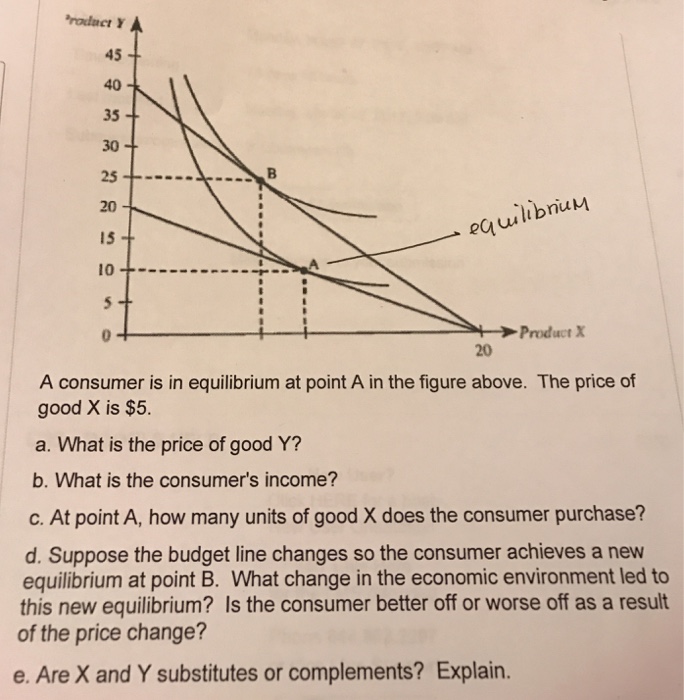
38 a consumer is in equilibrium at point a in the diagram below. the price of good x is $5.
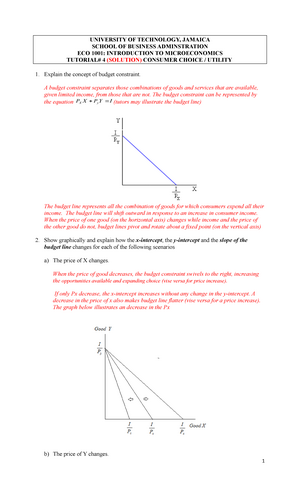
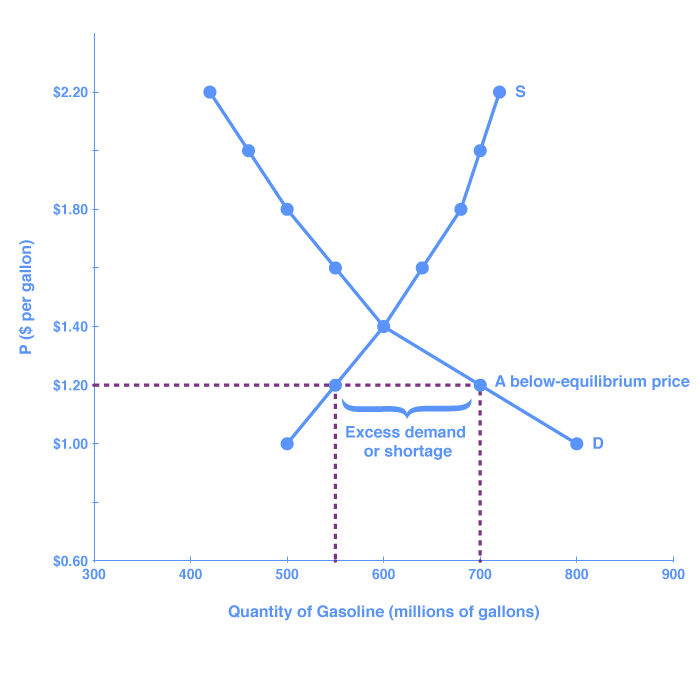
At a price below the equilibrium, there is a tendency for the price to rise. Figure 3.7 The Determination of Equilibrium Price and Quantity When we combine the demand and supply curves for a good in a single graph, the point at which they intersect identifies the equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity. It can be seen from the given diagrams that Figure B is derived from Figure A. In figure A, initially, consumer equilibrium is attained at point E, where MU (10) = Price (10). Corresponding to point E, we derive point E 1 in figure B. Due to fall in price (suppose from 10 to 8), MU > Price at the given quantity.
5. A consumer will start buying less of good-X and more of Good-Y, when: (a) MUx/Px = MUm (b) MUx/PxMUy/Py 6. According to IC approach, at the point of equilibrium: (a) slope of IC > slope of price line (b) slope of IC < slope of price line (c) Slope of IC # slope of price line (d) slope of IC = slope of price ...

A consumer is in equilibrium at point a in the diagram below. the price of good x is $5.
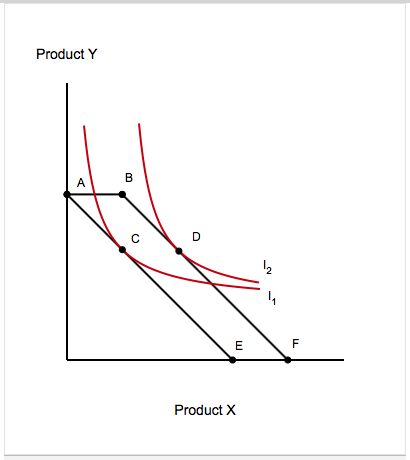
So at point C, all three conditions for the stable-consumer's equilibrium are satisfied. Summing up, the consumer is in equilibrium at point C where the budget line PT is tangent to the indifference IC 2. The market basket OH of good X and OE of good Y yields the greatest satisfaction because it is on the highest attainable indifference curve. good, the price floor should be set below the existing market price of the good. (C) An effective price floor will increase the quantity demanded of the good. (D) The price floor would tend to create a short- age of the good in the market. (E) The creation of the price floor would not change the quantity supplied of the good if the supply curve were upward-sloping to the right. … Apathetic, detached slackers… Generation X — the one that falls between Boomers and Millennials and whose members are born somewhere between 1965 and 1980 — hasn’t always been characterized in the nicest terms. Let’s go over a few of the mo...
A consumer is in equilibrium at point a in the diagram below. the price of good x is $5.. It means, by moving left or right of point E, a consumer can obtain higher amount of either good X or good Y. Thus point E is not an equilibrium point. A consumer will therefore be in equilibrium when at the point of tangency of indifference curve and the budget line, the indifference curve is convex to the origin. Therefore, he reaches the equilibrium at point Q on curve IC 3. Notice that at this point, the budget line PL is tangential to the indifference curve IC 3. Also, in this position, the consumer buys OM quantity of X and ON quantity of Y. Since point Q is the tangent point, the slopes of line PL and curve IC 3 are equal at this point. Further ... The units of commodities are 5. The consumer attains his equilibrium by consuming3 units of the commodity. As by consuming 3 units of commodity the price is equals to the marginal utility i.e. 10. DIAGRAMATIC PRESENTATION. The consumer equilibrium in case of single commodity can be explained with the help of following diagram: CONSUMER EQUILIBRIUM If the pre-tax equilibrium price of Good X was $5 and the price that sellers receive after the imposition of a tax of $3 is $4, the incidence of the taxation on sellers is approximately _____. A) 1% B) 15% C) 33% D) 21%
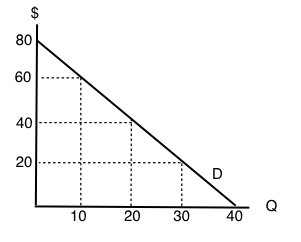
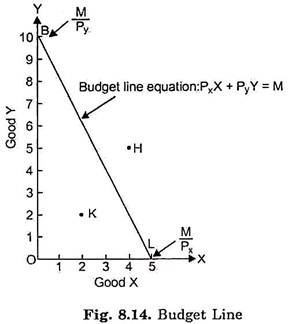
Since these units cost $ 5 each , her income must be $ 100 . c . At point A , the consumer spends ( $ 5 ) ( 10 ) = $ 50 on good Y , which means that the remaining $ 100 - $ 50 = $ 50 is being spent on good X . Since good X costs $ 5 per unit , point A corresponds to 10 units of good X . d . The price of good Y decreased to $ 2.50 . 11.12.2019 ... Get the detailed answer: A consumer is in equilibrium at point A in the diagram below. The price of good X is $5. A. What is the price of ... refer to the diagram. the budget line shift that moves the consumer's equilibrium from point A to point B suggests: that X is an inferior good. all of the following would reduce property crime by increasing its "price" except: A consumer is in equilibrium at point A in the accompanying figure. The price of good X is $5.. a. What is the price of good Y? b. What is the consumer's income? c. At point A, how many units of good X does the consumer purchase? d. Suppose the budget line changes so that the consumer achieves a new equilibrium at point B. What change in the economic environment led to this new equilibrium?
In the diagram below, a consumer maximizes utility by choosing point A, given BL1. Suppose that both good x is normal and good y is inferior, and the budget ... An example of a price level is the consumer price index ... The price-setting real wage at point A is 1.5 as we calculated above, and is shown in the lower panel. A characteristic of this model is that whatever the level of output and employment, the profit margin is 0.5. This implies that the price-determined real wage does not vary with employment and we therefore label the … At the current market equilibrium, the price of a good equals $40 and the quantity equals 10 units. At this equilibrium, the price elasticity of supply is … (2) ICC 2 is horizontal from point A, X is a normal good while У is a necessity of which Fig. 23 the consumer does not want to have more than the usual quantity as his income increases further. (3) ICC 1 is vertical from A, Y is a normal good here and X is satiated necessity; (4) ICC 4 is negatively inclined downwards, У becomes an inferior good form A onwards and X is a superior good; and
Nash Equilibrium Questions and Answers. Get help with your Nash equilibrium homework. Access the answers to hundreds of Nash equilibrium questions that are explained in a …
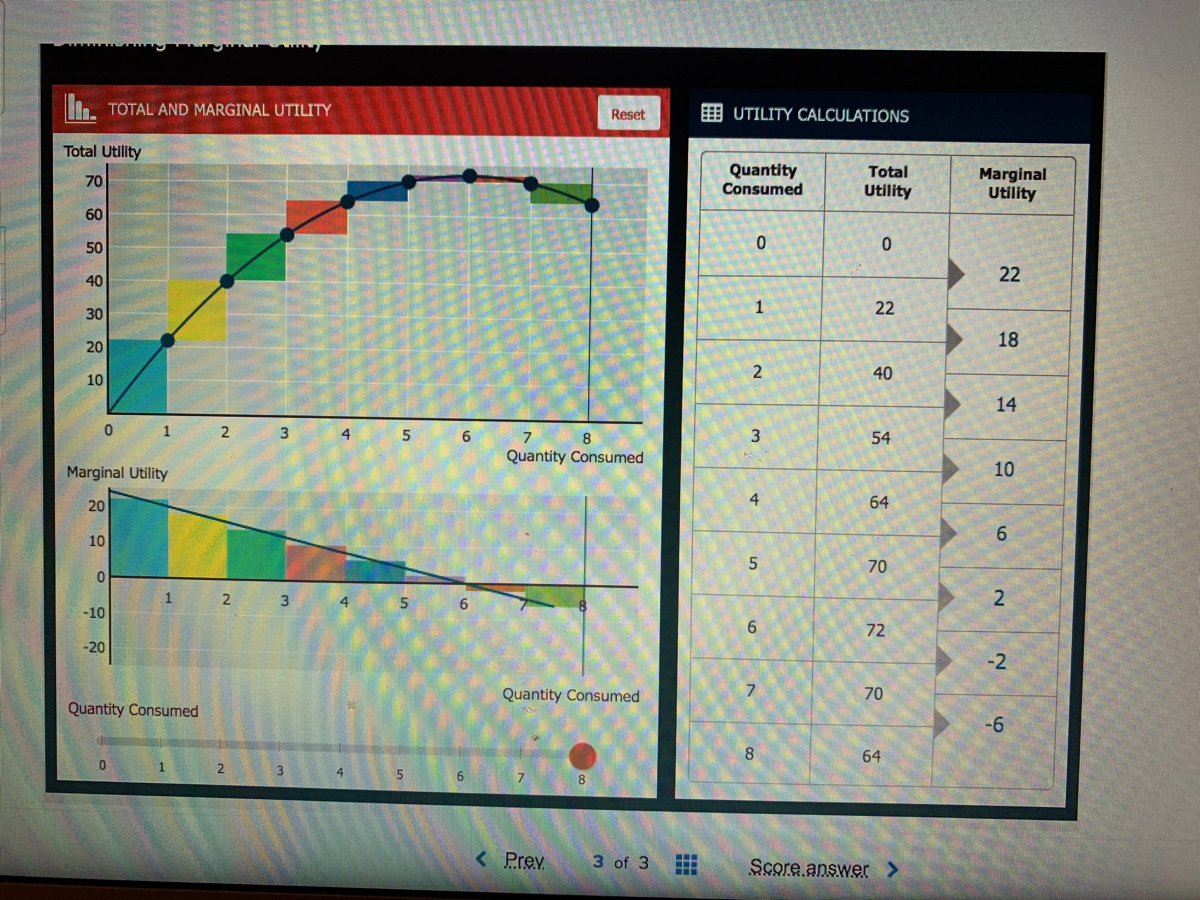
A consumer is said to be in equilibrium when he feels that he "cannot change his condition either by earning more or by spending more or by changing the quantities of thing he buys";. A rational consumer will purchase a commodity up to the point where price of the commodity is equal to the marginal utility obtained from the thing.
Calculate your paper price. Type of paper. Academic level. Deadline . Pages (550 words) − + Approximate price: -Here’s what our customers are saying about our services I have a tight working schedule and was always stuck with my assignments due to my busy schedule but this site has been really helpful. Keep up the good job guys. Michelle W. USA, New York. Your …
3) 4) In the below figure, a consumer is initially in equilibrium at point C. The consumer's income is $400, and the budget line through point C is given by $400 = $100 X + $200 Y. When the consumer is given a $100 gift certificate that is good only at store X, she moves to a new equilibrium at point D. Explanation a. P x = $100, P y = $200 ...
A consumer is in equilibrium at point A in the diagram below. The price of good X is $5. a. What is the price of good Y? $ b. What is the consumer's income? $ c. At point A, how many units of good X does the consumer purchase? units
View Homework Help - Graded HW 2 CH 4.docx from ECN 5150 at University of North Carolina, Pembroke. 1. A consumer is in equilibrium at point A in the diagram below. The price of good X is $5. a. What
Price discrimination is a microeconomic pricing strategy where identical or largely similar goods or services are sold at different prices by the same provider in different markets. Price discrimination is distinguished from product differentiation by the more substantial difference in production cost for the differently priced products involved in the latter strategy.
Class 12th Economics Chapter 5 - Market Competition NCERT Solution is given below. Question 1. Explain market equilibrium. Answer Market Equilibrium is a situation where the quantity demanded becomes equal to quantity supplied, corresponding to a particular price. It means Market demand = Market supply.
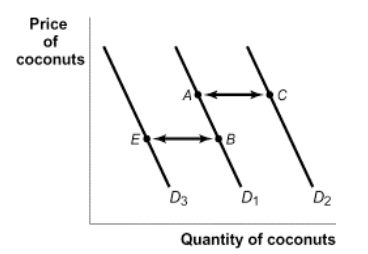
A. move from point x to point y. B. shift from D1 to D2. C. shift from D2 to D1. D. move from point y to point x. C. Refer to the diagram. A decrease in quantity demanded is depicted by a: A. move from point x to point y. B. shift from D1 to D2. C. shift from D2 to D1. D. move from point y to point x. D. In moving along a demand curve, which of the following is not held constant? A. …
21.01.2021 ... The price of good X is $5. a.... 1 answer below ». A consumer is in equilibrium at point A in the accompanying figure. The price ...
If the price ceiling of $40 per ticket is below the equilibrium price, then quantity demanded exceeds quantity supplied, so there will be a shortage of tickets. The policy decreases the number of people who attend classical music concerts, since the quantity supplied is lower because of the lower price. 2. a. The imposition of a binding price floor in the cheese market is shown in …
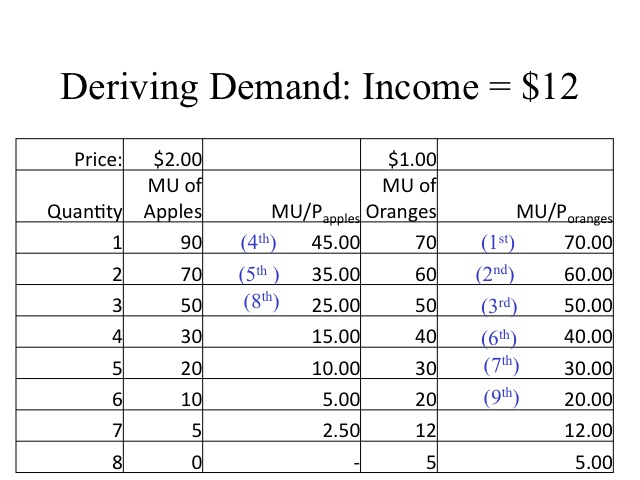
A consumer consumes only two goods X and Y and is in equilibrium. Show that when the price of good X rises, the consumer buys less of good X. Use utility analysis. [AI 2014] Answer: As, we know condition for consumer equilibrium is, Necessary Condition Marginal utility of last rupee spend on each commodity is same.
A consumer is in equilibrium at point A in the diagram below. The price of good X is $5. a. What is the price of good Y?$ b. What is the consumer's income?$ c. At point A, how many units of good X does the consumer purchase? d. Suppose the budget line changes so that the consumer achieves a new equilibrium at point B.
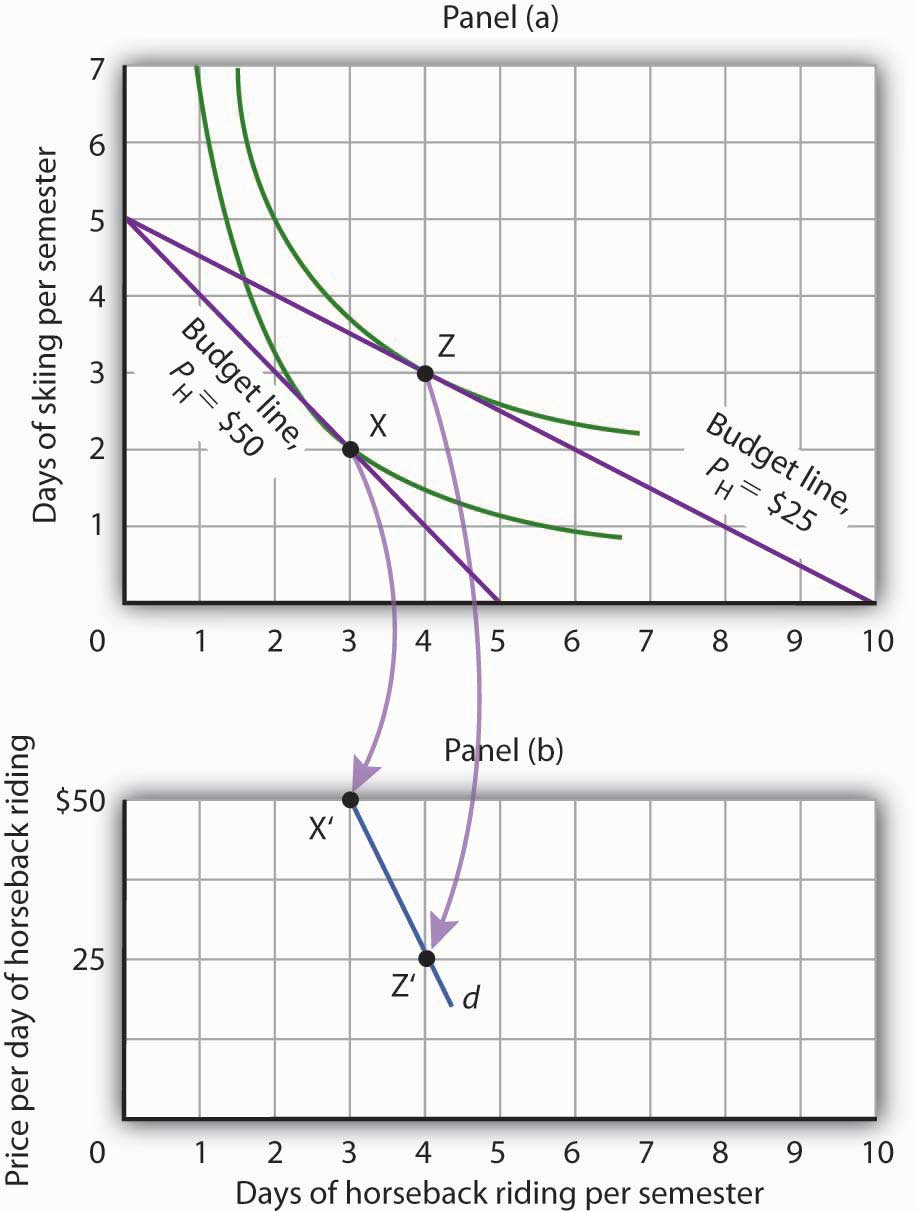
where P X and P Y are the prices of goods X and Y and Q X and Q Y are the quantities of goods X and Y chosen. The total income available to spend on the two goods is B, the consumer's budget.Equation 7.7 states that total expenditures on goods X and Y (the left-hand side of the equation) cannot exceed B.. Suppose a college student, Janet Bain, enjoys skiing and horseback riding.
Suppose the equilibrium price of good X is $10 and the equilibrium quantity is 60 units. If the price of good X is $4: a) The quantity demanded will be less than 60 units. b) The quantity supplied will be more than 60 units. c) There will be an excess demand for good X. d) There will be an excess supply of good X. 14.
And also budget line touches x-axis at point (20,0). It means that if consumer is spending all his income on good X he is able to buy 20 units of good X. It is …. View the full answer. Transcribed image text: A consumer is in equilibrium at point A in the diagram below. The price of good X is $5. Good Y 45 40 35 30-1 B 25 20 15 10 5 - 0 20 ...
Xacuti, xiaolongbao, ximenia, xoconostle and xpinec are just some of the foods that begin with the letter “X.” Because so few words begin with the letter “X” in English, all of these foods come from countries outside the United States. Xacu...
The price of good X is $5. a) What is the price of good Y? b) What is the consumer's income? c) At point A, how many units ...
A consumer is in equilibrium at point A in the diagram below. The price of good X is $5. ... Suppose the budget line changes so that the consumer achieves a new equilibrium at point B. What change in the economic environment led to this new equilibrium? The price of good Y decreased to $2.50. The price of good Y increased to $10.
When the price of good X is Px0, the consumer consumes X0 units of good X; when the price falls to P1x, the consumption of X increases to X1. This relationship between the price of good X and the quantity consumed of good X is graphed in Figure 4-20(b) and is the individual consumer's demand curve for good X.
A consumer must divide $250 between the consumption of product X and product Y. The relevant market prices are Px = $5 and Py = $10.a. Write the equation for the consumer’s budget line.b. Illustrate the consumer’s opportunity set in a carefully labeled diagram.c. Show how the consumer’s... View Answer.
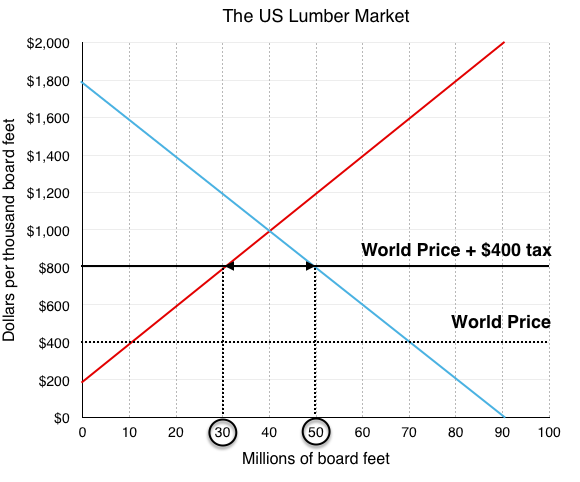
So, if the price is above the equilibrium level, incentives built into the structure of demand and supply will create pressures for the price to fall toward the equilibrium. Now suppose that the price is below its equilibrium level at $1.20 per gallon, as the dashed horizontal line at this price in Figure 3 shows.
a) The income of consumers who buy good X. b) The cost of labor used to produce ... The diagram below illustrates 3 possible demand curves for coconuts.
If you’re trying to figure out what x squared plus x squared equals, you may wonder why there are letters in a math problem. That’s because, in the case of an equation like this, x can be whatever you want it to be. To find out what x squar...
A consumer is in equilibrium and is spending income in such a way that the marginal utility of product X is 40 units and that of Y is 16 units. If the unit price of X is $5, then the price of Y must beA) $1 per unit. B) $2 per unit. C) $3 per unit. D) $4 per unit.
A consumer attains equilibrium at such level where marginal utility derived from the consumption of a commodity is equal to its one unit price. Marginal utility is the change in the total utility of a commodity. It is expressed as MU = TUn+1 - TUn. Here, MU stands for Marginal Utility. TU stands for Total utility.
The price of good X is $5. a. What is the price of good Y if the price of good x is $ 5 at equilibrium, Price of good Y would be $5. b. What is the consumer's income? X= m/p x The price of good X 1 P x =$5 and the maximum affordable quantity of good X is 20 units so 20= M/$5 so M = $100 which is the consumers income. c.
A consumer is in equilibrium at point A in the diagram below. The price of good X is $5. A. What is the price of good Y? $_____ B. What is the consumer's income? $_____ C. At point A, how many units of good X does the consumer purchase? _____ units. D. Suppose the budget line changes so that the consumer achieves a new equilibrium at point B.
8 In the diagram below D1 and S1 represent the demand and supply curves of a Malaysian industry in its home market. Equilibrium is at X. ... 12 In the diagram, point X shows the equilibrium price and quantity for a fruit drink. ... The table shows the quantity of the good demanded by consumer X and the market supply of the good.
Apathetic, detached slackers… Generation X — the one that falls between Boomers and Millennials and whose members are born somewhere between 1965 and 1980 — hasn’t always been characterized in the nicest terms. Let’s go over a few of the mo...
good, the price floor should be set below the existing market price of the good. (C) An effective price floor will increase the quantity demanded of the good. (D) The price floor would tend to create a short- age of the good in the market. (E) The creation of the price floor would not change the quantity supplied of the good if the supply curve were upward-sloping to the right. …
So at point C, all three conditions for the stable-consumer's equilibrium are satisfied. Summing up, the consumer is in equilibrium at point C where the budget line PT is tangent to the indifference IC 2. The market basket OH of good X and OE of good Y yields the greatest satisfaction because it is on the highest attainable indifference curve.



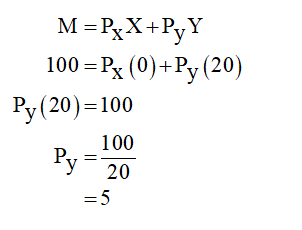

![ECON EXAM 1 [QUIZZES] Flashcards | Quizlet](https://quizlet.com/cdn-cgi/image/f=auto,fit=cover,h=200,onerror=redirect,w=240/https://o.quizlet.com/xcoEr2wnaRTdEudW2qSO1A.png)






![ECON EXAM 1 [QUIZZES] Flashcards | Quizlet](https://quizlet.com/cdn-cgi/image/f=auto,fit=cover,h=200,onerror=redirect,w=240/https://o.quizlet.com/kdUI8o7eSPwlP98qzu4hLQ.png)



0 Response to "38 a consumer is in equilibrium at point a in the diagram below. the price of good x is $5."
Post a Comment