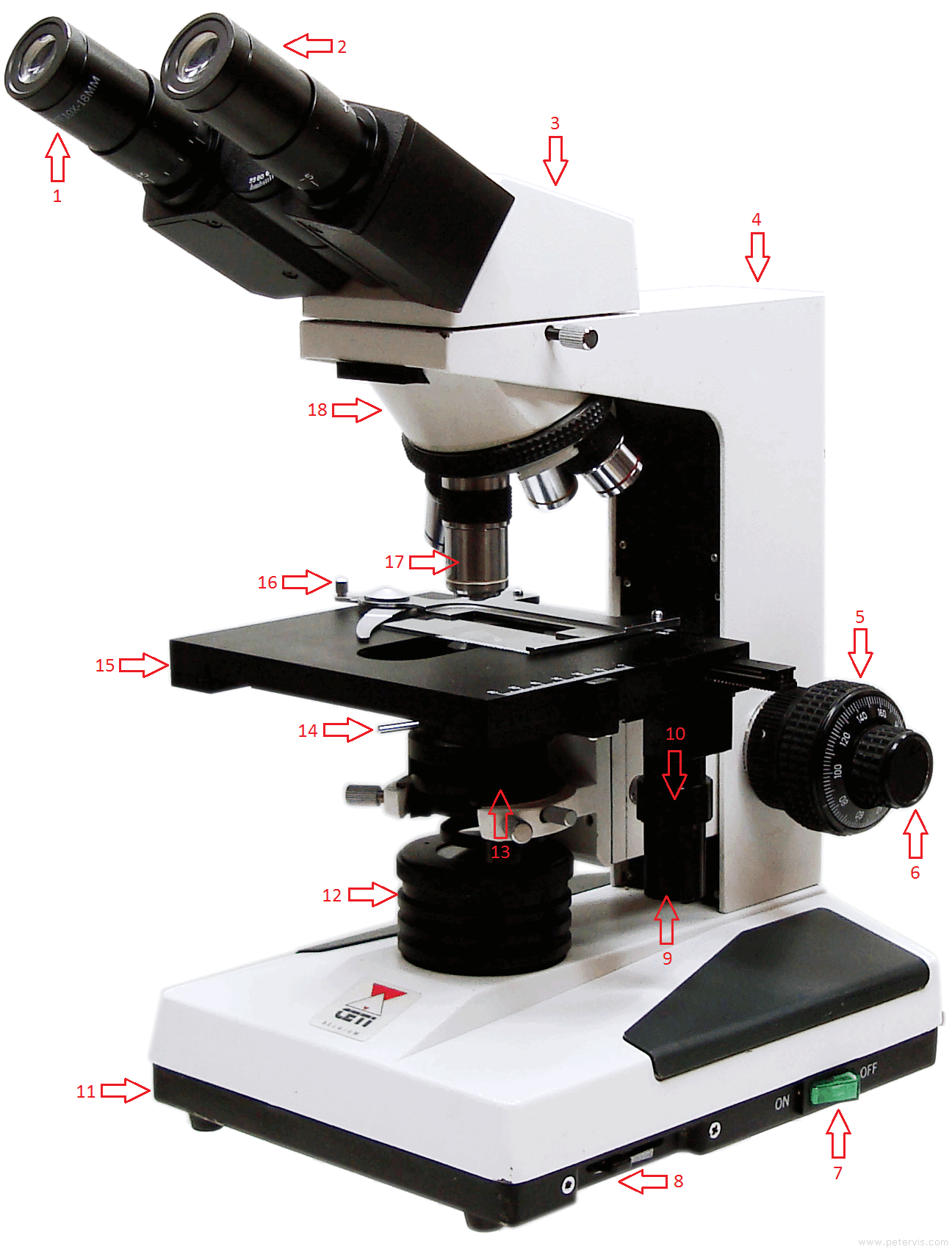


0 Response to "41 diagram of the microscope"
Post a Comment