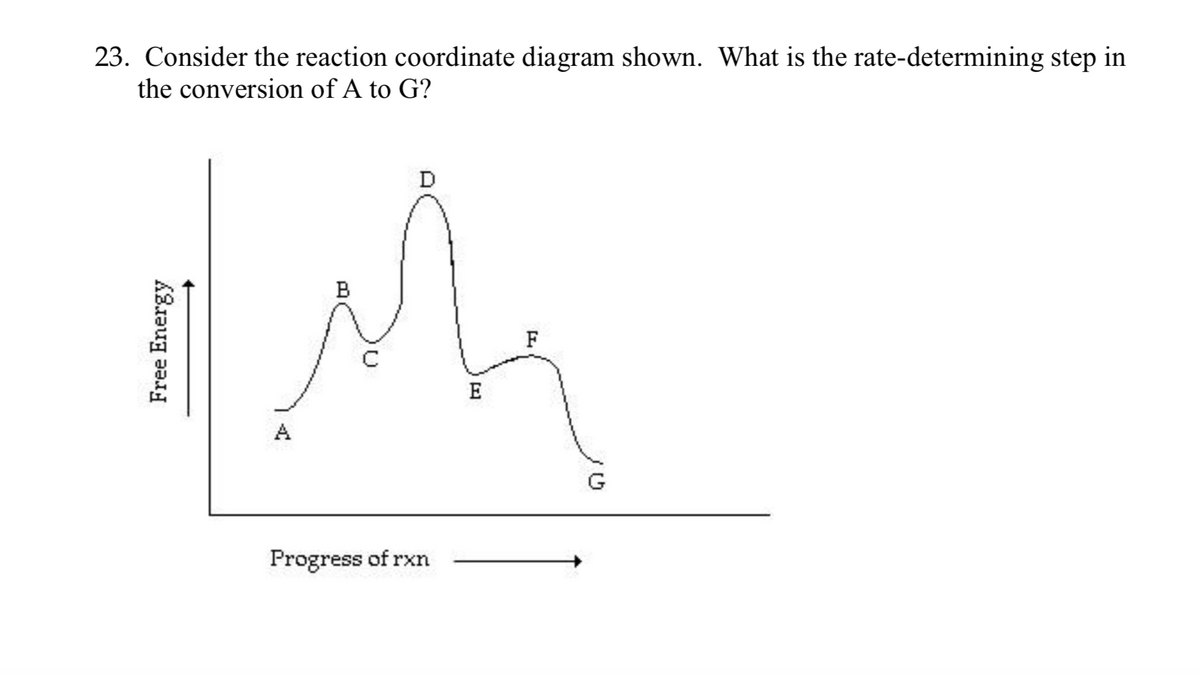
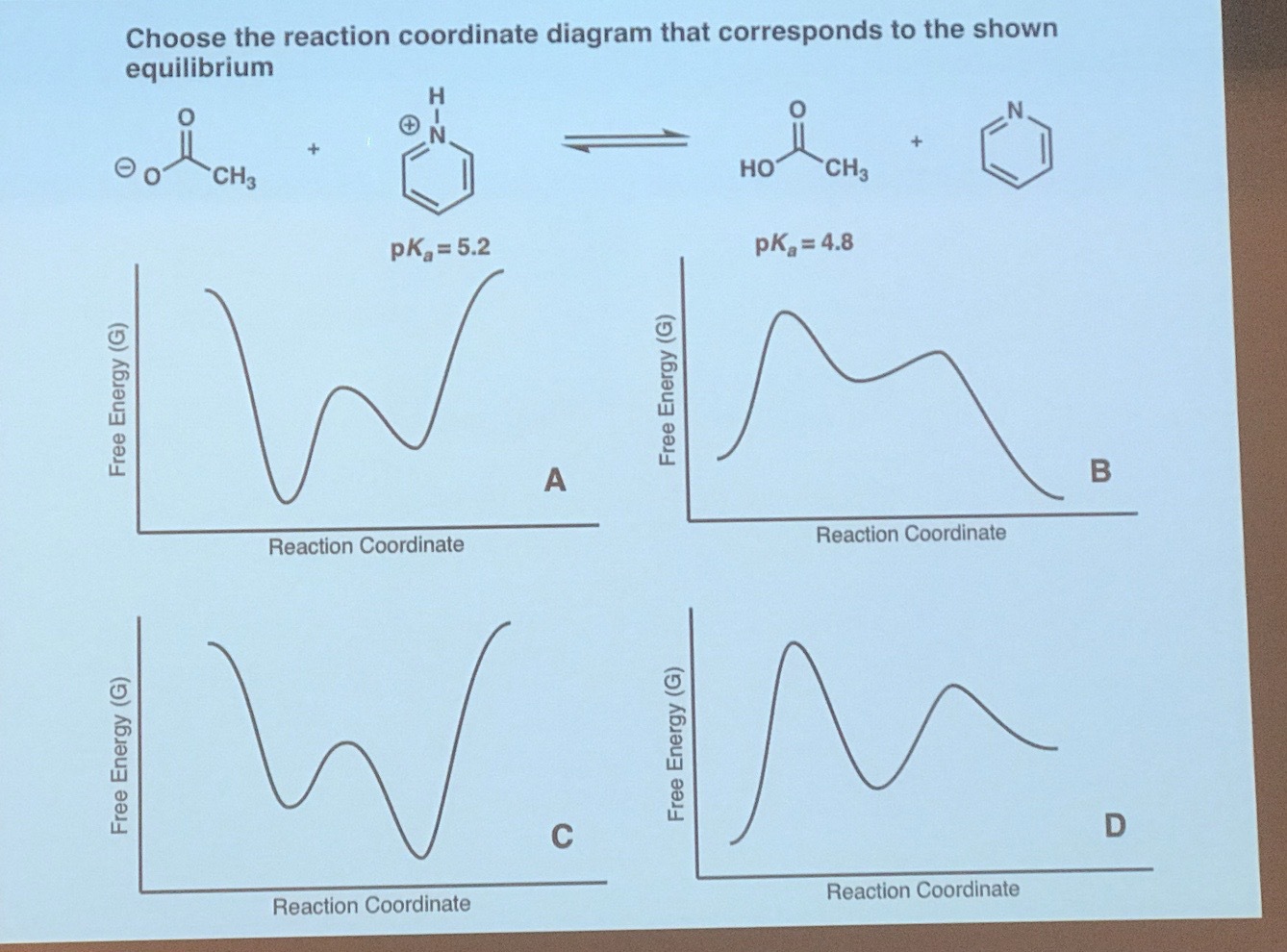
42 energy reaction coordinate diagram
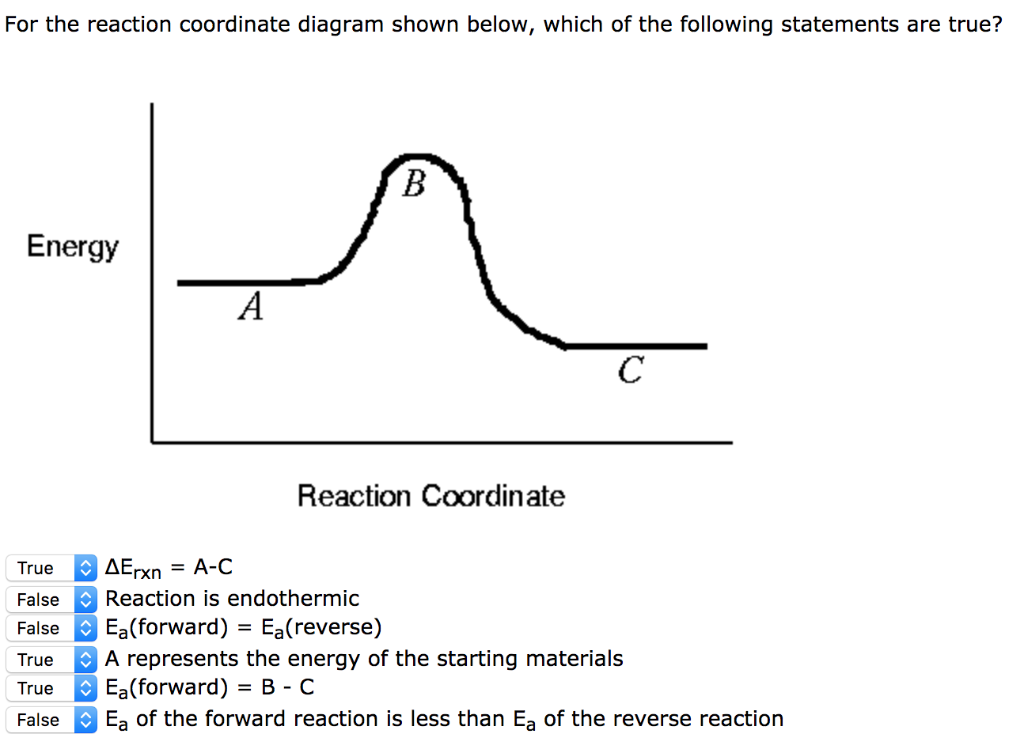
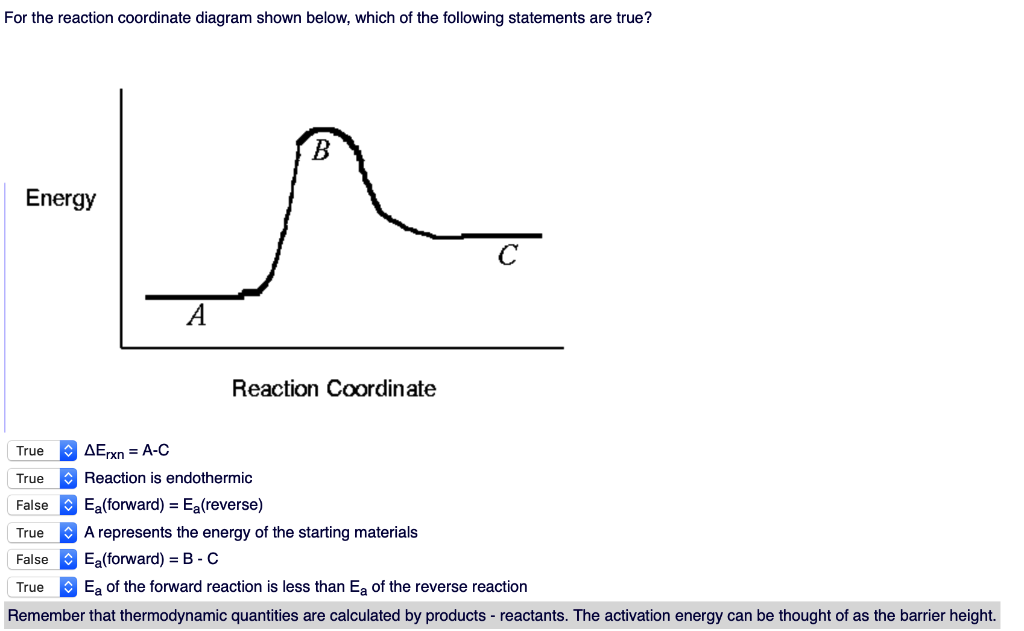
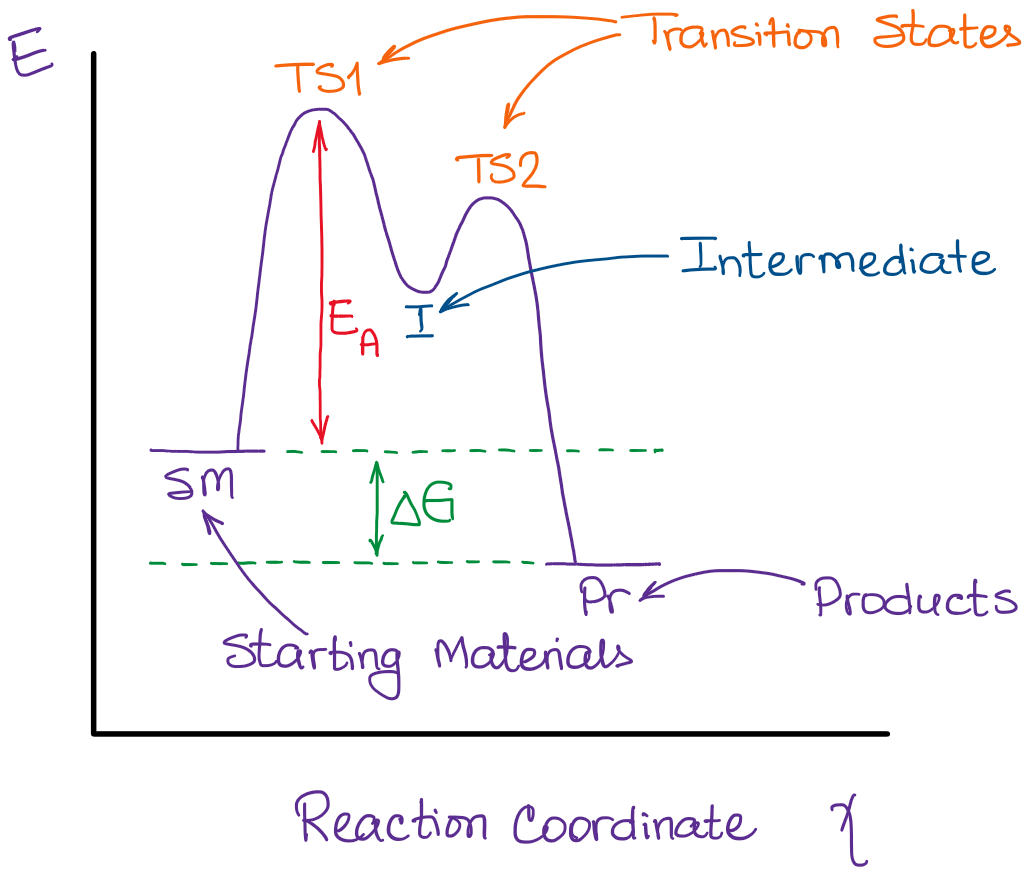
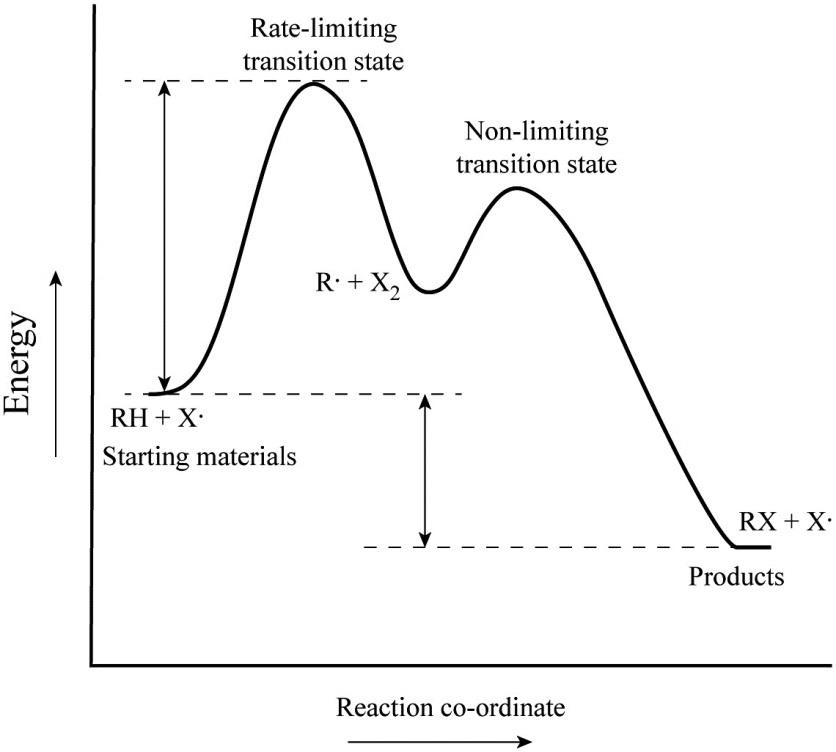
Reaction Coordinate Diagrams Let's consider a general reaction where a reactant or set of reactants, A, is transformed into a product or set of products, B. The diagram below is called a reaction coordinate diagram. It shows how the energy of the system changes during a … Explanation: The fully filled in reaction coordinate diagram is displayed below. 2. The arrow marked in the question represents the activation energy, ...
Δ r G, Gibbs free energy change per mole of reaction, Δ r G°, Gibbs free energy change per mole of reaction for unmixed reactants and products at standard conditions (i.e. 298 K, 100 kPa, 1 M of each reactant and product), R, gas constant, T, absolute temperature, ln, natural logarithm, Q r, reaction quotient (unitless),
Energy reaction coordinate diagram
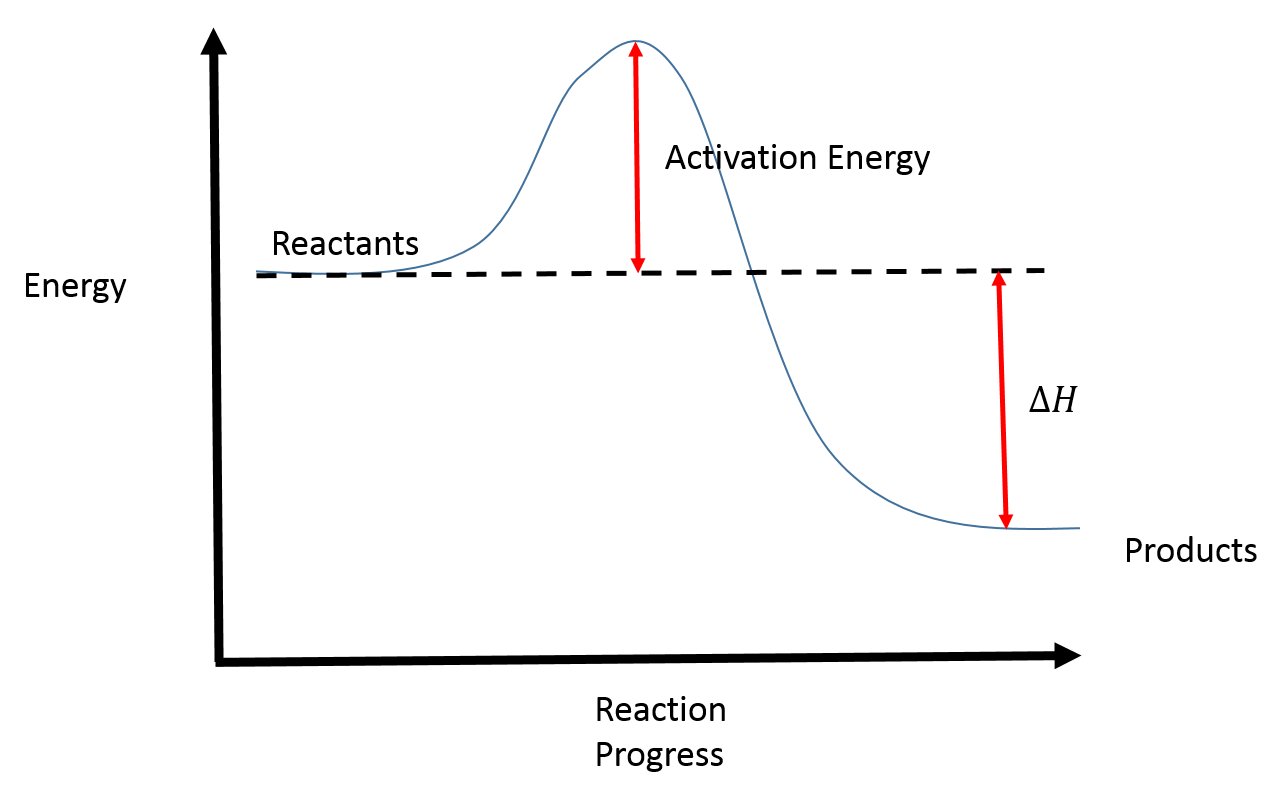
In an energy diagram, the vertical axis represents the overall energy of the reactants, while the horizontal axis is the ‘reaction coordinate’, tracing from left to right the progress of the reaction from starting compounds to final products. The energy diagram for a typical one-step reaction might look like this: As shown in the energy diagram, the hydrogenation of alkenes is exothermic, and heat is released corresponding to the ΔE (colored green) in the diagram. This heat of reaction can be used to evaluate the thermodynamic stability of alkenes having different numbers of alkyl substituents on the double bond. We can see what is happening to the energy in a reaction using a reaction coordinate diagram. A reaction coordinate diagram is a diagram that plots energy ...
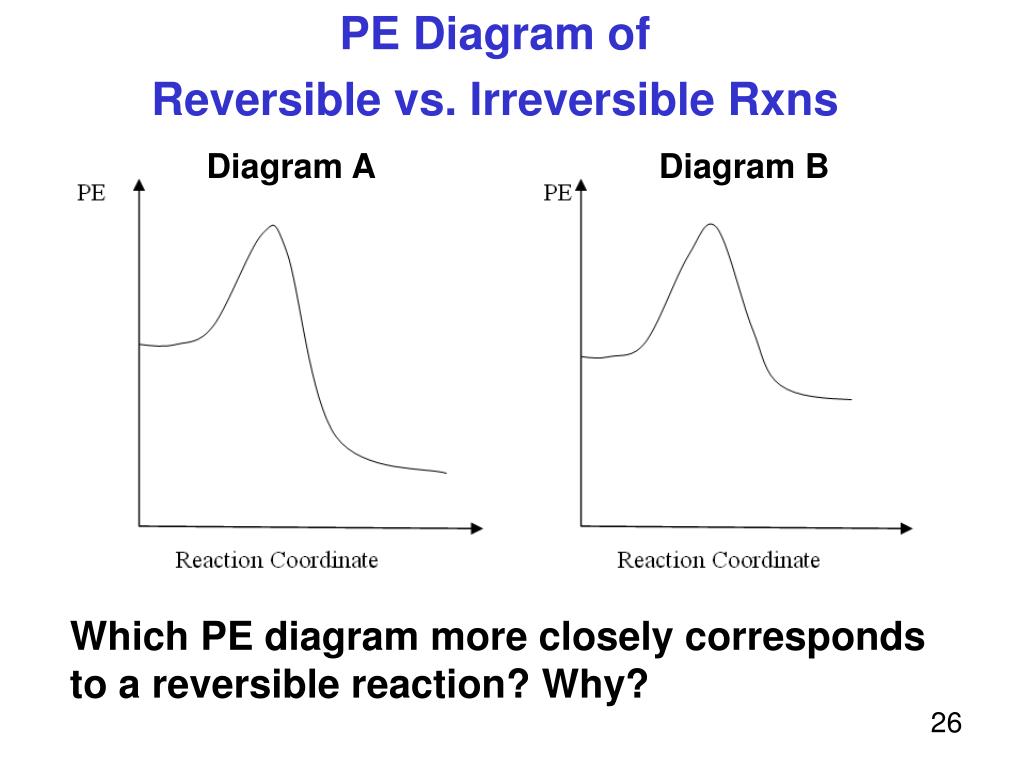
Energy reaction coordinate diagram. Catalysis is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance Catalyzed reactions have a lower activation energy (rate-limiting free energy of activation) than the corresponding uncatalyzed reaction, resulting in a higher reaction . This effect can be illustrated with an energy profile diagram. Despite its apparent simplicity, this energy diagram conveys some very important ideas about the thermodynamics and kinetics of the reaction. Recall that when ... 11-11-2014 · Re: M.O. Diagram for B2 Post by Chem_Mod » Tue Nov 11, 2014 11:21 pm As discussed in class the MO diagram for B 2 shows that it has two unpaired electrons (which makes it paramagnetic) and these electrons are in bonding molecular orbitals resulting in the equivalent bond strength of one bond. Convert a 2D coordinate into a triangle-based coordinate system for a prettier phase diagram. Parameters. coord – coordinate used in the convex hull computation. Returns. coordinates in a triangular-based coordinate system. uniquelines (q) [source] ¶ Given all the facets, convert it into a set of unique lines.
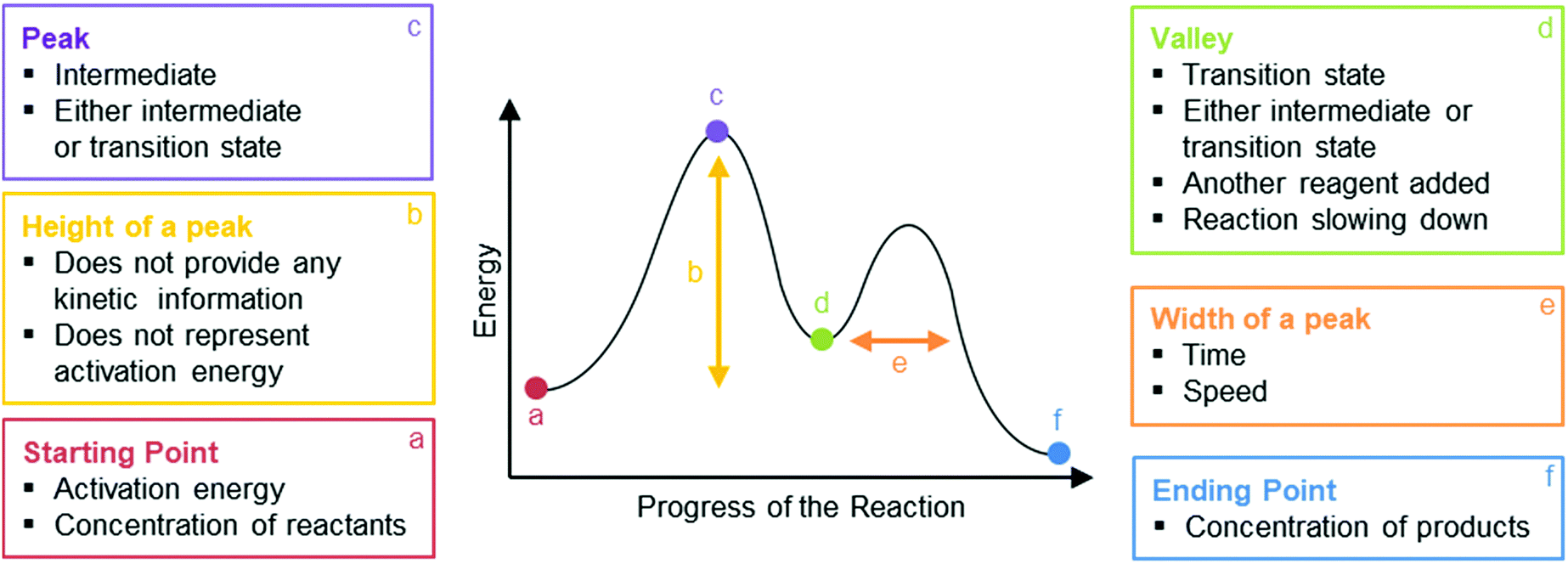
The reaction coordinate is typically chosen to follow the path along the gradient (path of shallowest ascent/deepest descent) of potential energy from reactants to products. [1] For example, in the homolytic dissociation of molecular hydrogen , an apt coordinate system to choose would be the coordinate corresponding to the bond length . by JM Scholey · 2013 · Cited by 6 — Reaction coordinate diagrams are used to relate the free energy changes that occur during the progress of chemical processes to the rate and equilibrium ... You may recall from general chemistry that it is often convenient to describe chemical reactions with energy diagrams. In an energy diagram, the vertical axis represents the overall energy of the reactants, while the horizontal axis is the ‘reaction coordinate’, tracing from left to right the progress of the reaction from starting compounds to final products. Initially at stage 1, or the first coordinate, only the energy of the reactant molecules is being considered. On the diagram above the final stage, or the final coordinate, of the reaction is when the energy of product molecules are considered but not reactant molecules. The reaction coordinate (reaction path) is not the same as time.
We can see what is happening to the energy in a reaction using a reaction coordinate diagram. A reaction coordinate diagram is a diagram that plots energy ... As shown in the energy diagram, the hydrogenation of alkenes is exothermic, and heat is released corresponding to the ΔE (colored green) in the diagram. This heat of reaction can be used to evaluate the thermodynamic stability of alkenes having different numbers of alkyl substituents on the double bond. In an energy diagram, the vertical axis represents the overall energy of the reactants, while the horizontal axis is the ‘reaction coordinate’, tracing from left to right the progress of the reaction from starting compounds to final products. The energy diagram for a typical one-step reaction might look like this:





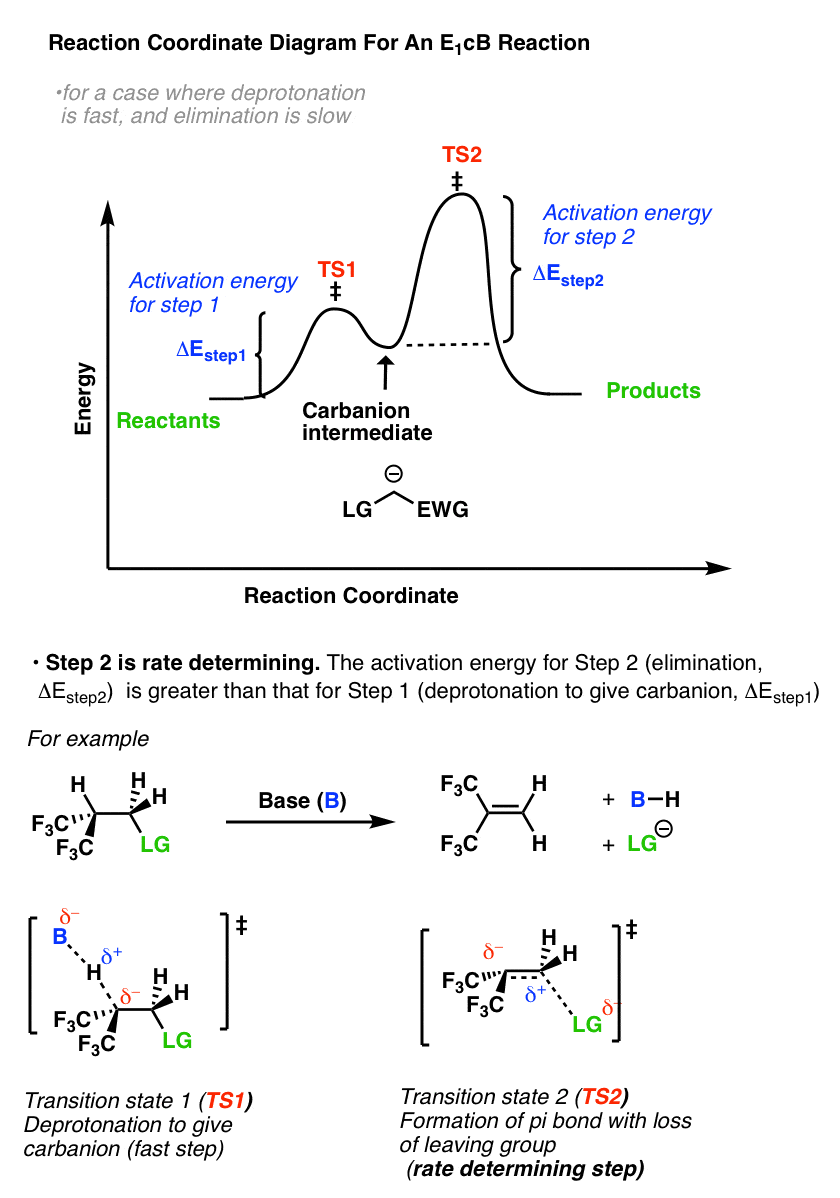



















0 Response to "42 energy reaction coordinate diagram"
Post a Comment