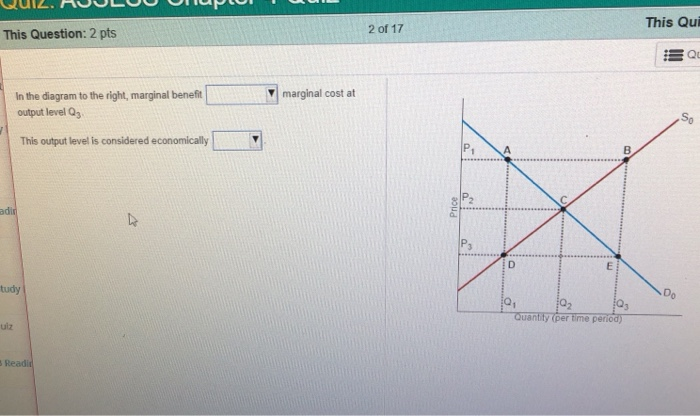
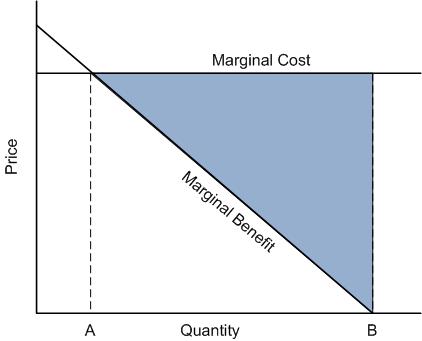
37 in the diagram to the right, marginal benefit
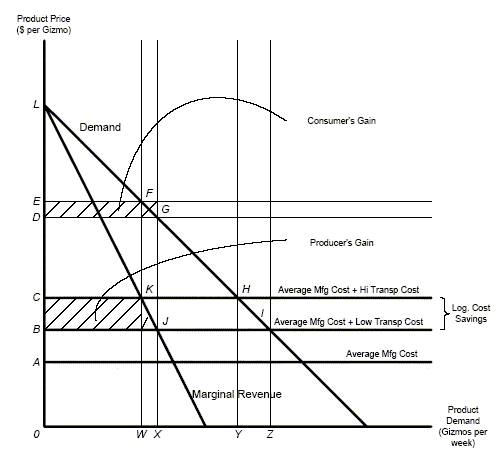
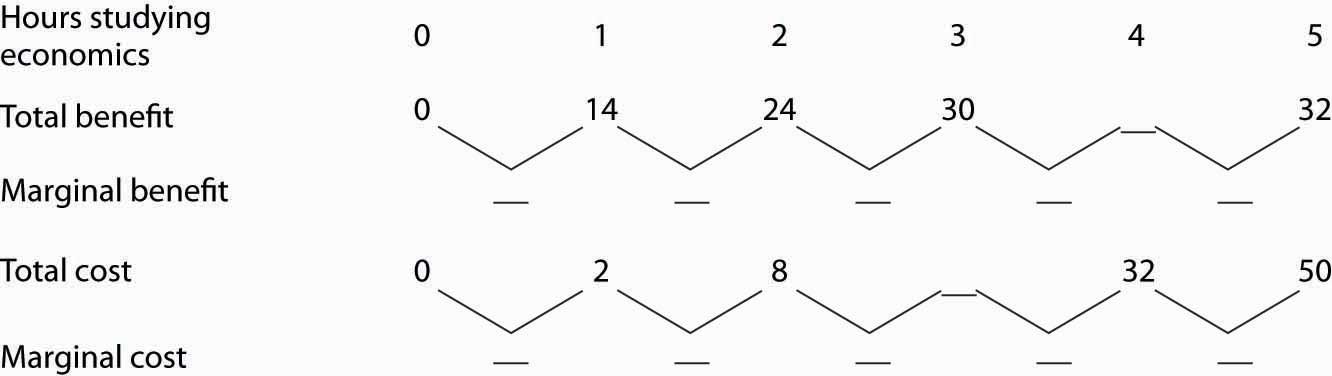
Marginal revenue (or marginal benefit) is a central concept in microeconomics that describes the additional total revenue generated by increasing product sales by 1 unit. To derive the value of marginal revenue, it is required to examine the difference between the aggregate benefits a firm received from the quantity of a good and service produced last period and the current period … Since the marginal benefit from spending in the private sector equals Rs. 1, it holds for public sector as well. Let us now take the case of lumpy projects. The B/C ratio in the private sector is taken to equal 1. The public project is undertaken if the B/C ratio exceeds 1, it, therefore, suggests that only projects I, II and VI in Table 1 will be undertaken. Our aim above has been to show ...
The properties of the average and marginal cost curves and their relationship to each other are as described in Fig. 14.4. From the diagram the following relationships can be discovered. (1) AFC declines continuously, approaching both axes asymptomatically (as shown by the decreasing distance between ATC and AVC) and is a rectangular hyperbola.
In the diagram to the right, marginal benefit
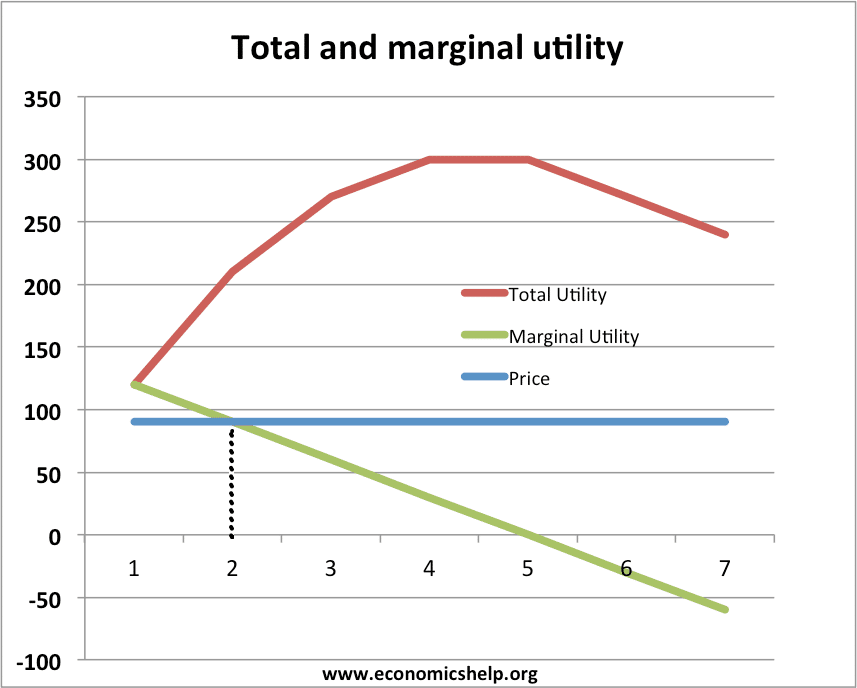
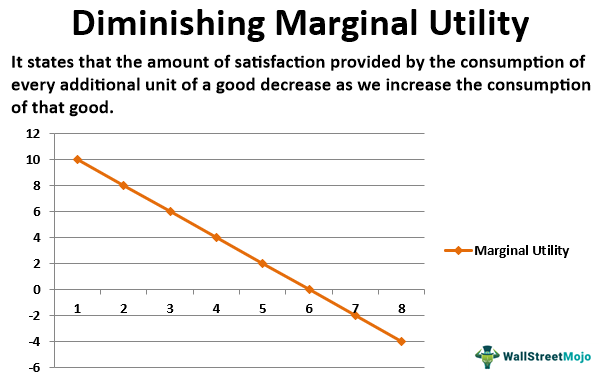
The marginal cost may first decline, as in the diagram, if the additional cost per unit is high if the firm operates at too low a level of output, or it may start flat or rise immediately. At some point, the marginal cost rises as increases in the variable inputs such as labor put increasing pressure on the fixed assets such as the size of the building. In the long run, the firm would increase ... Coverage Diagram. On maps at scales of 1:100,000 and larger, a coverage diagram may be used. It is normally in the lower or right margin and indicates the methods by which the map was made, dates of photography, and reliability of the sources. On maps at 1:250,000 scale, the coverage diagram is replaced by a reliability diagram. Special Notes ... 28/09/2021 · In the diagram number of oranges are shown on OX-axis and marginal utility on the OY-axis. MU shows the decreasing trends of all the units of oranges. The 5th unit of orange gives zero (0) MU while the 6th unit gives negative marginal utility. A is the point of satiety thereafter consumers should not consume additional units of oranges. There are three stages …
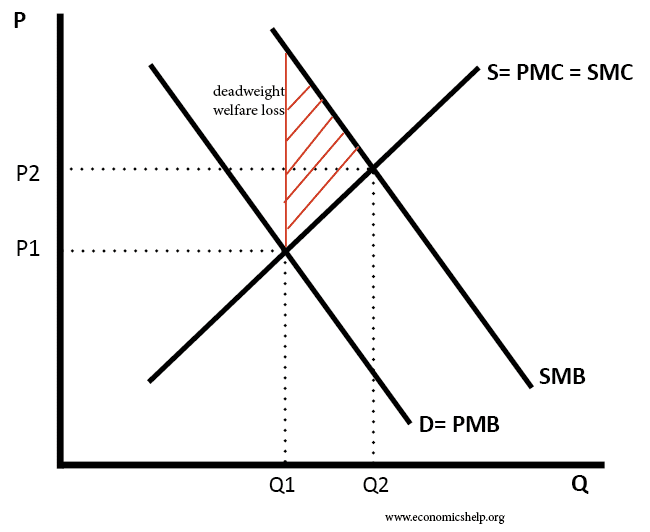
In the diagram to the right, marginal benefit. The externality starts when the marginal cost of consuming or producing an additional unit of a public good is zero but a price above zero is being charged. This violates the Paretian welfare maximization criterion of equating marginal social cost and marginal social benefit. This is because the benefits of a public good must be provided at a ... mar·gin·al (mär′jə-nəl) adj. 1. Of, relating to, located at, or constituting a margin, a border, or an edge: the marginal strip of beach; a marginal issue that had no bearing on the election results. 2. Being adjacent geographically: states marginal to Canada. 3. Written or printed in the margin of a book: marginal notes. 4. Barely within a lower ... Transcribed image text: In the diagram to the right, marginal benefit marginal cost at output level Q1 This output level is considered economically : D Do ...1 answer · Top answer: Ans) Marginal Benefit is greater than mar... 3. Diagram: Explanation: In the diagram, X-axis represents no. of units consumed while the Y-axis represents Marginal Utility. Various points of MU are plotted on the graph as per the given schedule. When the locus of all the points is joined, the MU curve is derived. MU curve is a downward sloping curve from left to right. It indicates that an ...
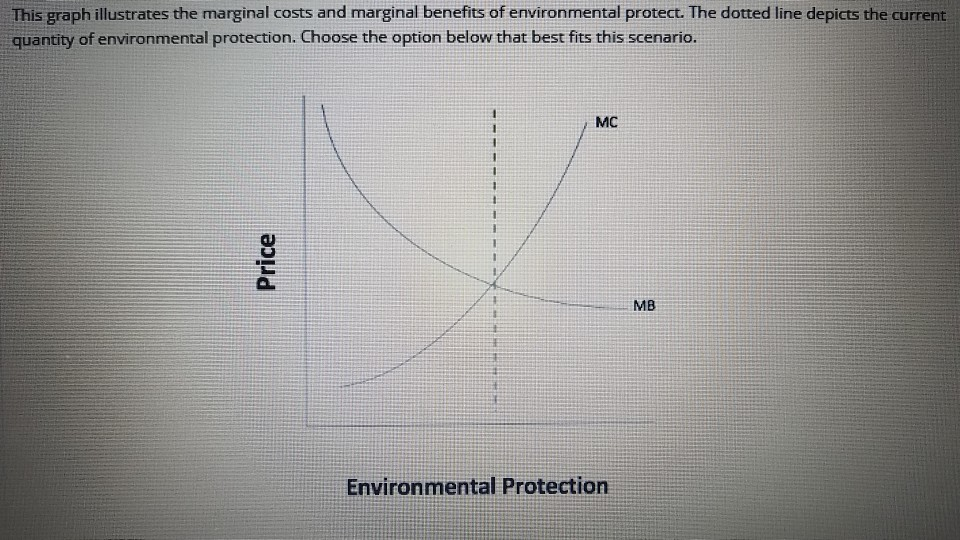
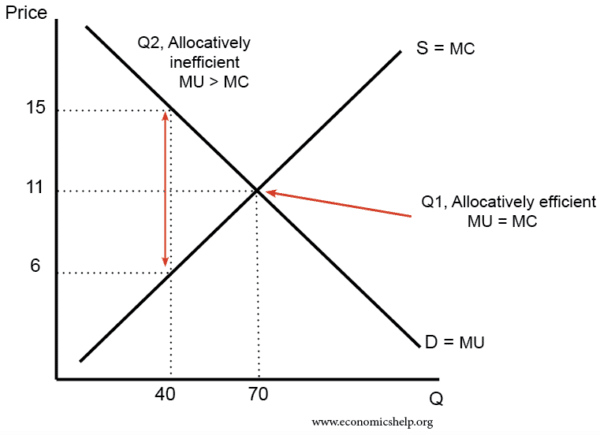
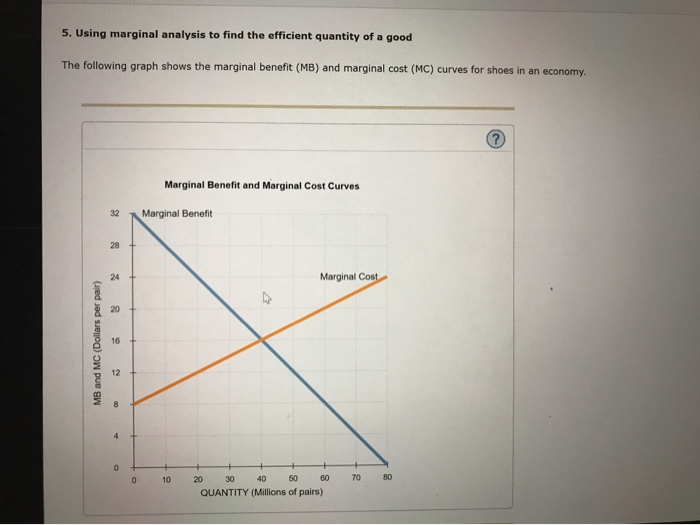
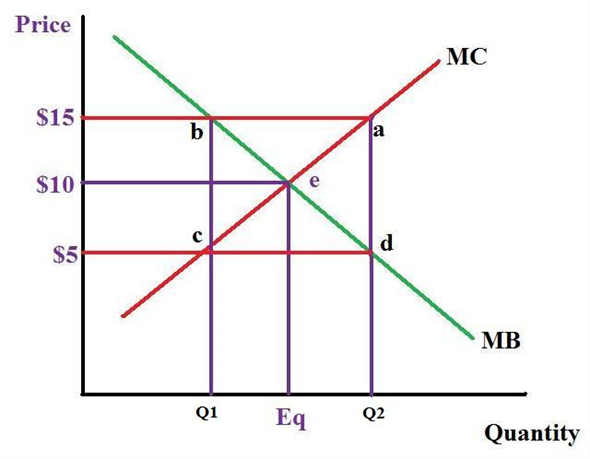
marginal benefit and marginal cost are equal. No resources beyond that point should be allocated to production. Theory: Resources are efficiently allocated to any product when the MB and MC are equal. Essential Graph: Application: External Costs and External Benefits External Costs and Benefits occur when some of the costs or the benefits of the good or service are … 28/09/2021 · In the diagram number of oranges are shown on OX-axis and marginal utility on the OY-axis. MU shows the decreasing trends of all the units of oranges. The 5th unit of orange gives zero (0) MU while the 6th unit gives negative marginal utility. A is the point of satiety thereafter consumers should not consume additional units of oranges. There are three stages … Coverage Diagram. On maps at scales of 1:100,000 and larger, a coverage diagram may be used. It is normally in the lower or right margin and indicates the methods by which the map was made, dates of photography, and reliability of the sources. On maps at 1:250,000 scale, the coverage diagram is replaced by a reliability diagram. Special Notes ... The marginal cost may first decline, as in the diagram, if the additional cost per unit is high if the firm operates at too low a level of output, or it may start flat or rise immediately. At some point, the marginal cost rises as increases in the variable inputs such as labor put increasing pressure on the fixed assets such as the size of the building. In the long run, the firm would increase ...

:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/13353/coronary-arteries-and-cardiac-veins_english.jpg)




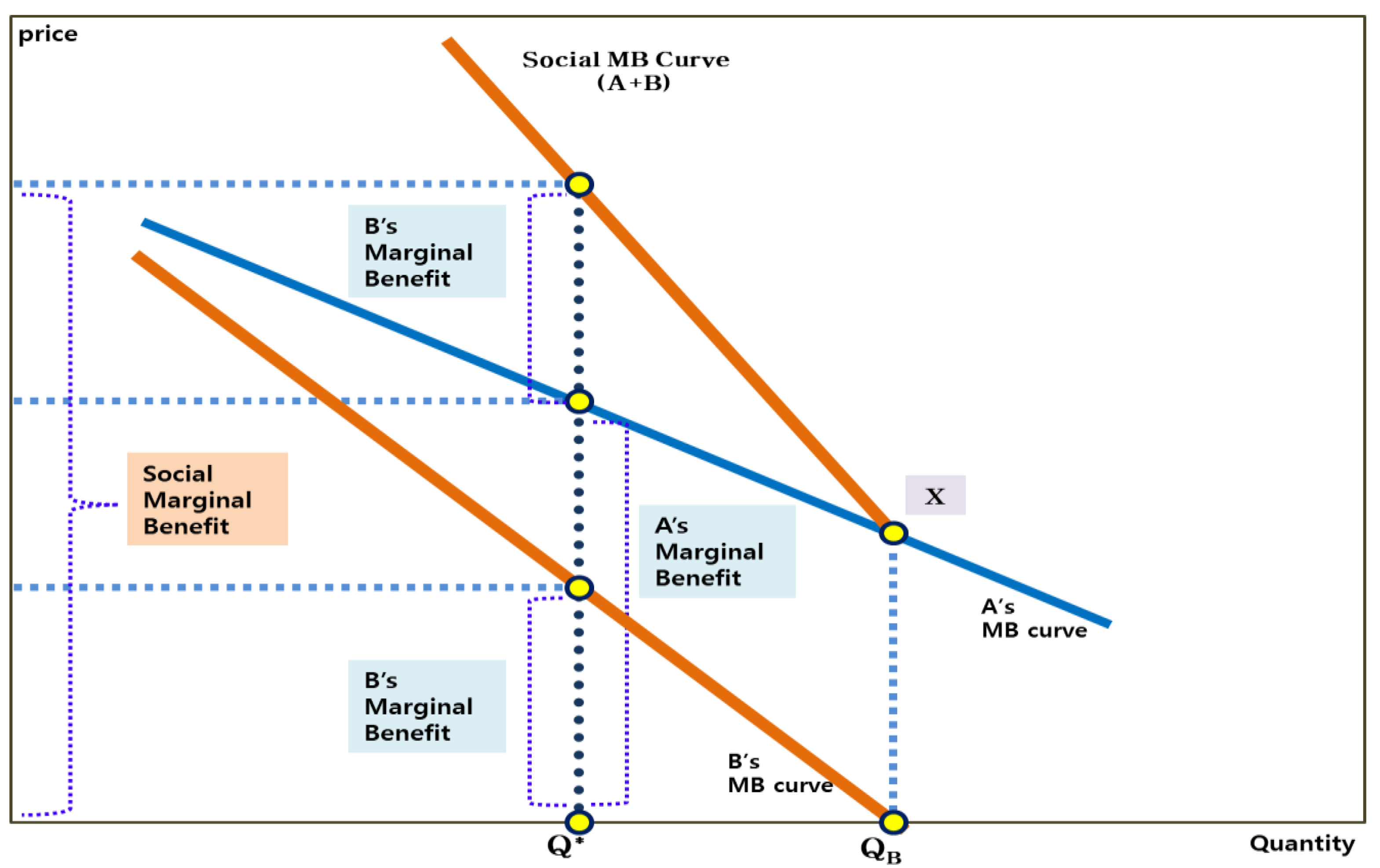









/dotdash_Final_Law_of_Diminishing_Marginal_Productivity_Oct_2020-01-d3c30a9c6ba442b9bccc7b99158251e3.jpg)
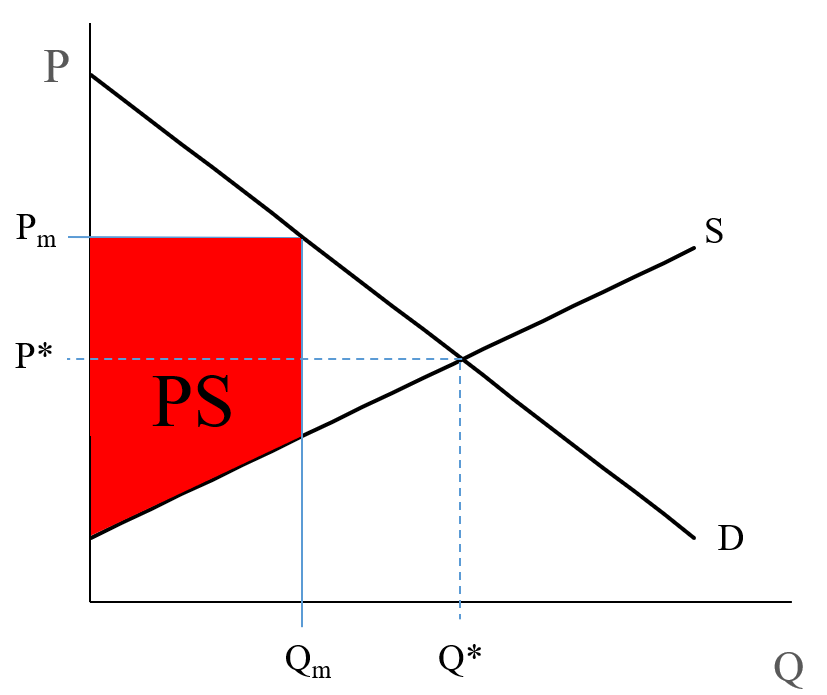

0 Response to "37 in the diagram to the right, marginal benefit"
Post a Comment