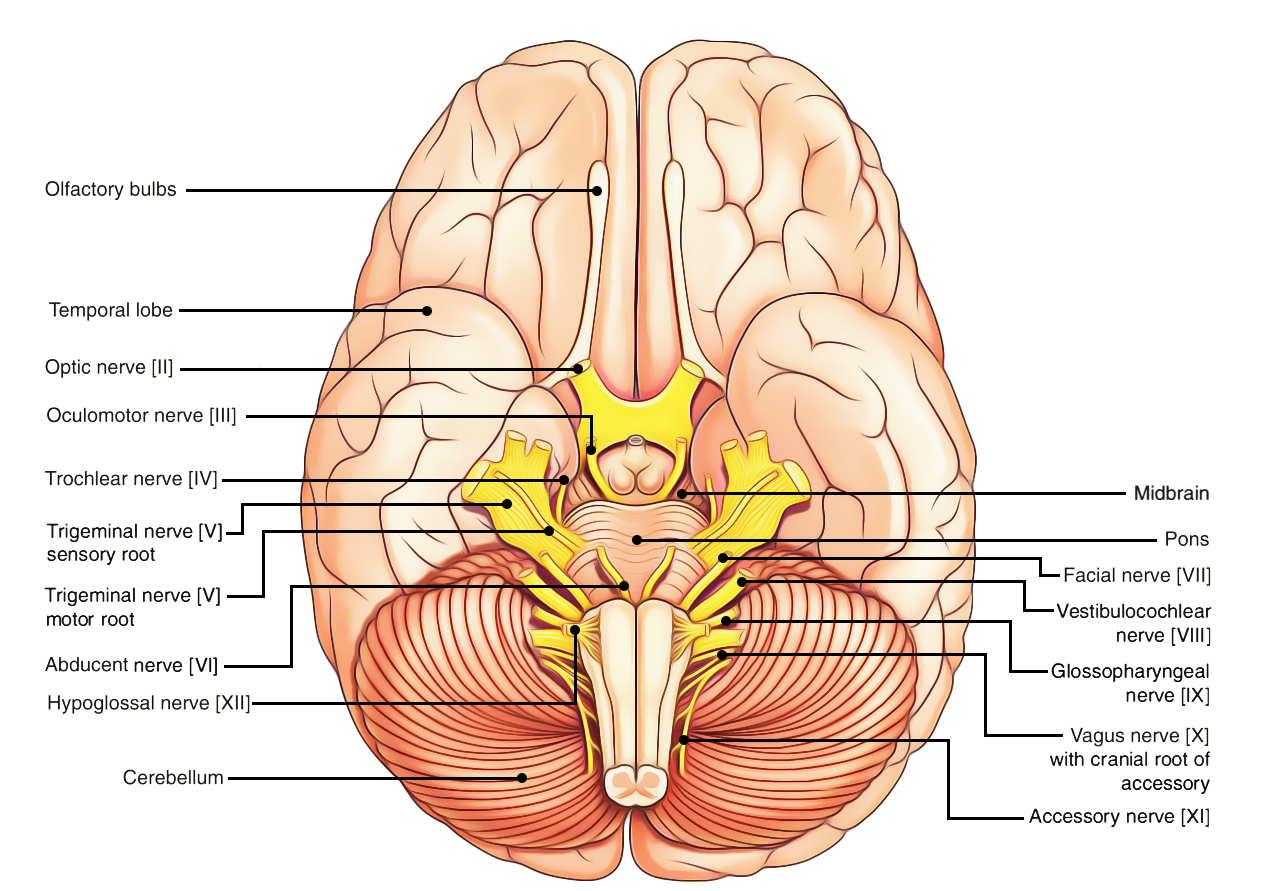
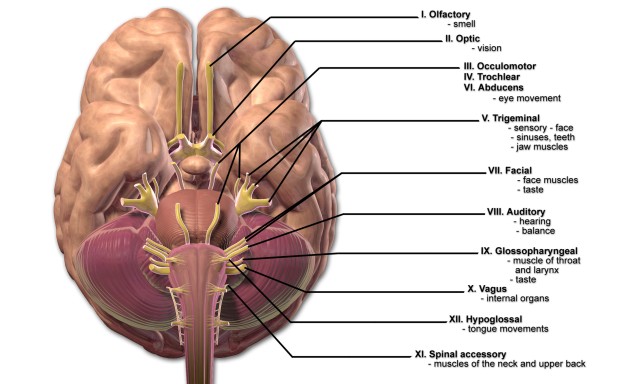
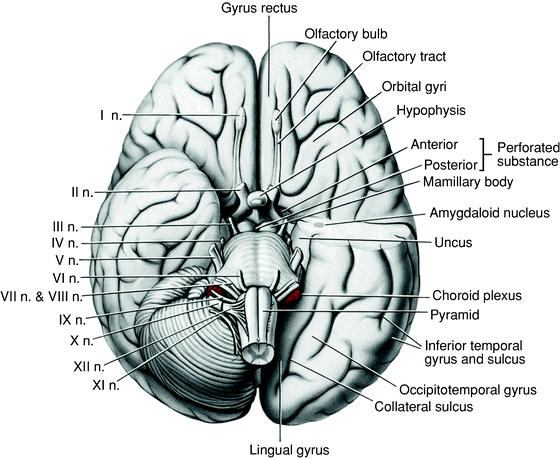
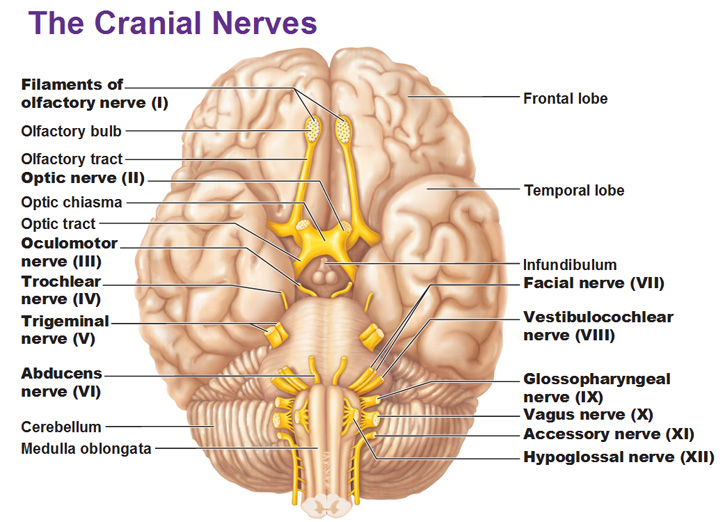
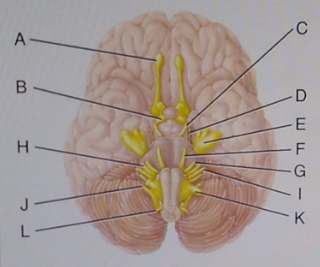
41 which cranial nerve in the diagram is primarily involved in the sense of vision?
55) Which cranial nerve in the diagram is primarily involved in the sense of vision? B) 56) Which cranial nerve in the diagram has a somatic motor function primarily involved in moving the upper eyelid and eyeball?
The maxillary branch of this labeled cranial nerve is found in the area where dentists apply anesthetic drugs for numbing the upper jaw. E Which cranial nerve in the diagram has an autonomic motor function primarily involved in near vision accommodation and constriction of the pupil
The 12 pairs of cranial nerves are each involved in highly specialized functions. Cranial nerve impairment can occur due to face, head, or neck trauma. When you have impairment of one or more cranial nerves without a history of trauma, it can be a sign of a serious medical issue.
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/5405/CJo3irIIYoR5UqGqPMq5Rw_8.Vestibulocochlear_Nerve.png.jpeg)
Which cranial nerve in the diagram is primarily involved in the sense of vision?
Which cranial nerve in the diagram is primarily involved in the sense of vision? A)A B)B C)C D)D E)E. Free. Multiple Choice . Unlock to view answer ... Unlock to view answer. Q 57 Q 57. Which cranial nerve in the diagram has an autonomic motor function primarily involved in near vision accommodation and constriction of the pupil? A)A B)B C)C D ...
Which cranial nerve in the diagram is primarily involved in the sense of vision. Chapter 47 Diseases Of The Cranial Nerves Adams And Medium learning objective 1. Which cranial nerve in the diagram has a somatic motor function primarily involved in chewing. A e b g c h d i e j. Asked sep 25 2015 in anatomy physiology by vanderland.
Cranial nerves relay information between the brain and parts of the body, primarily to and from regions of the head and neck. Do all nerves go through the spinal cord? All nerves ultimately connect to the brain The nerves of the peripheral nervous system (PNS) extend down the spinal canal and branch out in 31 pairs at openings in the vertebrae ...
Which cranial nerve in the diagram is primarily involved in the sense of vision?.
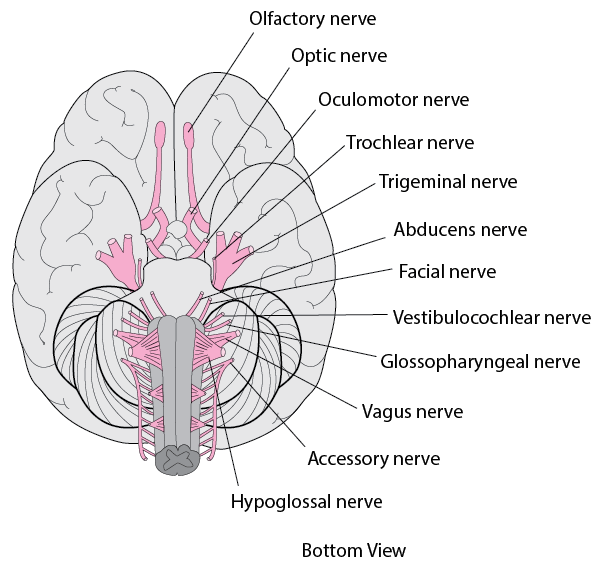
The cranial nerves are components of the peripheral nervous system (PNS). They are directly connected to the brain, in 12 pairs. The cranial nerves are named in relation to their function or distribution. Each nerve is numbered by its position along the brain's longitudinal axis, starting at the cerebrum.
Which cranial nerve in the diagram is primarily involved in the sense of vision? a) A b) B c) C d) D e) E . ... Answer: c. Which cranial nerve in the diagram has an autonomic motor function primarily involved in near vision accommodation and constriction of the pupil? a) A b) B c) C d) D e) F. Answer: c. Damage to which of the cranial nerves in ...
The functions of the cranial nerves are sensory, motor, or both: Sensory cranial nerves help a person to see, smell, and hear. Motor cranial nerves help control muscle movements in the head and neck.
Which cranial nerve in the diagram is primarily involved in the sense of vision? b . Which cranial nerve in the diagram has a somatic motor function primarily involved in moving the upper eyelid and eyeball? C . Damage to which cranial nerve in the diagram will cause the inability of an eyeball to move laterally beyond the midpoint? ...
Which cranial nerve in the diagram is primarily involved in the sense of vision? C) oculomotor nerve. Which cranial nerve in the diagram has an autonomic motor function primarily involved in near vision accommodation and constriction of the pupil? E) trigeminal nerve.
6 Special Senses . The human body experiences its environment by reacting to stimuli that reach the brain via the nervous system. The somatic or general senses, including touch, temperature perception, pain, and proprioception (the awareness of one's position and movement in space), use the free nerve endings in the skin, muscles, and membranes of the body to detect change and communicate ...
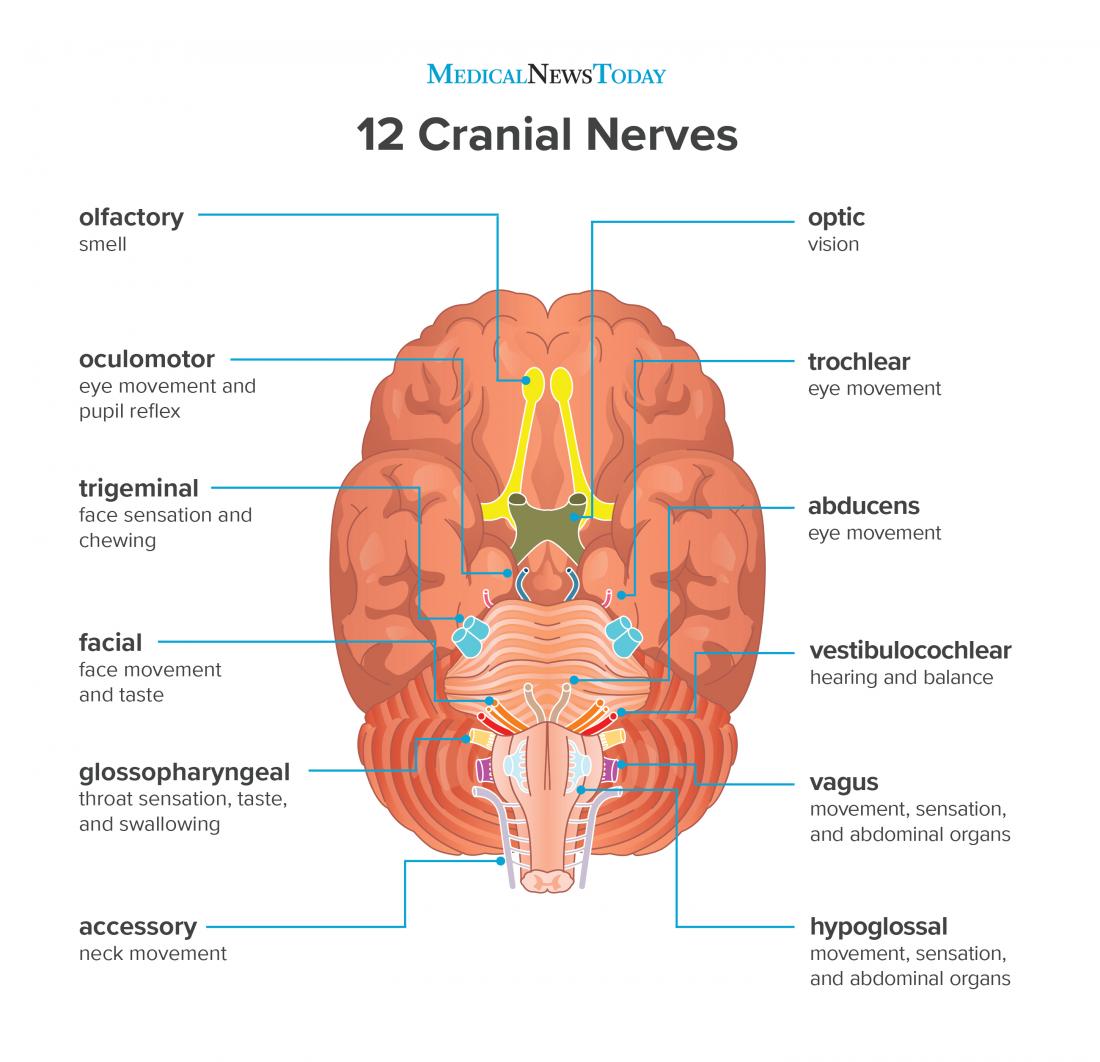
Four Cranial Nerve pairs control the eyes themselves, including; the Optic Nerve, the Oculomotor Nerve, the Trochlear Nerve and the Abducens Nerve. CNII (Cranial Nerve 2), carries Vision to the brain. This nerve does not contain Schwann cells. CN3, (Cranial Nerve 3) has two functions it controls: CN IV (Cranial Nerve 4), controls eyeball ...
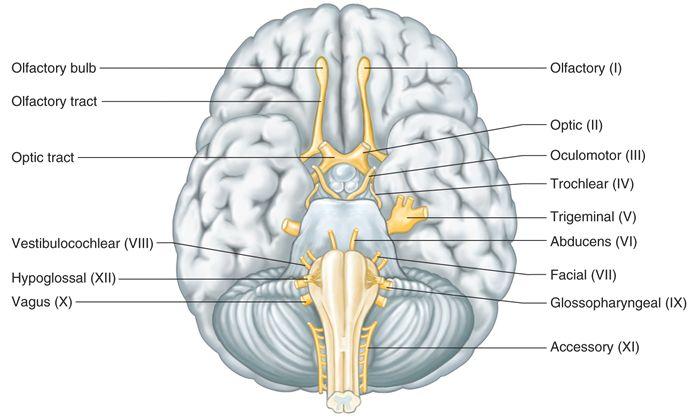
Cranial Nerves. The cranial nerves are composed of twelve pairs of nerves that emanate from the nervous tissue of the brain.In order to reach their targets they must ultimately exit/enter the cranium through openings in the skull.Hence, their name is derived from their association with the cranium. The following are the list of cranial nerves, their functions, and tumor examples:
Which cranial nerve in the diagram is primarily involved in the sense of vision? A) A B) B C) C D) D E) E. C) C. Which cranial nerve in the diagram has an autonomic motor function primarily involved in near vision accommodation and constriction of the pupil? A) A B) B C) C D) D E) F. C) E. Which cranial nerve in the diagram has a somatic motor ...
Cranial Nerve 2 is directly related to sight. it is the cranial nerve that is tested when using the Snellen Chart at the eye doctor. Cranial nerves 3,4, and 6 are also related to eyes as they ...
Sensory nerves are involved with your senses, such as smell, hearing, and touch. Motor nerves control the movement and function of muscles or glands. Keep reading to learn more about each of the ...
The cranial nerve functions are broken up into managing different aspects of your bodys daily tasks from chewing and biting to motor function hearing sense of smell and vision. 60 which cranial nerve in the diagram has a somatic motor function primarily involved in chewing.
Which cranial nerve in the diagram is primarily involved in the sense of vision? a. A. b. B. c. C. d. ... Which cranial nerve in the diagram has an autonomic motor function primarily involved in near vision accommodation and constriction of the pupil? ... Which cranial nerve in the diagram is involved with speech and swallowing and has a purely ...
Which cranial nerve in the diagram has a somatic motor function primarily involved in moving the upper eyelid and eyeball and an autonomic function involved in iris muscle contraction? C. The right hemisphere exhibits greater activity for which functions? Select all that apply.
56) Which cranial nerve in the diagram has a somatic motor function primarily involved in moving the upper eyelid and eyeball? a) A b) B c) C d) D e) F Answer: c 57) Which cranial nerve in the diagram has an autonomic motor function primarily involved in near vision accommodation and constriction of the pupil?
Which cranial nerve in the diagram is primarily involved in the sense of vision? Which is a branch of the trigeminal ( V ) nerve? Which of the following is a branch of the trigeminal (V) nerve? Which of the following is a nucleus found in the midbrain that releases dopamine? Which region of the brain serves as the major relay station for most ...
Cranial nerves carry information from the brain to other parts of the body, primarily to the head and neck. These nerves are paired and present on both sides of the body. They are mainly responsible for facilitating smell, vision, hearing, and movement of muscles. Cranial nerves are concerned with the head, neck, and other facial regions of the ...
Aspects of vision, like peripheral vision, are under the control of the optic cranial nerve (II). Medical professionals can test visual acuity using a Snellen chart. The trigeminal cranial nerve is the largest of the cranial nerves. It is involved in corneal reflex and facial sensation along with chewing.
This article will provide an introduction to the cranial nerves which are considered primarily sensory nerves, which includes the olfactory nerve, the optic nerve, and the vestibulocochlear nerve. The terminal nerve (CN 0, or CN N), although not conventionally included in the list of cranial nerves, will also be discussed among this group.
Which cranial nerve in the diagram is primarily involved in the sense of vision? C. Which cranial nerve in the diagram has an autonomic motor function primarily involved in near vision accommodation and constriction of the pupil? E.
The olfactory nerve, or cranial nerve I, is the first of the 12 cranial nerves. It is instrumental in the sense of smell. The olfactory nerve is the shortest of the 12 cranial nerves and only one of two cranial nerves (the other being the optic nerve) that do not join with the brainstem.
Which cranial nerve in the diagram is primarily involved in the sense of vision. A e b g c h d i e j. Trigeminal Nerve Anatomy Gross Anatomy Branches Of The Trigeminal Second the oculomotor nerve carries parasympathetic fibers to the iris causing the iris to constrict when youre in bright light.

:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/5394/BYySjgjRVXYjx901ThMA_Ganglio_ciliare_01.png.jpeg)

















/GettyImages-1092334754-fd0644493b3148288970e38fd26aead0.jpg)



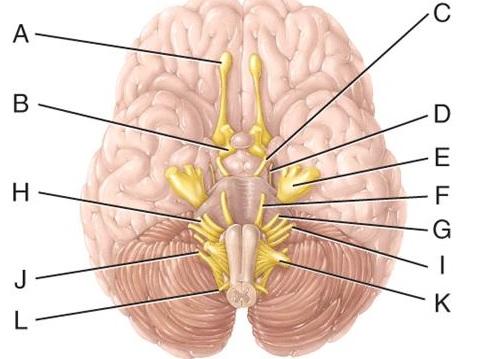



0 Response to "41 which cranial nerve in the diagram is primarily involved in the sense of vision?"
Post a Comment