42 saturated fatty acid diagram
Is it a saturated fatty acid or unsaturated fatty acid? 2. What is the functional group in a fatty acid? 3. Draw the structure of triethanolamine. Circle and identify the functional groups in this molecule ; Question: a. Six Flags EF Lab #9 - Post Lab Questions 1. Draw the structura of stearic acid. Is it a saturated fatty acid or unsaturated ... Fatty acids are composed of long hydrocarbon chains terminated by carboxylic acid groups. Fatty acids are basically the primary derivative of lipids. Chain length from 4 to usually 24C atoms. They contain even number of C atoms majority of fatty acids are those containing 16 and 18 C atoms. Fatty Acid Structure Described Below.
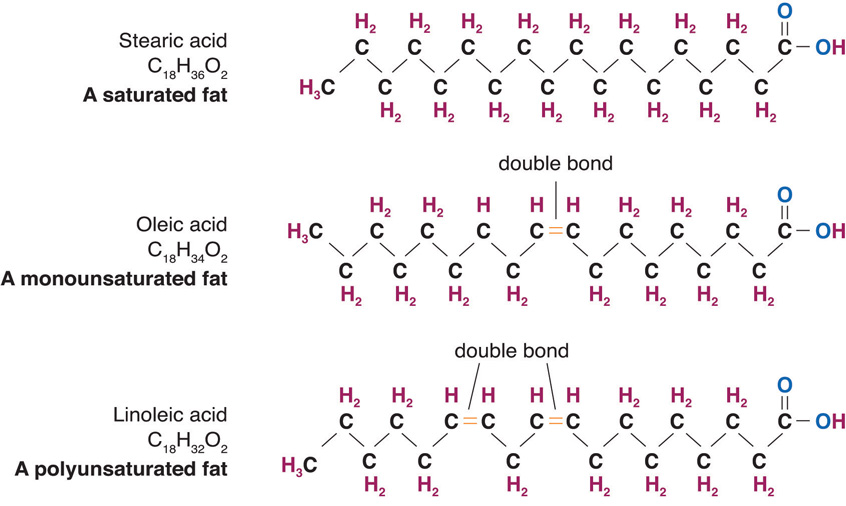
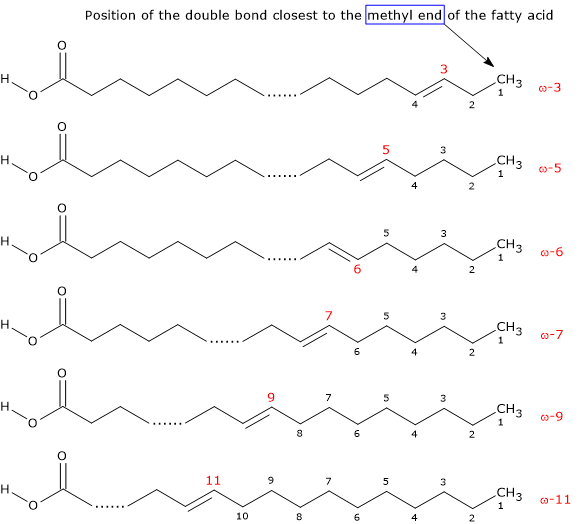
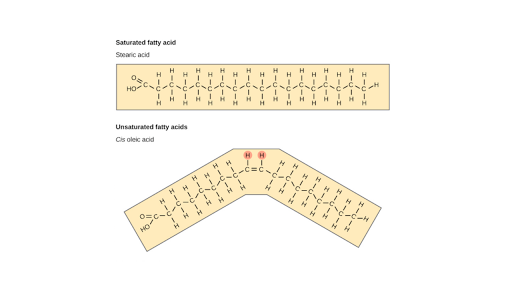
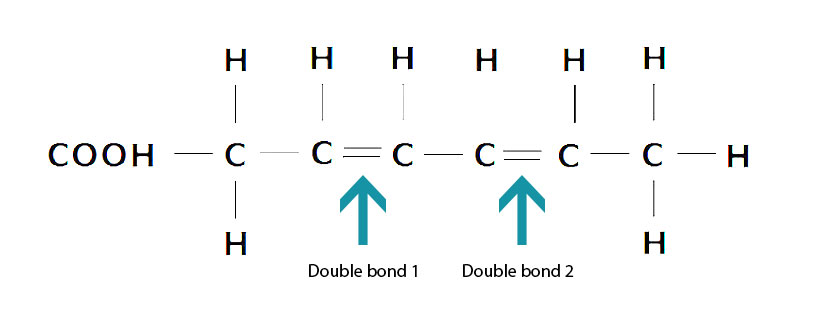
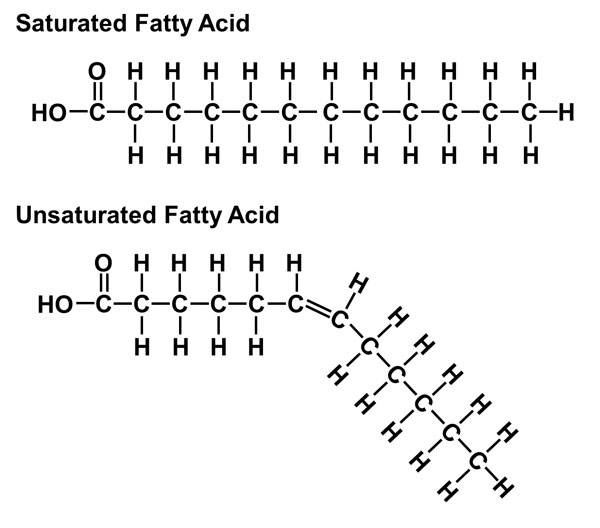
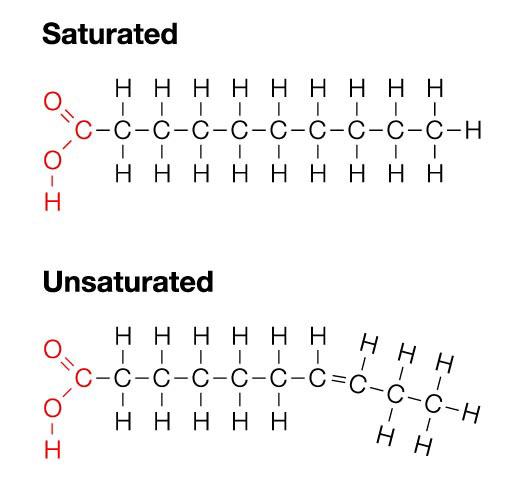
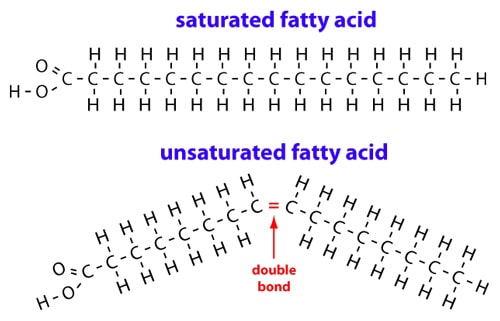
Saturated fatty acids have no double bonds in the hydrocarbon chain, and the maximum amount of hydrogen. The absence of double bonds decreases fluidity, making the membrane very strong and stacked tightly. Unsaturated fatty acids have at least one double bond, creating a “kink” in the chain.

Saturated fatty acid diagram
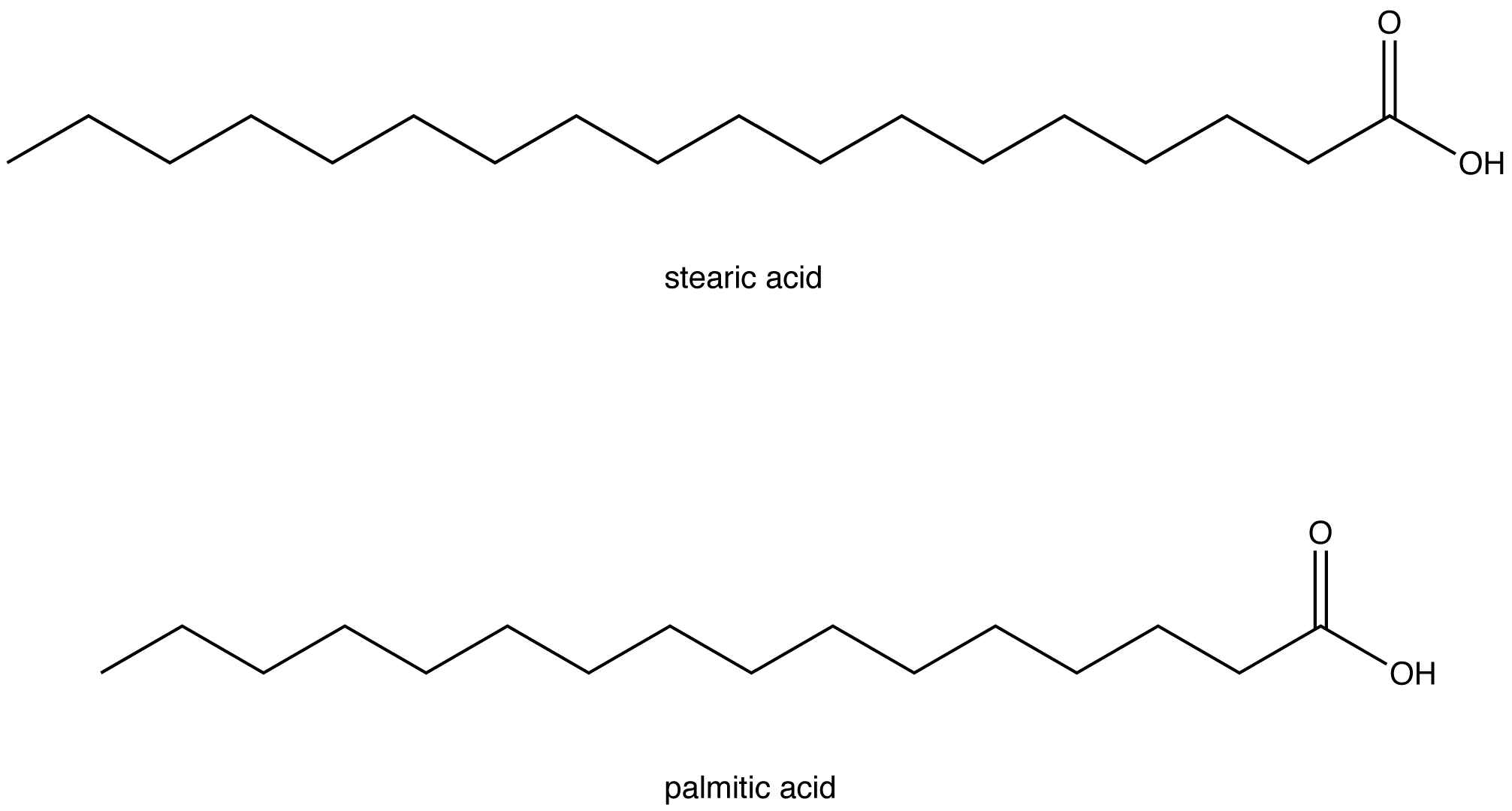
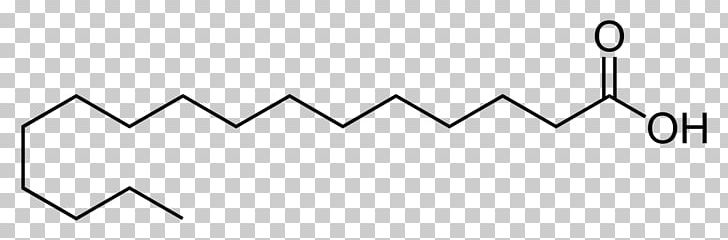
Saturated fatty acids (SFA) are fatty acids that contain no double bonds and have general formula R-COOH. The R- group is a straight-chain hydrocarbon of the form CH 3 (CH 2) n with varying length ranging from short chain length (volatile liquids) to chain lengths of 30 or more carbon atoms (waxy solids), though the most common and important fatty acids, found in many different plant and ... Saturated fatty acids are saturated with hydrogen and have only single (C-C) bonds, whereas unsaturated fatty acids have one or more double (C=C) BONDS. A principle of biology is that structure determines functions. Saturated fatty acid structure; Saturated fatty acids are fatty acids that do not contain double bonds and have the general formula R-COOH. The R- group is a straight-chain hydrocarbon in the form CH3 (CH2) n. Their length varies from short chains (volatile liquids) to chains of 30 or more carbon atoms (waxy solids), but the most important ...
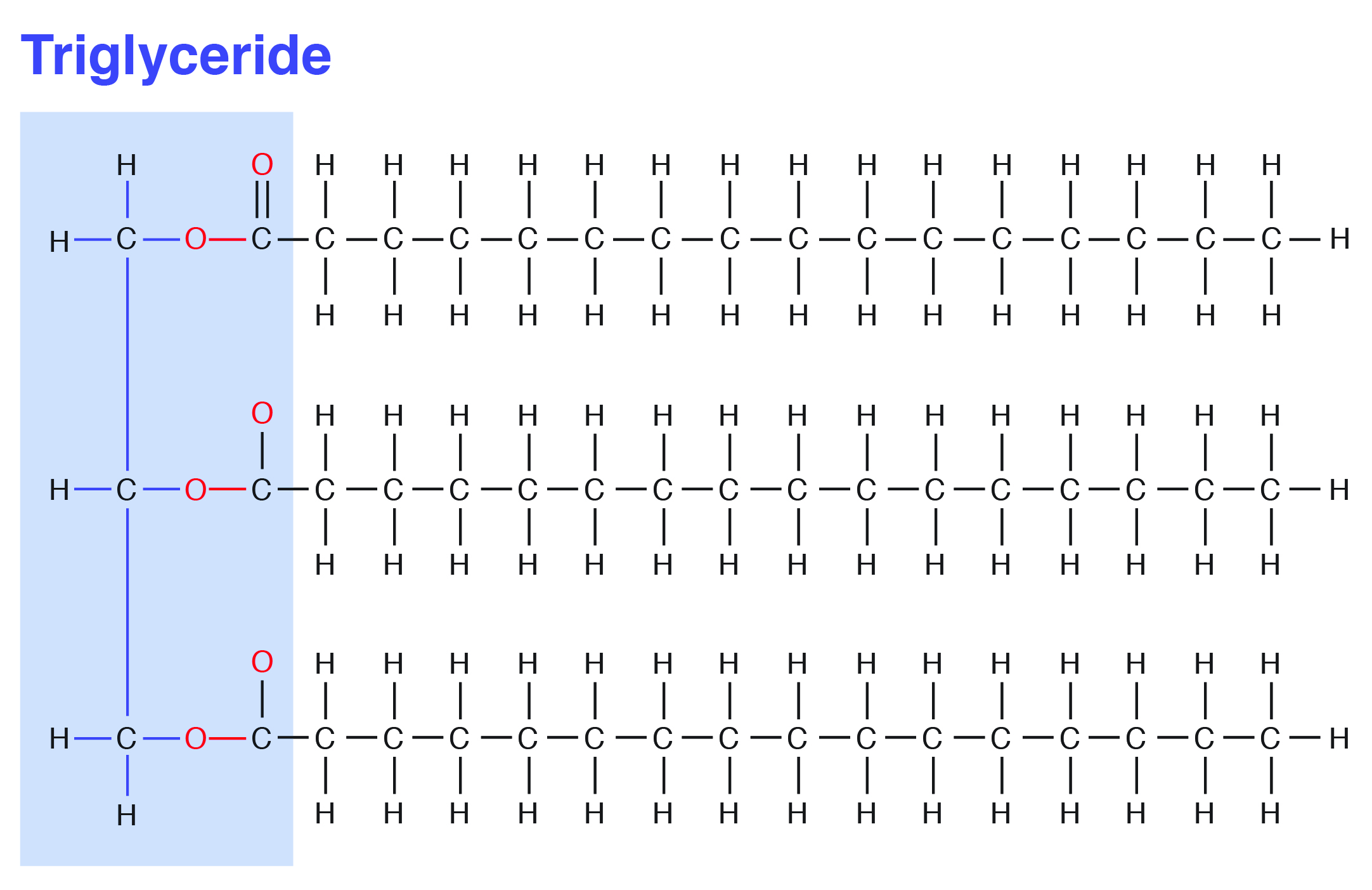
Saturated fatty acid diagram. Moreover, when it comes to the unsaturated fatty acids, there is a minimum of one double bond in the fatty acid chain. Definition of Saturated Fatty Acids. Saturated fatty acid refers to a type of fatty acid that has no linkages of unsaturated between carbon atoms. This type of fatty acid cannot absorb more hydrogen due to the lack of double bonds. Fatty acids may be saturated or unsaturated. In a fatty acid chain, if there are only single bonds between neighboring carbons in the hydrocarbon chain, the fatty acid is saturated. Saturated fatty acids are saturated with hydrogen; in other words, the number of hydrogen atoms attached to the carbon skeleton is maximized. Saturated fatty acids do not contain double bonds C-C (only single bonds), whereas unsaturated fatty acids contain one or more double bonds C=C. The chain length of most common fatty acids is of 16-18 number of carbon. The triglyceride is considered as the common and simple type of fat, having three fatty acids and glyceride. As Figure 1 demonstrates, though butter and coconut oil are both classified as saturated fat, they have very different fatty acid profiles. Coconut oil is the highest natural source of lauric acid. Lauric acid and its derivative monolaurin constitute around 50% of coconut fat-derived lipids [].The shorter chain length influences absorption such that medium-chain fatty acids are mostly absorbed ...
Saturated fatty acid structure; Saturated fatty acids are fatty acids that do not contain double bonds and have the general formula R-COOH. The R- group is a straight-chain hydrocarbon in the form CH3 (CH2) n. Their length varies from short chains (volatile liquids) to chains of 30 or more carbon atoms (waxy solids), but the most important ... Saturated fatty acids are saturated with hydrogen and have only single (C-C) bonds, whereas unsaturated fatty acids have one or more double (C=C) BONDS. A principle of biology is that structure determines functions. Saturated fatty acids (SFA) are fatty acids that contain no double bonds and have general formula R-COOH. The R- group is a straight-chain hydrocarbon of the form CH 3 (CH 2) n with varying length ranging from short chain length (volatile liquids) to chain lengths of 30 or more carbon atoms (waxy solids), though the most common and important fatty acids, found in many different plant and ...














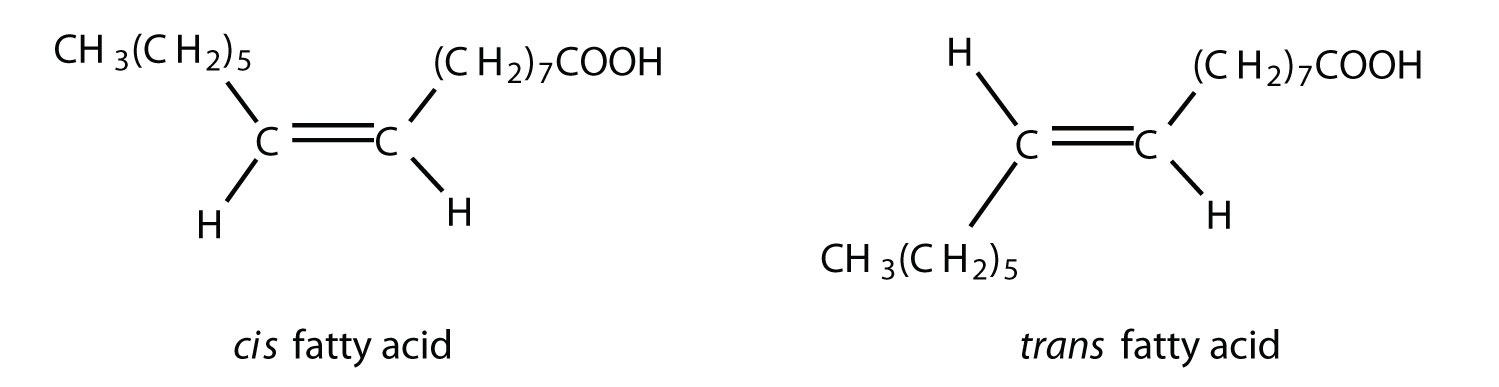










0 Response to "42 saturated fatty acid diagram"
Post a Comment