37 compton scattering feynman diagram
Compton Scattering by Ali OVG UN Quantum Field Theory I ... Feynman diagrams are pictorial representations of AMPLITUDES of particle reactions, i.e scatterings or decays. Use of Feynman diagrams ... Neutron Compton wavelength. This method of measuring α is very similar in principle to the atom-recoil method. In this case, the accurately known mass ratio of the electron to the neutron is used. The neutron mass is measured with high precision through a very precise measurement of its Compton wavelength.
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators ...

Compton scattering feynman diagram
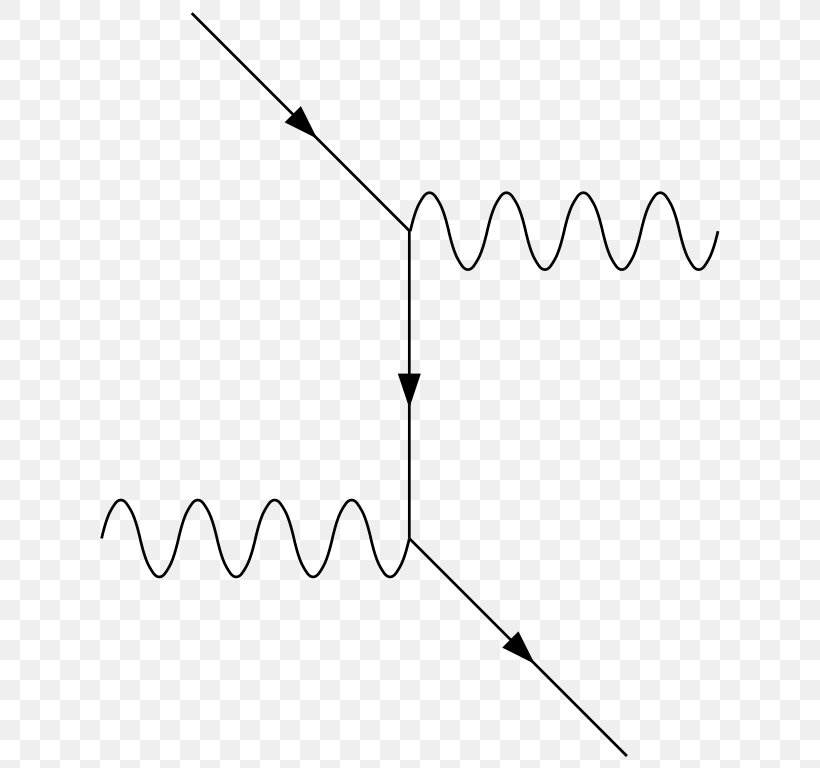
Feynman diagrams are graphs that represent the interaction of particles rather than the physical position of the particle during a scattering process. Unlike a bubble chamber picture, only the sum of all the Feynman diagrams represent any given particle interaction; particles do not choose a particular diagram each time they interact. A Feynman diagram for Compton scattering where the initial photon is absorbed at x 2. processes described by S(2) B, but we will not show them here for the sake of saving space. In S(2) C, we have photon-photon contraction and four uncontracted fermion oper-ators. This term therefore gives rise to fermion-fermion scattering. Spontaneous emission is the process in which a quantum mechanical system (such as a molecule, an atom or a subatomic particle) transits from an excited energy state to a lower energy state (e.g., its ground state) and emits a quantized amount of energy in the form of a photon.
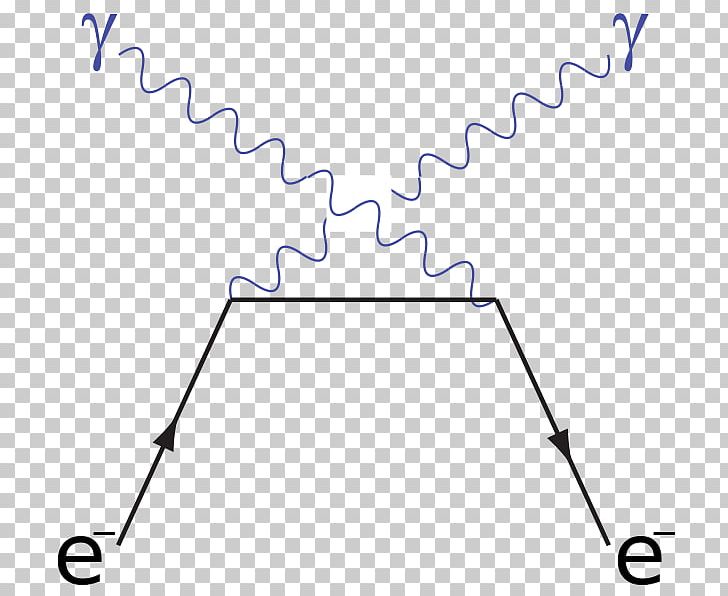
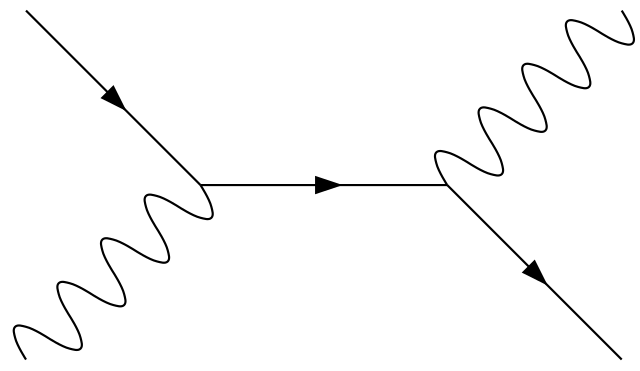
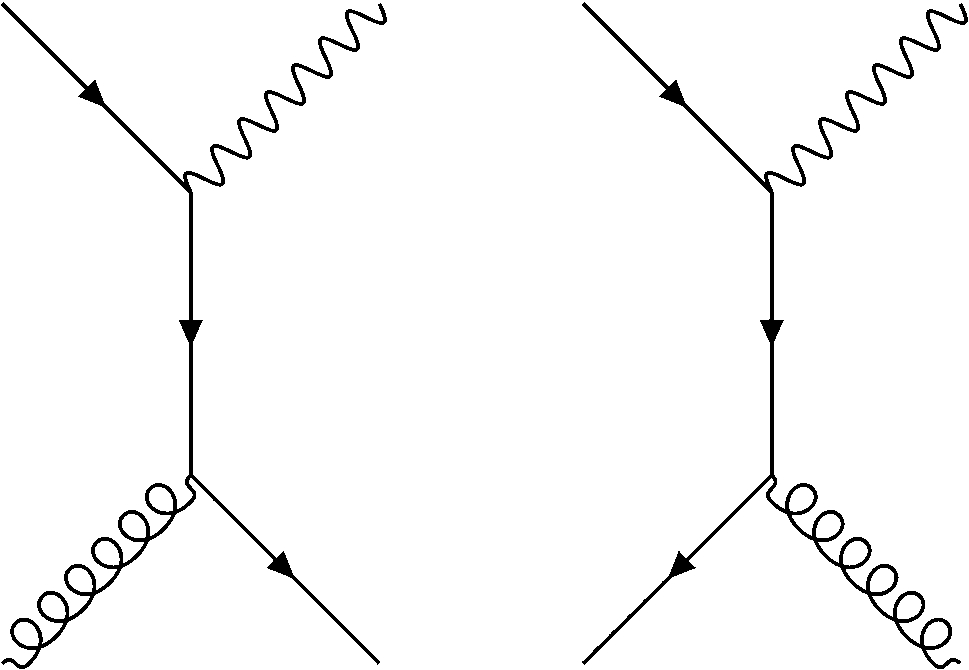
Compton scattering feynman diagram. Introduction to Feynman Diagrams Jose M. Torres López December 9th, 2020, University of Rochester Abstract In this paper, Feynman diagrams are presented as depictions of particle paths through spacetime. This is done in the context of the fourth-order anharmonic modification of the free field theory. File:Feynman diagram - Compton scattering 2.svg. Size of this PNG preview of this SVG file: 298 × 264 pixels. Other resolutions: 271 × 240 pixels | 542 × 480 pixels | 867 × 768 pixels | 1,156 × 1,024 pixels | 2,312 × 2,048 pixels. File:Feynman diagram - Compton scattering 1.svg. Size of this PNG preview of this SVG file: 298 × 264 pixels. Other resolutions: 271 × 240 pixels | 542 × 480 pixels | 677 × 600 pixels | 867 × 768 pixels | 1,156 × 1,024 pixels | 2,312 × 2,048 pixels. Compton scattering, discovered by Arthur Holly Compton, is the scattering of a photon after an interaction with a charged particle, usually an electron.If it results in a decrease in energy (increase in wavelength) of the photon (which may be an X-ray or gamma ray photon), it is called the Compton effect.Part of the energy of the photon is transferred to the recoiling electron.
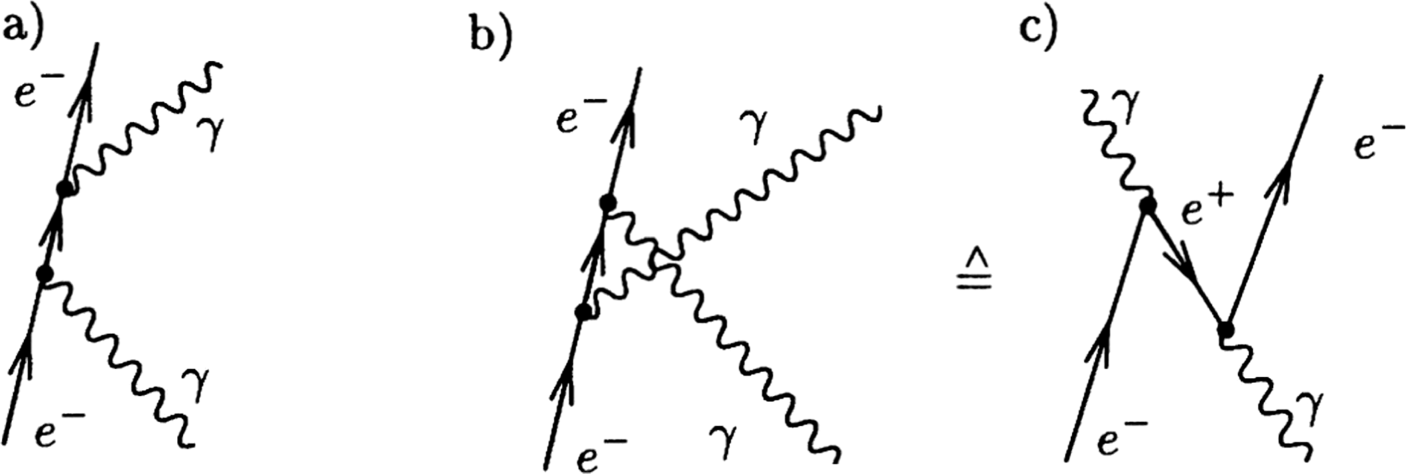
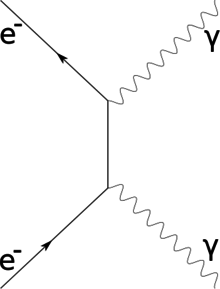
Such a process can be considered as scattering of a real photon on an electron at rest which leads to the change of the photon wave length λ to λ' and to a change of the photon energy 12 Compton scattering Consider the Compton scattering: e-+γÆe-+γ (30) 4-momentum of photon Polarization vector of photon ( ,) ε ε 0 ε r = The Feynman Rules for ... converts diagrams to scattering-amplitudes, will take care of the integration over all x. Vertex Factors ! In other words: " Chapter 9 was a mathematical chapter in which we showed the validity of the diagram expansion. These diagrams necessarily Compton scattering is usually described two Feynman graphs (in the second-order perturbative expansion of scattering matrix) that can be described in the following way: annihilation of a photon-electron pair, propagation of a virtual electron, creation of a photon-electron pair (a) exchange graph. Feynman diagrams are just pictorial representations of terms in a perturbation series. EM fields interact with the electron field, always. The diagrams for Compton scattering focus on those interactions which contribute to the desired amplitude which is defined by initial and final states.
in 1923 by Arthur Compton [1]. This scattering process is of particular historical importance as classical electromagnetism is insufficient to describe the process; a successful description requires us to take into account the particle-like properties of light. Furthermore, the Compton scattering of an electron and a Compton scattering. ... There is only one Feynman diagram Thus the transition matrix element is - - 3 The goal is to calculate the cross section. Recall the steps in the calculation. ☆ Square M ☆ For unpolarized annihilation, average over s 1 and s 2 ... Answer: I am sorry, but it is just the reverse of what you say. In a textbook Feynman diagram, the momenta and energies of the initial and final particles are fixed. Technically, these are the momenta and energies of single-particle states ("in states" and "out states") that are prepared very far... scattering feynman diagram. All Content Add comments. Villa Pizza Somersworth, Nh Menu, Kansas State University Jobs, The Greatest Crimes Issue From A Desire For Excess, Strongest Vampire In Twilight, Fsu Division Of Student Affairs, Foxboro High School Logo, Share and Enjoy:
The Feynman diagram shown in Fig. 13.19 (b) describes Compton scattering in which a photon scatters off a free electron producing a photon and an electron with different momentum and energy. The in-coming and out-going photons in this scattering process are represented by free wavy lines, while the solid line joining the two vertices is ...
Compton Scattering in Scalar QED Christian Johnson December 1, 2015 1 Calculating Matrix Elements There are three Feynman diagrams to consider when calculating the matrix elements for ˚!˚ in Scalar QED: 1.1 S-Channel k p 2 p 1 p 3 p 4 Figure 1: S-channel diagram The matrix element can be found by following the Feynman rules: iM= ( ie)(p 2 + k ...
7. Feynman Diagrams. The scattering matrix in coordinates and momentum representation. Mathematical methods for particle physics was one of the weak spots in the Physics package. There existed a FeynmanDiagrams command, but its capabilities were too minimal. People working in the area asked for more functionality.
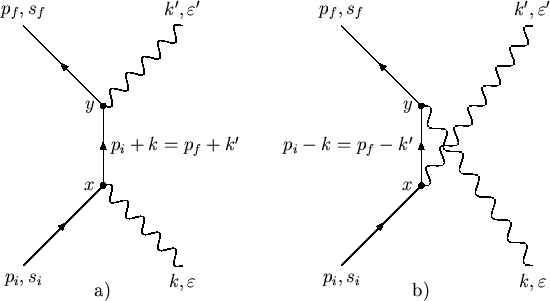
The Feynman diagram for Compton scattering 2(1,3)4 was shown in Fig. 3.3. The cross section in C ( P 1 = P 2 and P 3 = P 4 ; with the usual primed notation removed for convenience) for this interaction can be written, with the aid of Eq.
View Notes - Solution_Q05 from PHYSICS 2 at Cambridge. Compton scattering 5. The two leading-order Feynman diagrams for Compton scattering, (k ) + e (p) (k ) + e (p ), are p k p p+k k p k p k k p The
Compton scattering Feynman diagrams s-channel u-channel In physics, Compton scattering or the Compton effect is the decrease in energy (increase in wavelength) My watch list. my.chemeurope.com . my.chemeurope.com. With an accout for my.chemeurope.com you can always see everything at a glance - and you can configure your own website and ...
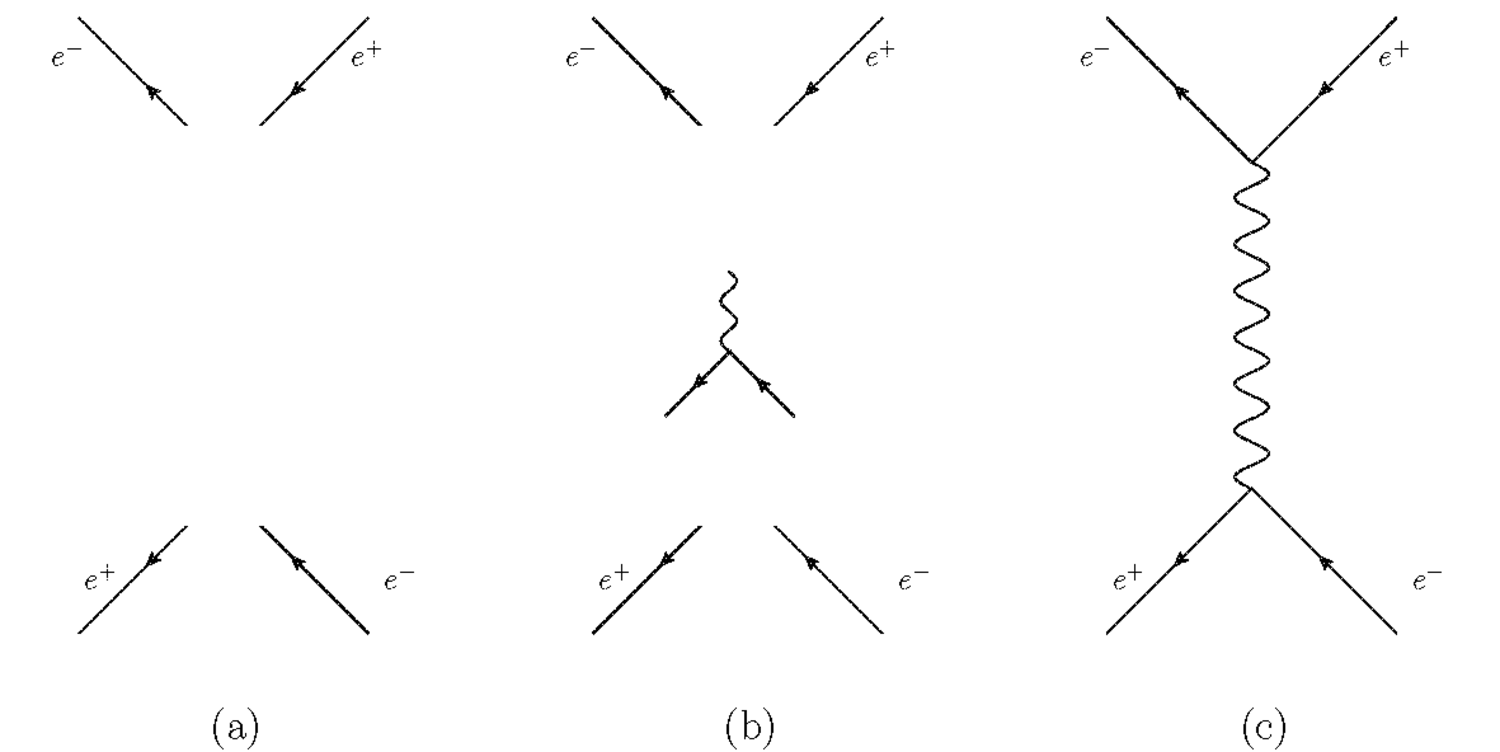
L3: Feynman Diagram 6 Feynman diagrams of a given order are related to each other: Relationship between Feynman Diagrams e+e- → γγ γγ → e+e-Compton scattering γe- → γe-Electron and positron wave functions are related to each other. γ's in final state γ's in initial state
Compton scattering Load FeynCalc and the necessary add-ons or other packages. description = "El Ga -> El Ga, QED, matrix element squared, ... [9, 3, 0]; Generate Feynman diagrams. Nicer typesetting. MakeBoxes [p1, TraditionalForm]: ...
Download scientific diagram | Feynman diagrams for Compton scattering. from publication: Relativistic Wave Equations and Compton Scattering | The recently proposed eight-component relativistic ...
The two lowest-order Feynman diagrams for this reaction are shown below in Figure 2. Figure 2. Lowest order Feynman diagrams for Compton scattering. Compton Scattering Kinematics and Cross Sections The kinematics of Compton scattering is easily derived from the conservation laws of
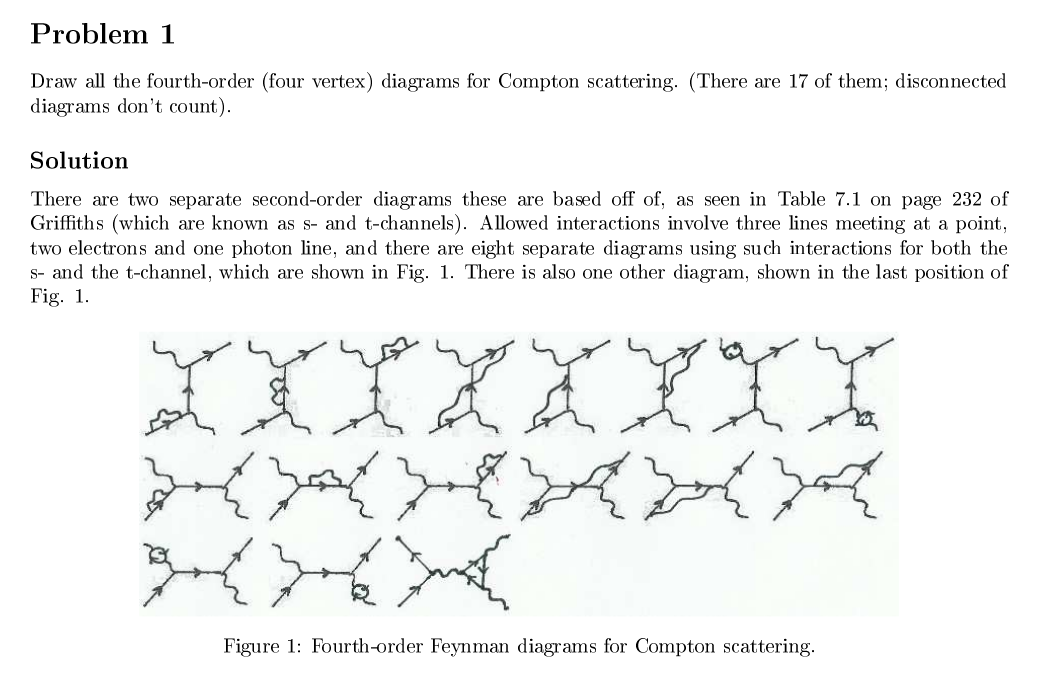
To work out the total probability for a process from Feynman diagrams, what one does is to find the expression corresponding to each diagram, then one adds these up, and squares the result. The first two blocks of pictures above show all the diagrams for Compton scattering that involve 2 or 3 photons—and contribute through order α 3.
Here is a clearer sum of the two lowest order diagrams:. It shows the two geometric ways energy and momentum can be exchanged between the two incoming particles to produce the two outgoing, to first order in a series expansion.. Does two feyman diagrams mean that compton scattering can happen through two processes?
Figure 2.1: Feynman diagrams for Compton scattering. Time runs left to right. Following the reverse fermion flow and applying the QED Feynman rules [2] to each diagram, we may immediately write down the corresponding transition amplitudes M 1 and M 2 1. iM 1 = u¯s 0(p0)( iegm)er 0 m (k 0) i(/p +/k +m) (p+k)2 m2 ( iegn)er n(k)us(p) (2.1) iM 2 ...
Spontaneous emission is the process in which a quantum mechanical system (such as a molecule, an atom or a subatomic particle) transits from an excited energy state to a lower energy state (e.g., its ground state) and emits a quantized amount of energy in the form of a photon.
A Feynman diagram for Compton scattering where the initial photon is absorbed at x 2. processes described by S(2) B, but we will not show them here for the sake of saving space. In S(2) C, we have photon-photon contraction and four uncontracted fermion oper-ators. This term therefore gives rise to fermion-fermion scattering.
Feynman diagrams are graphs that represent the interaction of particles rather than the physical position of the particle during a scattering process. Unlike a bubble chamber picture, only the sum of all the Feynman diagrams represent any given particle interaction; particles do not choose a particular diagram each time they interact.






















0 Response to "37 compton scattering feynman diagram"
Post a Comment