38 cellular respiration electron transport chain diagram
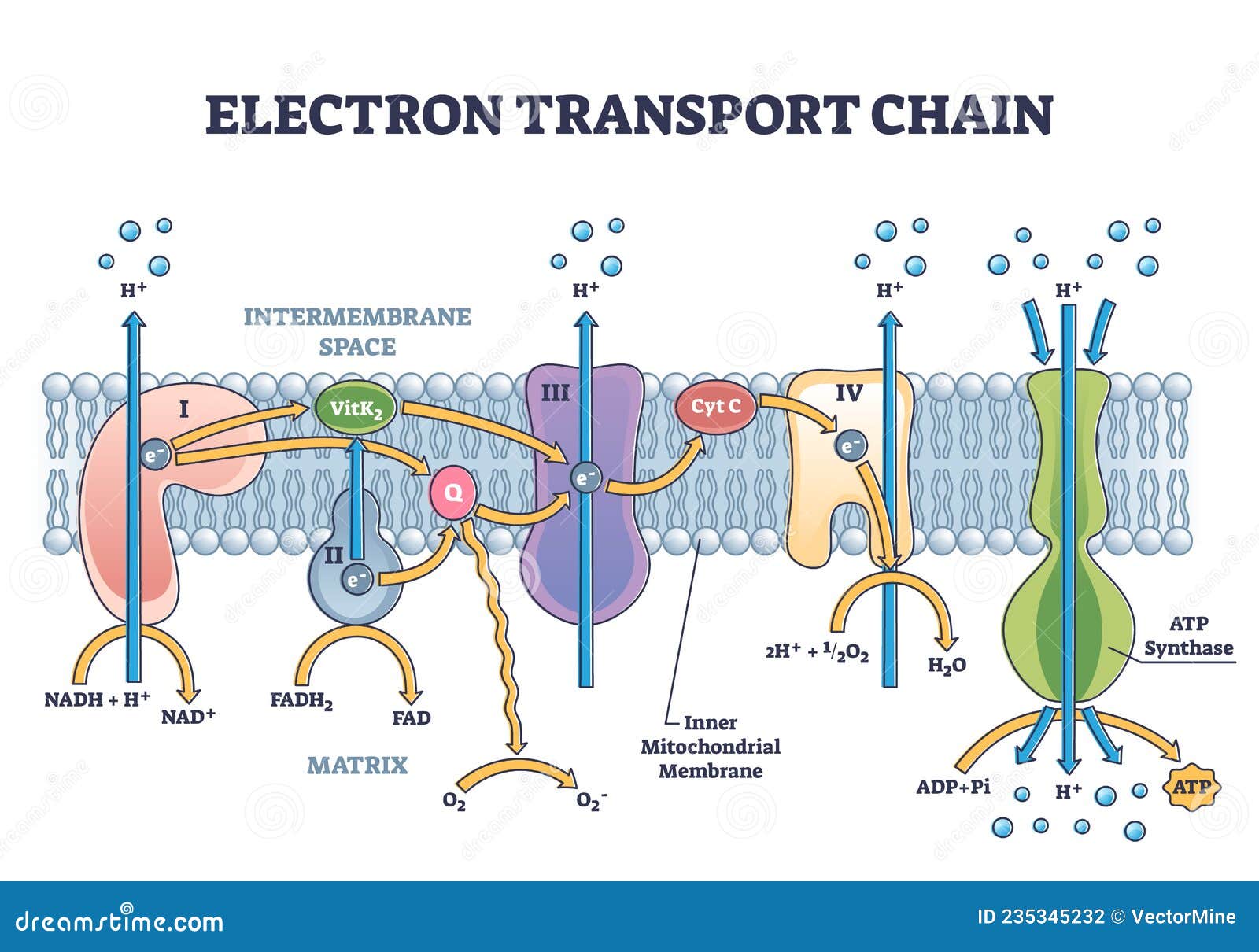
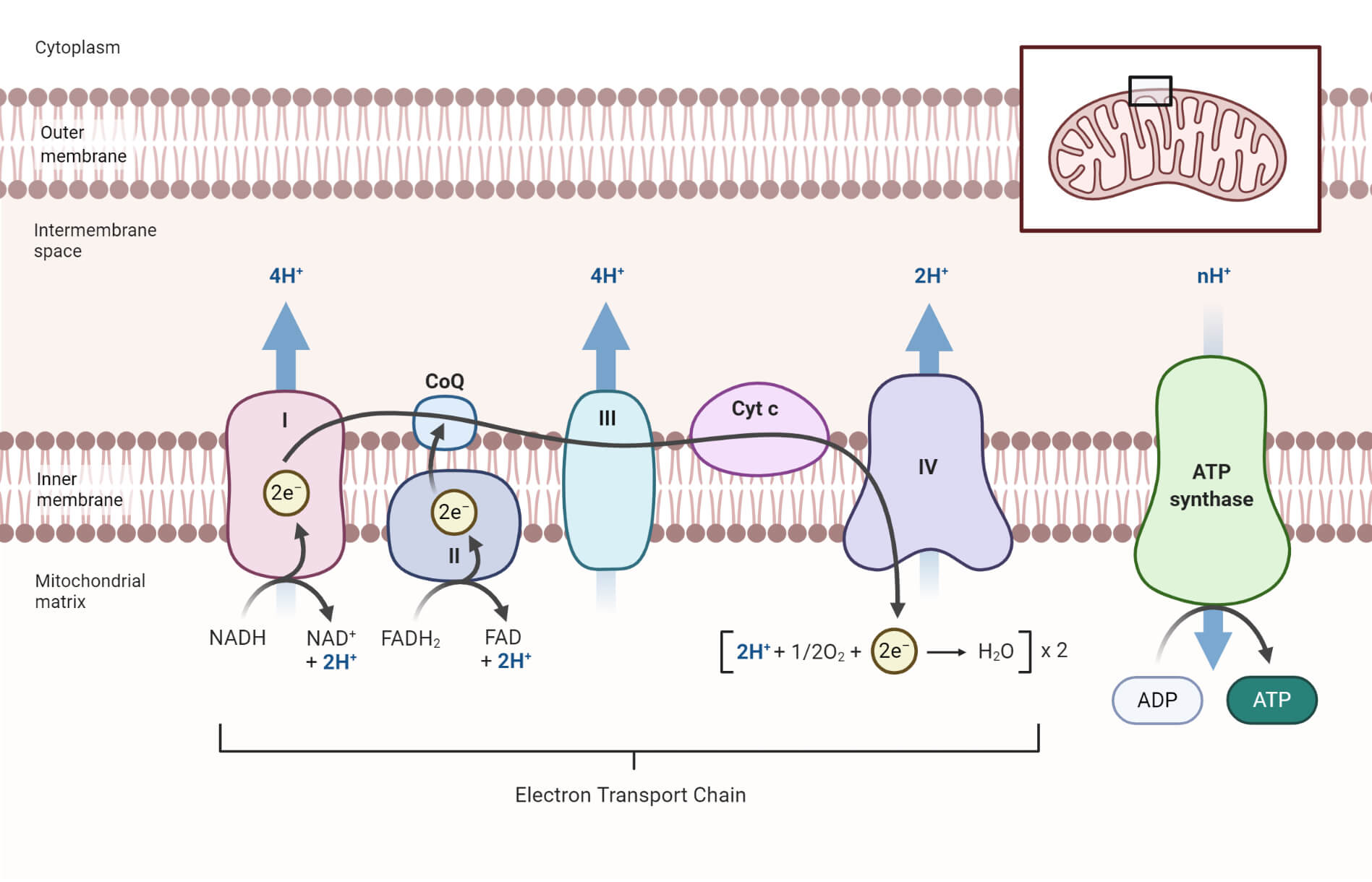
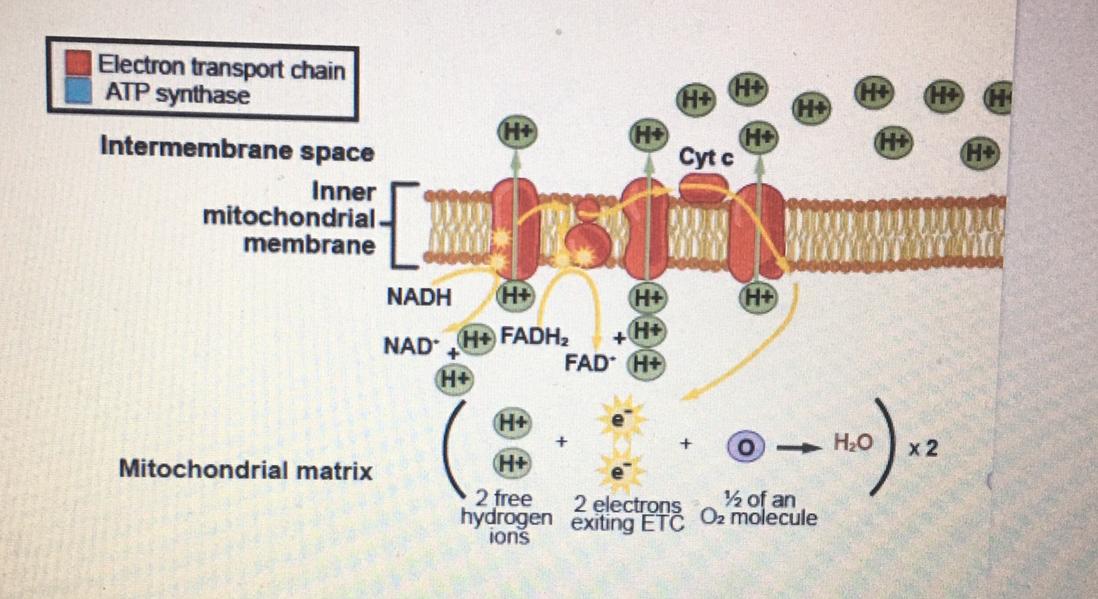
The electron transport chain is a series of four protein complexes that couple redox reactions, creating an electrochemical gradient that leads to the creation of ATP in a complete system named oxidative phosphorylation. It occurs in mitochondria in both cellular respiration and photosynthesis. In the former, the electrons come from breaking down organic molecules, and energy is released. Sep 13, 2021 · All aerobic cells require oxygen to perform aerobic cellular respiration, as it is the final step and is essential for continuing the flow of electrons through the …
Aug 24, 2021 · The electron transport chain has two essential functions in the cell: Regeneration of electron carriers: Reduced electron carriers NADH and FADH 2 pass their electrons to the chain, turning them back into NAD + and FAD. This function is vital because the oxidized forms are reused in glycolysis and the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) during cellular …

Cellular respiration electron transport chain diagram
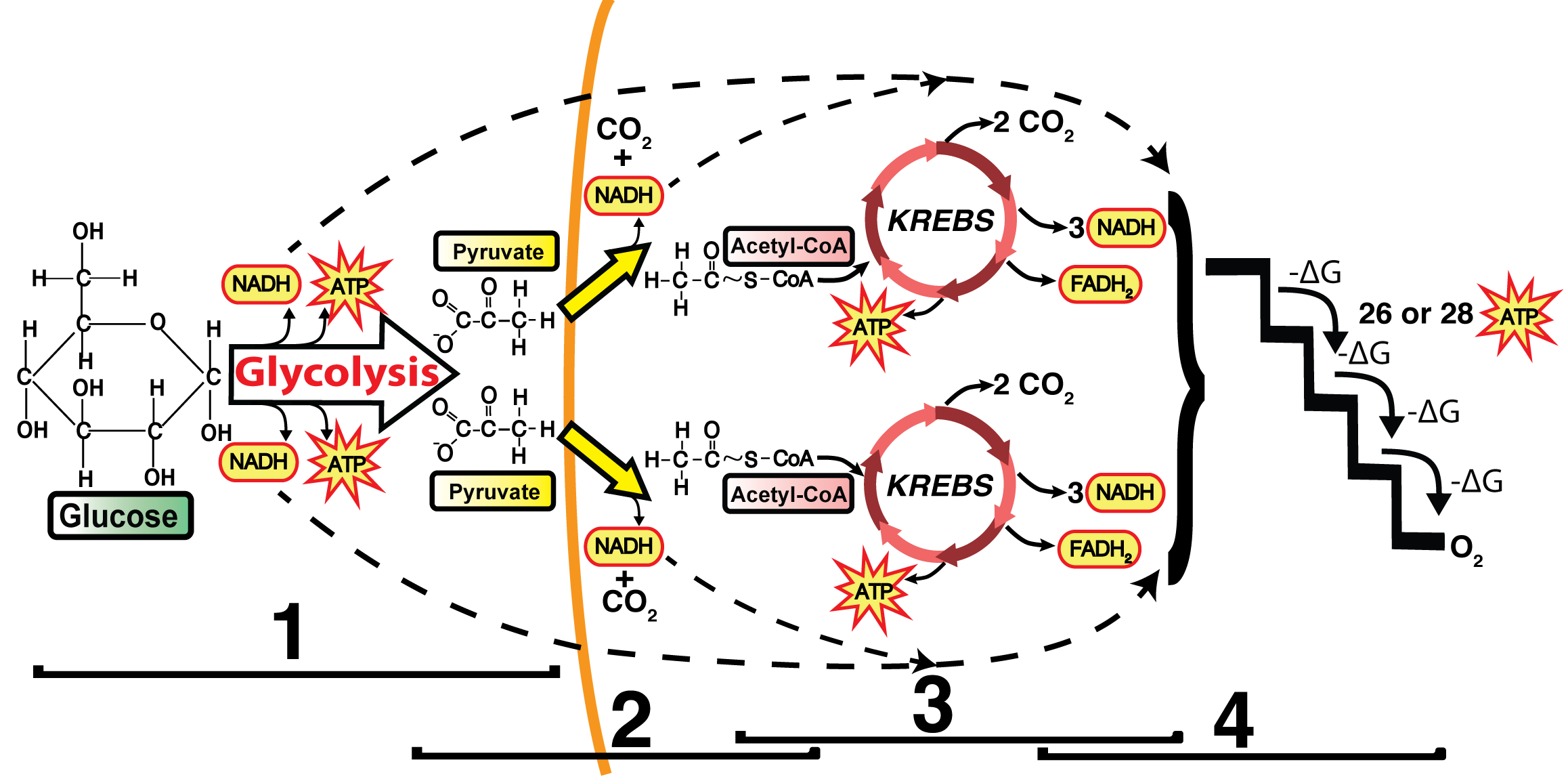
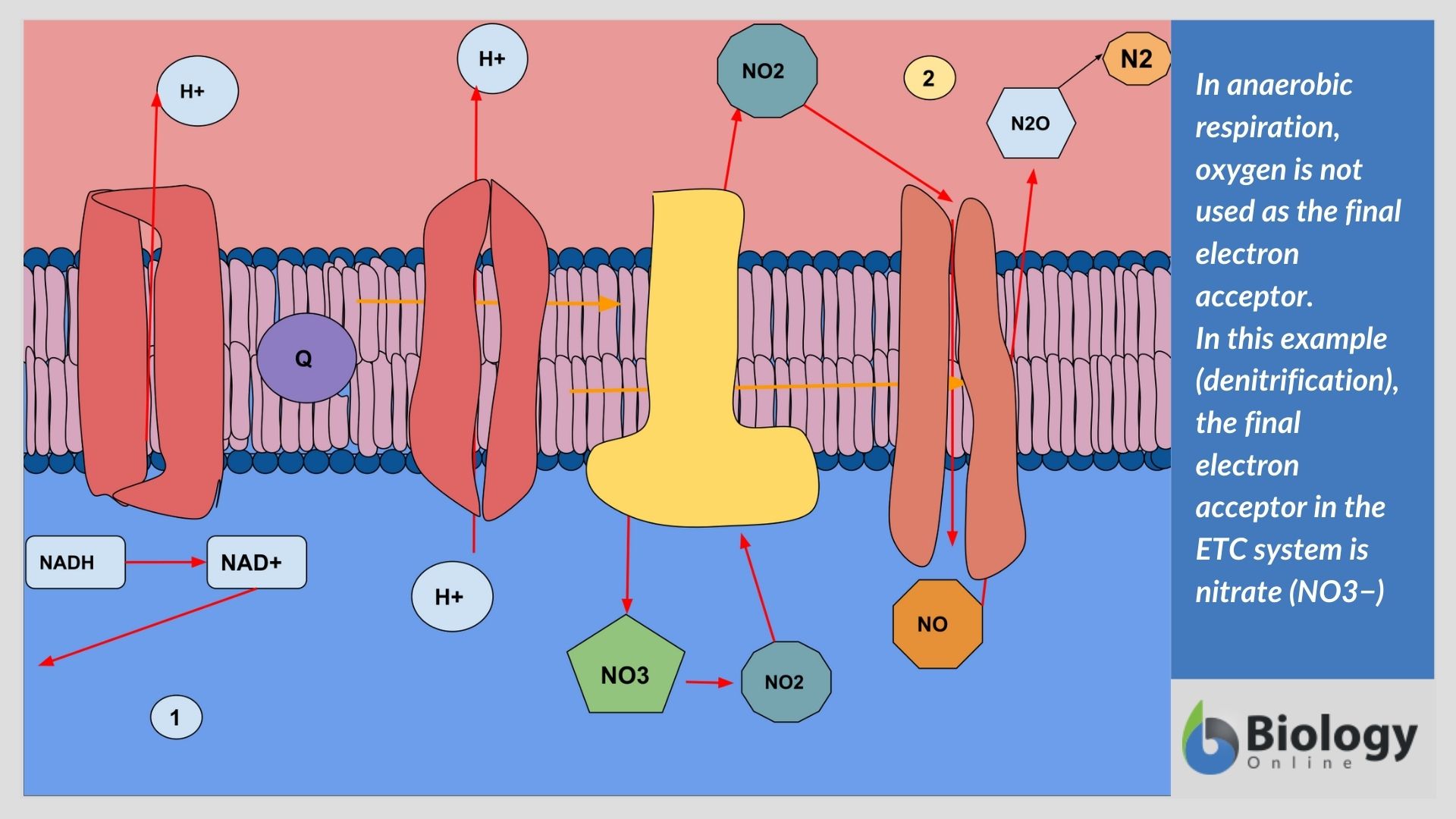
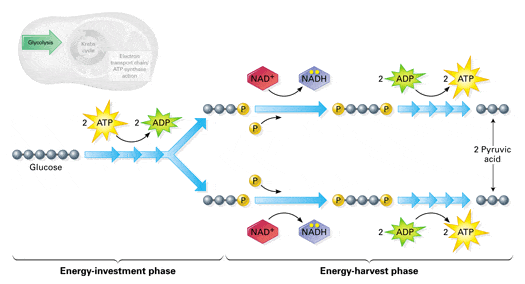
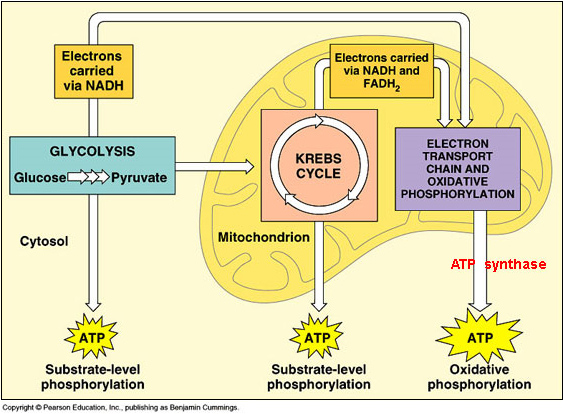
Dec 07, 2021 · Cellular Respiration Equation: Every machine needs specific parts and fuel in order to function. Likewise, “biological machines” also require well engineered parts and good energy source in order to work.Perhaps the second most important molecule (DNA is the first) is adenosine triphosphate (also known as ATP).Basically, ATP serves as the main energy … ADVERTISEMENTS: The electron transport chains of bacteria (prokaryotes) operate in plasma membrane (mitochondria are absent in prokaryotes). Some bacterial electron transport chains resemble the mitochondrial electron transport chain. Paracoccus denitrificans is a gram-negative, facultative anaerobic soil bacterium. It is a model prokaryote for studies of respiration. When this bacterium grows ... More About Cellular Respiration So now we know that cellular respiration is a three stage process that converts glucose and oxygen to ATP and releases carbon dioxide and water. What are the 3 phases that do this? 1) Glycolysis 2) Krebs Cycle 3) The Electron Transport Chain (ETC) This is a very simple overview of these 3 stages: Glycolysis (Stage 1)
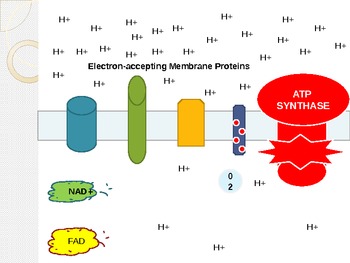
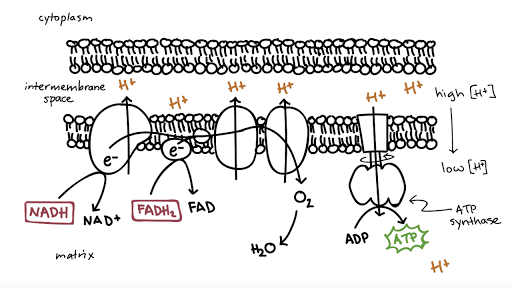
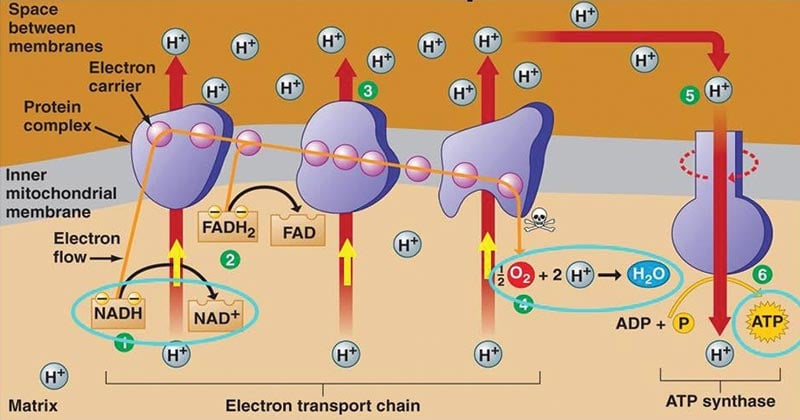
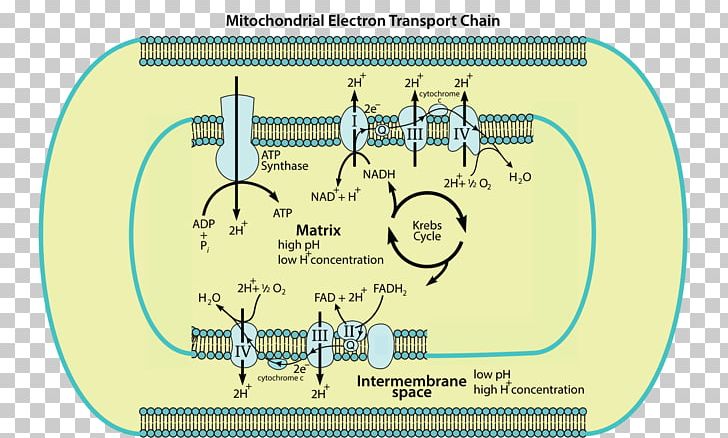
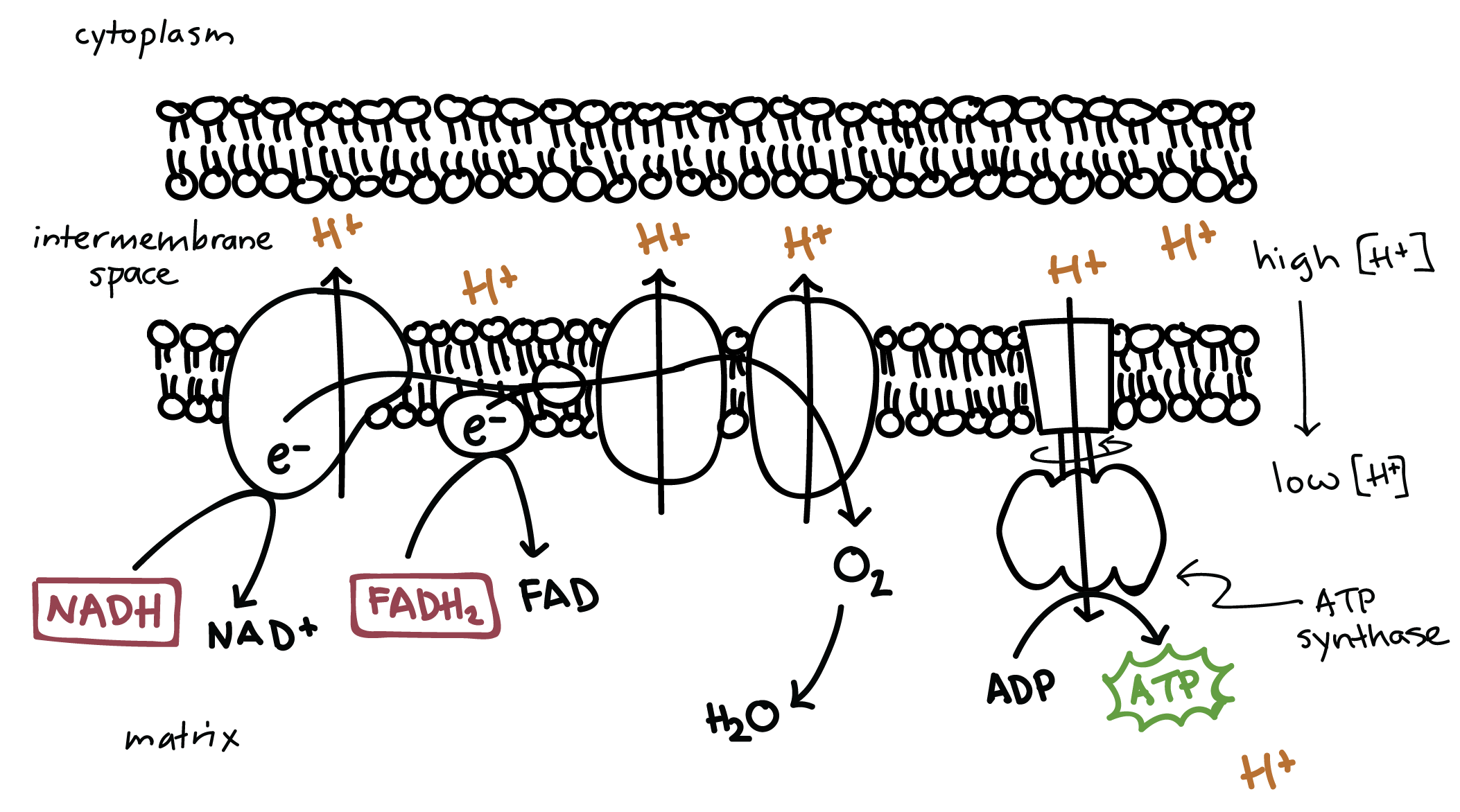
Cellular respiration electron transport chain diagram. The electron transport chain is present in multiple copies in the eukaryote inner mitochondrial membrane and in the prokaryote plasma membrane. But note that the prokaryote electron transport chain may not require oxygen as some live-in anaerobic conditions. All electron transport chains are commonly characterized by the presence of a proton ... The electron transport chain is a group of proteins embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane, or cristae. There are two events in the electron transport chain: Electron Donation (setting up a gradient): High energy electrons from NADH and FADH 2 (from Stages 1 and 2) are transferred to the ETC proteins. Electron Transport Chain Definition. The electron transport chain is a cluster of proteins that transfer electrons through a membrane within mitochondria to form a gradient of protons that drives the creation of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). ATP is used by the cell as the energy for metabolic processes for cellular functions. Electron Transport Chain Steps Explained with Diagram. The electron transport chain is an essential metabolic pathway that produces energy by carrying out a series of redox reactions. This BiologyWise article provides a simple explanation of this pathway.
The electron transport chain is the last stage of the respiration pathway and is the stage that produces the most ATP molecules. The electron transport chain is a collection of proteins found on ... Electron Transport Chain ATP ATP Name_____ Class_____ Date_____ Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration Section 9–1 Chemical Pathways(pages 221–225) This section explains what cellular respiration is. It also describes what happens during a process called glycolysis and describes two types of a ... Name:_____&& Date:_____& Cellular&Respiration&Review& & 2 Write(the(complete(overall(chemical(equation(for(cellular(respiration(using(chemical(symbols(instead(of The mitochondrial electron transport chain is composed of three main membrane-associated electron carriers flavoproteins (FMN, FAD), cytochromes, and quinones (coenzyme Q, also known as ubiquinone because it is a ubiquitous quinone in biological systems). All these electron carriers reside within the inner membrane of the mitochondria and ...
Paul Andersen covers the processes of aerobic and anaerobic cellular respiration. He starts with a brief description of the two processes. He then describe... Jun 08, 2021 · Electron Transport Chain Definition. The Electron Transport System also called the Electron Transport Chain, is a chain of reactions that converts redox energy available from oxidation of NADH and FADH 2, into proton-motive force which is used to synthesize ATP through conformational changes in the ATP synthase complex through a process called … Nov 05, 2021 · The electron transport chain is the final stage in cellular respiration. It occurs on the inner mitochondrial membrane and consists of several electron carriers. The purpose of the electron transport chain is to form a gradient of protons that produces ATP. Electron transport is defined as a series of redox reaction that is similar to the relay race. It is a part of aerobic respiration. It is the only phase in glucose metabolism that makes use of atmospheric oxygen. When electrons are passed from one component to another until the end of the chain the electrons reduce molecular oxygen thus ...
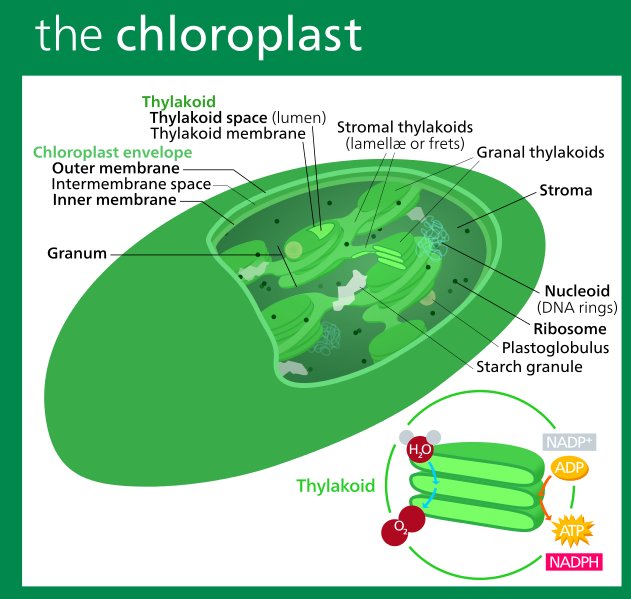
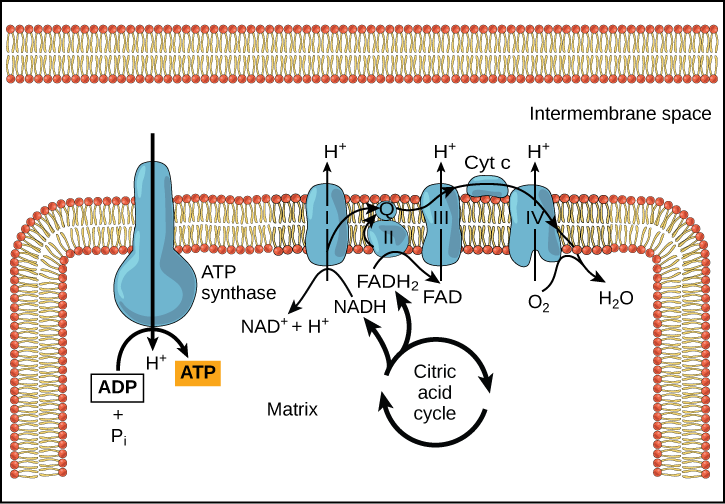
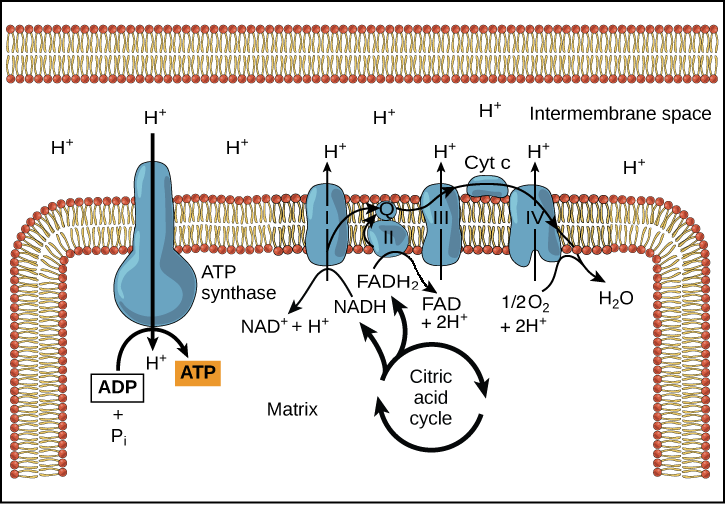
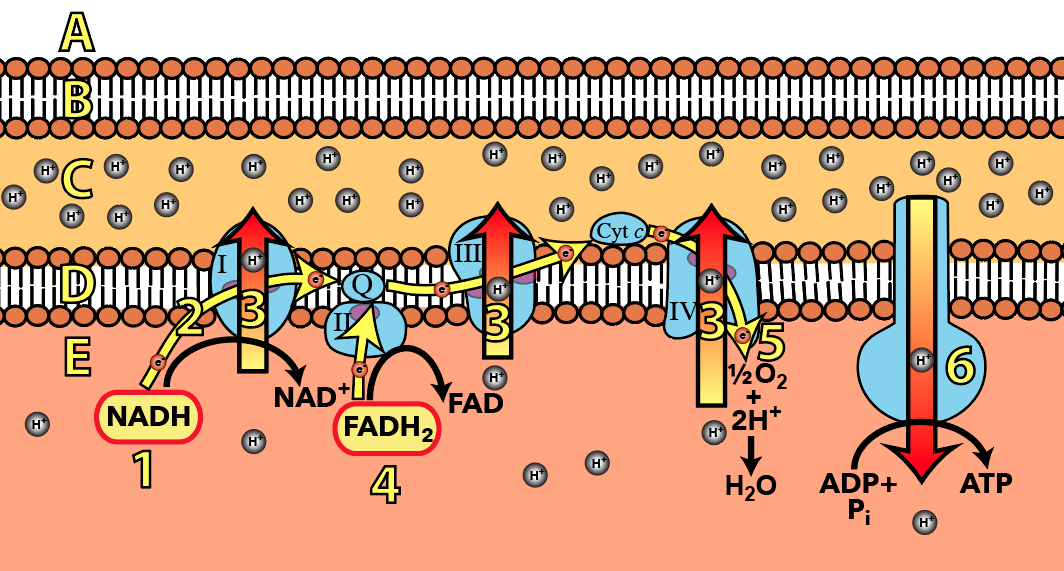
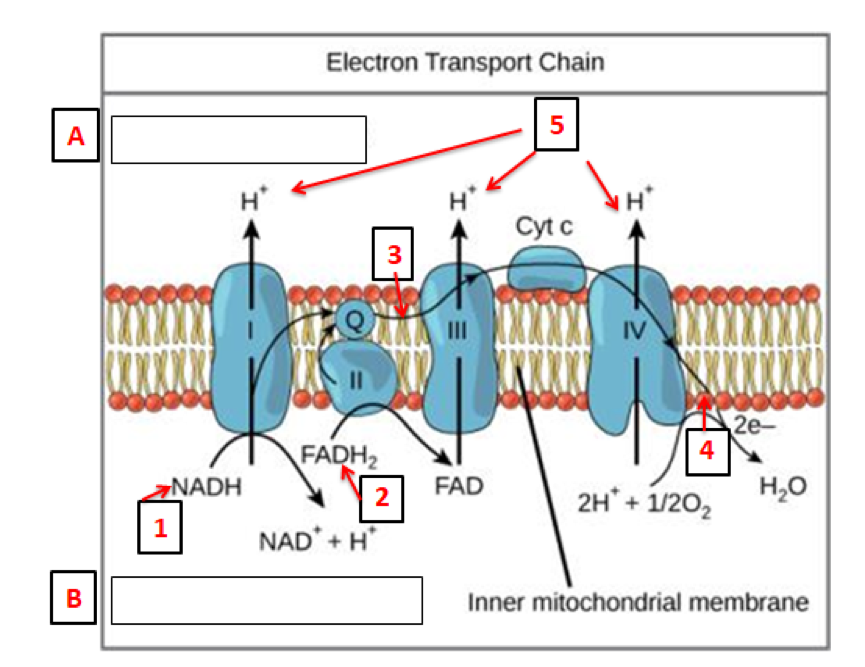
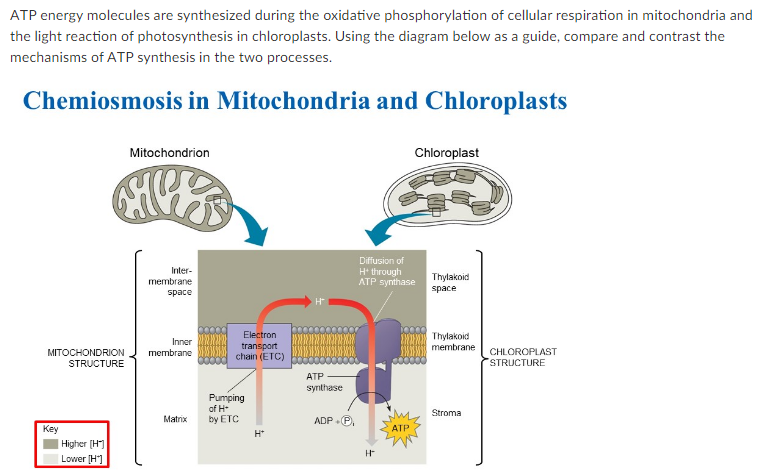
Label the steps of electron transport leading to oxidative phosphorylation where ATP is synthesized from ADP using the energy stored by the electron-transport chain. Energy is required to move electrons and protons into the intermembrane space, and this energy is released when the protons move back into the matrix through ATP synthase.
More About Cellular Respiration So now we know that cellular respiration is a three stage process that converts glucose and oxygen to ATP and releases carbon dioxide and water. What are the 3 phases that do this? 1) Glycolysis 2) Krebs Cycle 3) The Electron Transport Chain (ETC) This is a very simple overview of these 3 stages: Glycolysis (Stage 1)
ADVERTISEMENTS: The electron transport chains of bacteria (prokaryotes) operate in plasma membrane (mitochondria are absent in prokaryotes). Some bacterial electron transport chains resemble the mitochondrial electron transport chain. Paracoccus denitrificans is a gram-negative, facultative anaerobic soil bacterium. It is a model prokaryote for studies of respiration. When this bacterium grows ...
Dec 07, 2021 · Cellular Respiration Equation: Every machine needs specific parts and fuel in order to function. Likewise, “biological machines” also require well engineered parts and good energy source in order to work.Perhaps the second most important molecule (DNA is the first) is adenosine triphosphate (also known as ATP).Basically, ATP serves as the main energy …















0 Response to "38 cellular respiration electron transport chain diagram"
Post a Comment