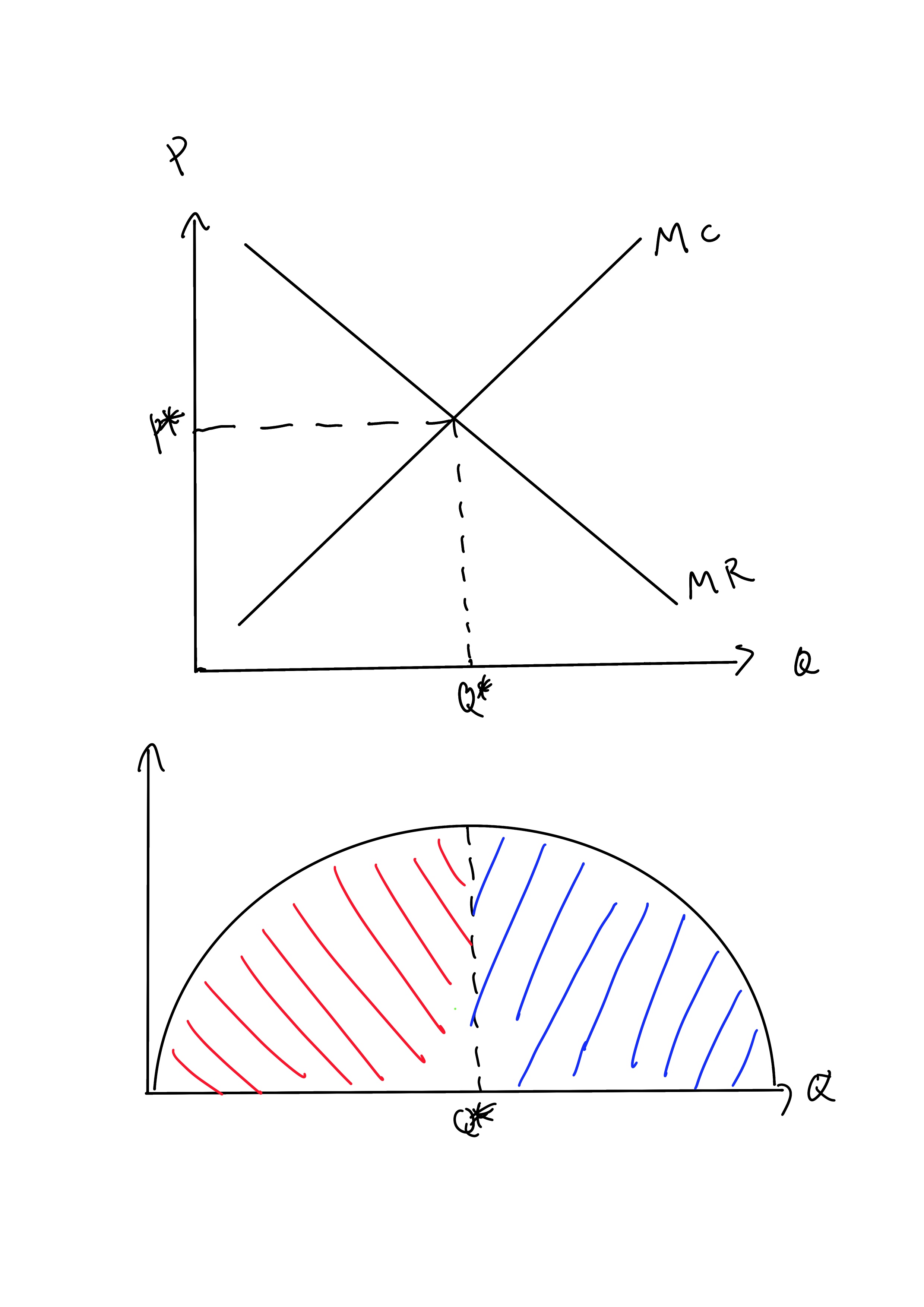
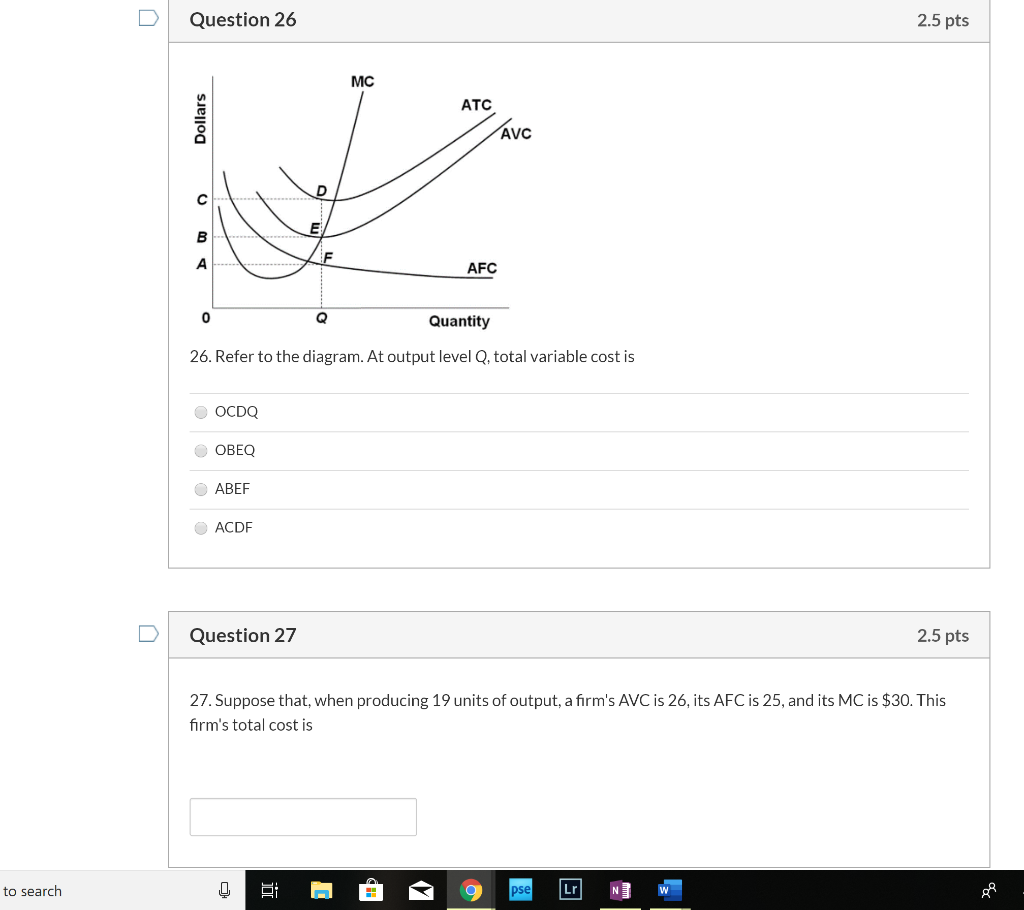
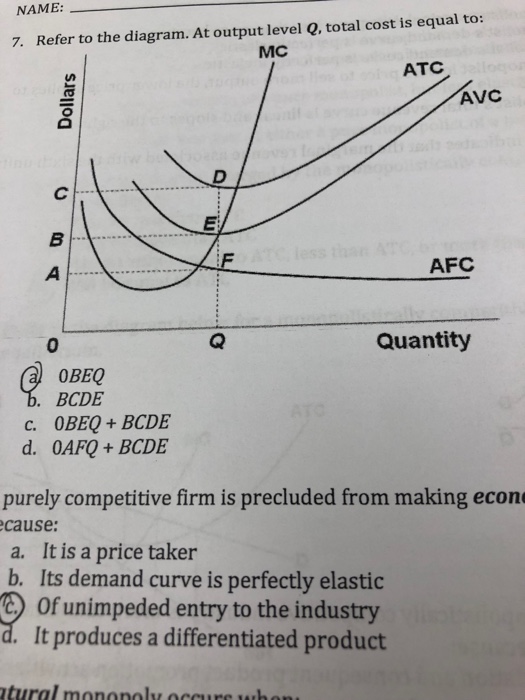
40 refer to the diagram. by producing at output level q,
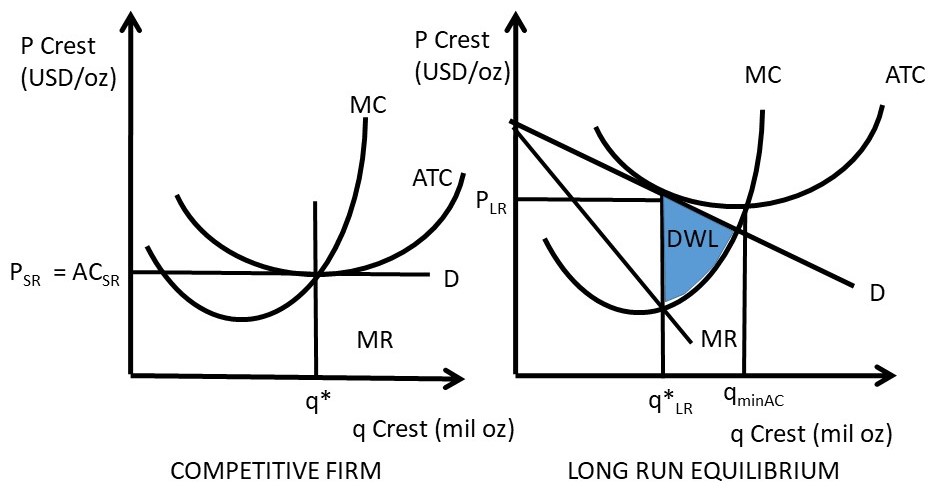
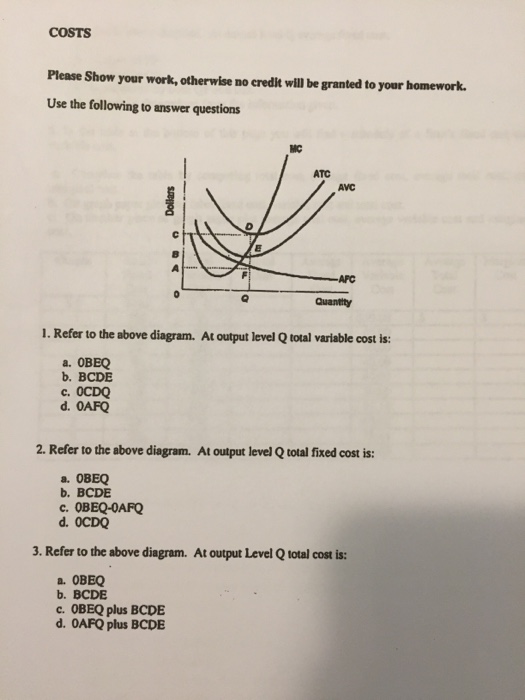
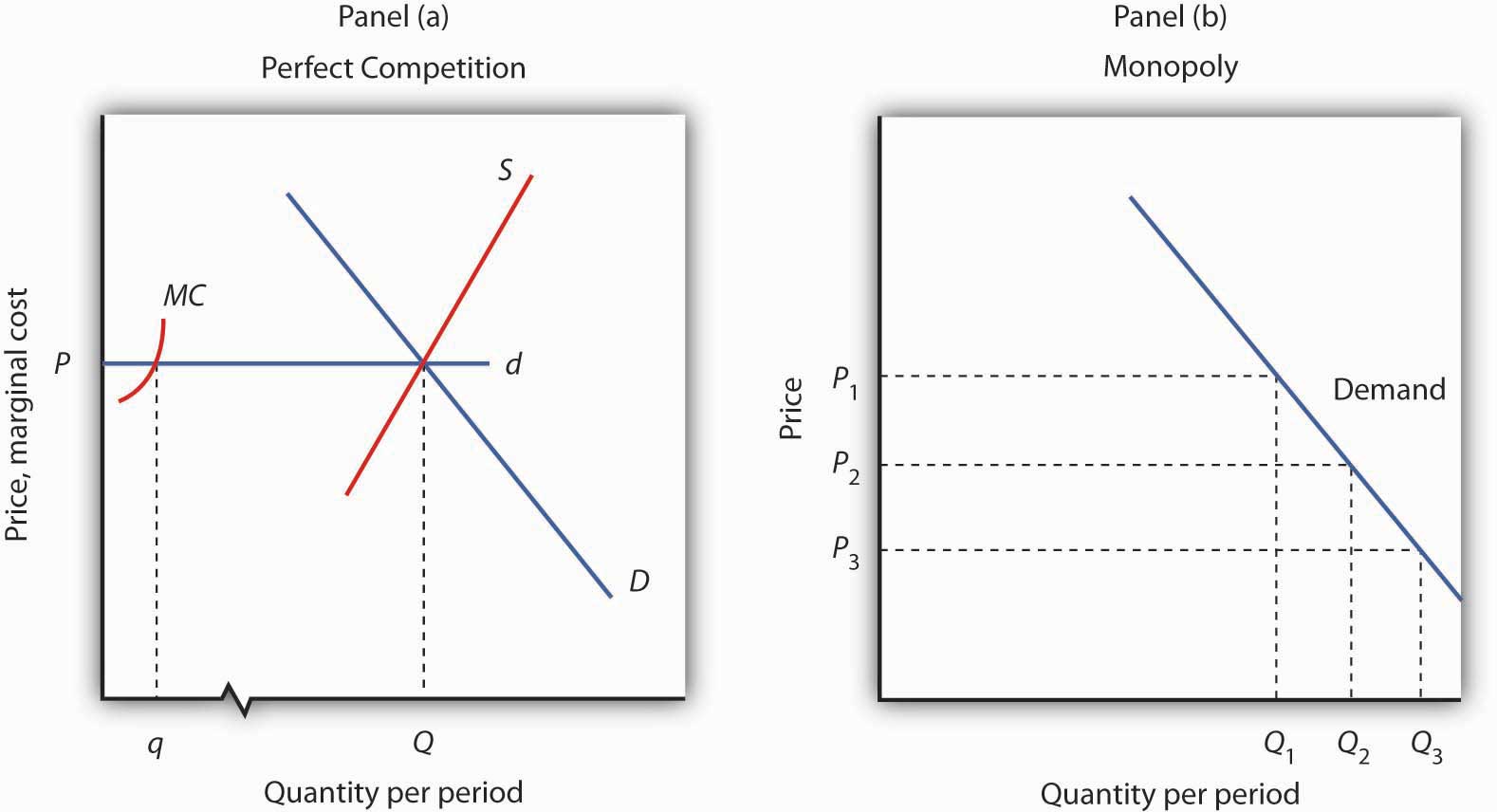
Use the... - Martinsville Indiana Computer Repair - Facebook 197. Refer to the above diagram. If this competitive firm produces output Q, it will: A) suffer an economic loss. B) earn a normal profit. C) earn an economic profit. D) achieve productive efficiency, but not allocative efficiency. Answer: B. Type: G Topic: 5 E: 433 MI: 189 198. Refer to the above diagram. By producing output level Q: Refer to the above diagram At output level Q total cost is ... C is the correct answer. . 22. Refer to the above diagram. At output level Q average 24. Refer to the above diagram. The vertical distance between ATC and AVC reflects: A) the law of diminishing returns. B) the average fixed cost at each level of output. C) marginal cost at each level of output. D) the presence of economies of scale.
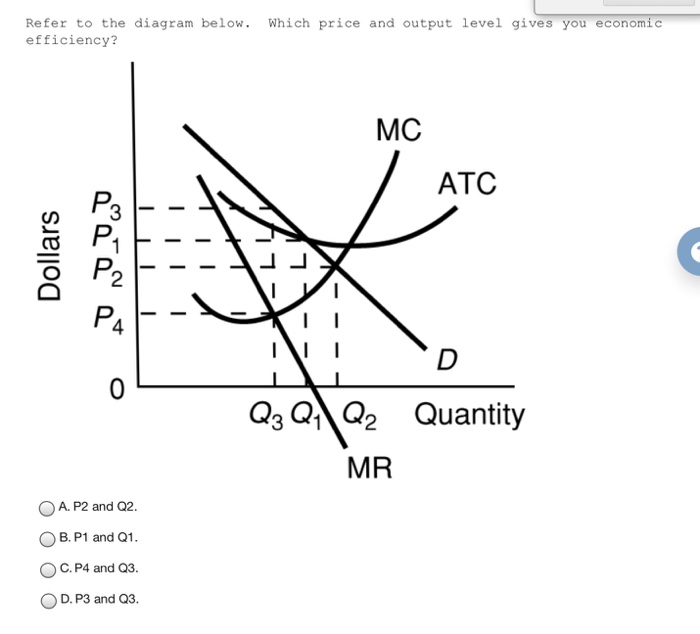
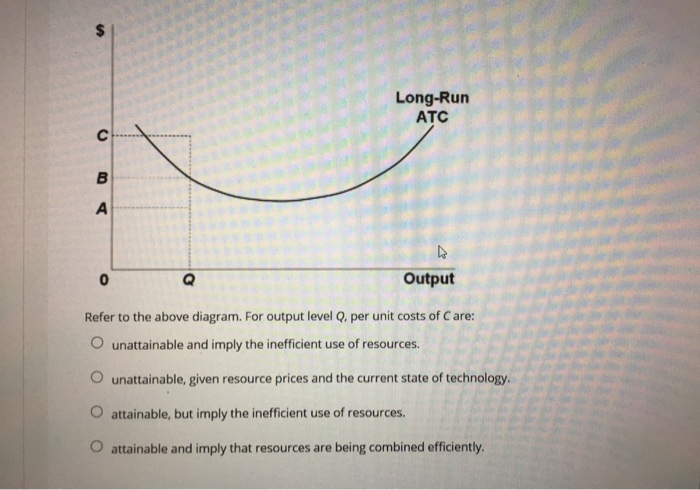
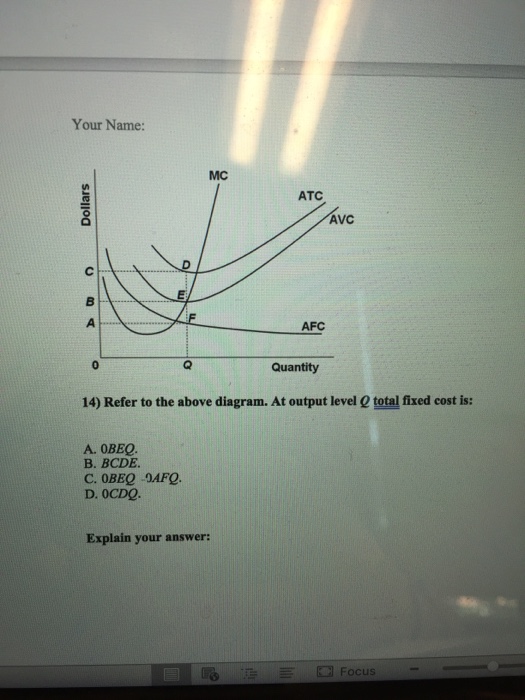
Refer to the above diagram For output level Q per unit ... Refer to the above diagram. For output level Q , per unit costs of B are: A. unattainable and imply the inefficient use of resources. B. unattainable, given resource prices and the current state of technology. C. attainable, but imply the inefficient use of resources. D. attainable and imply least-cost production of this level of output.
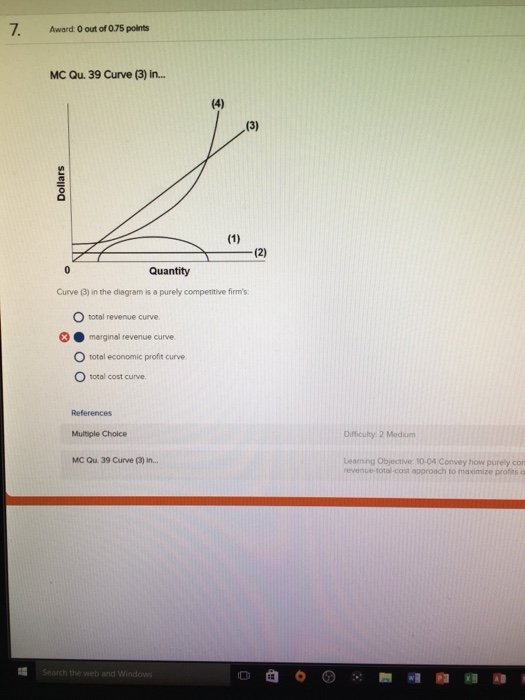
Refer to the diagram. by producing at output level q,
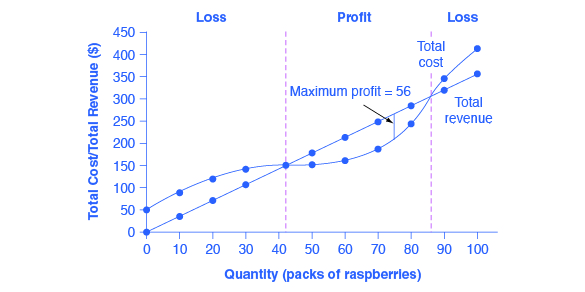
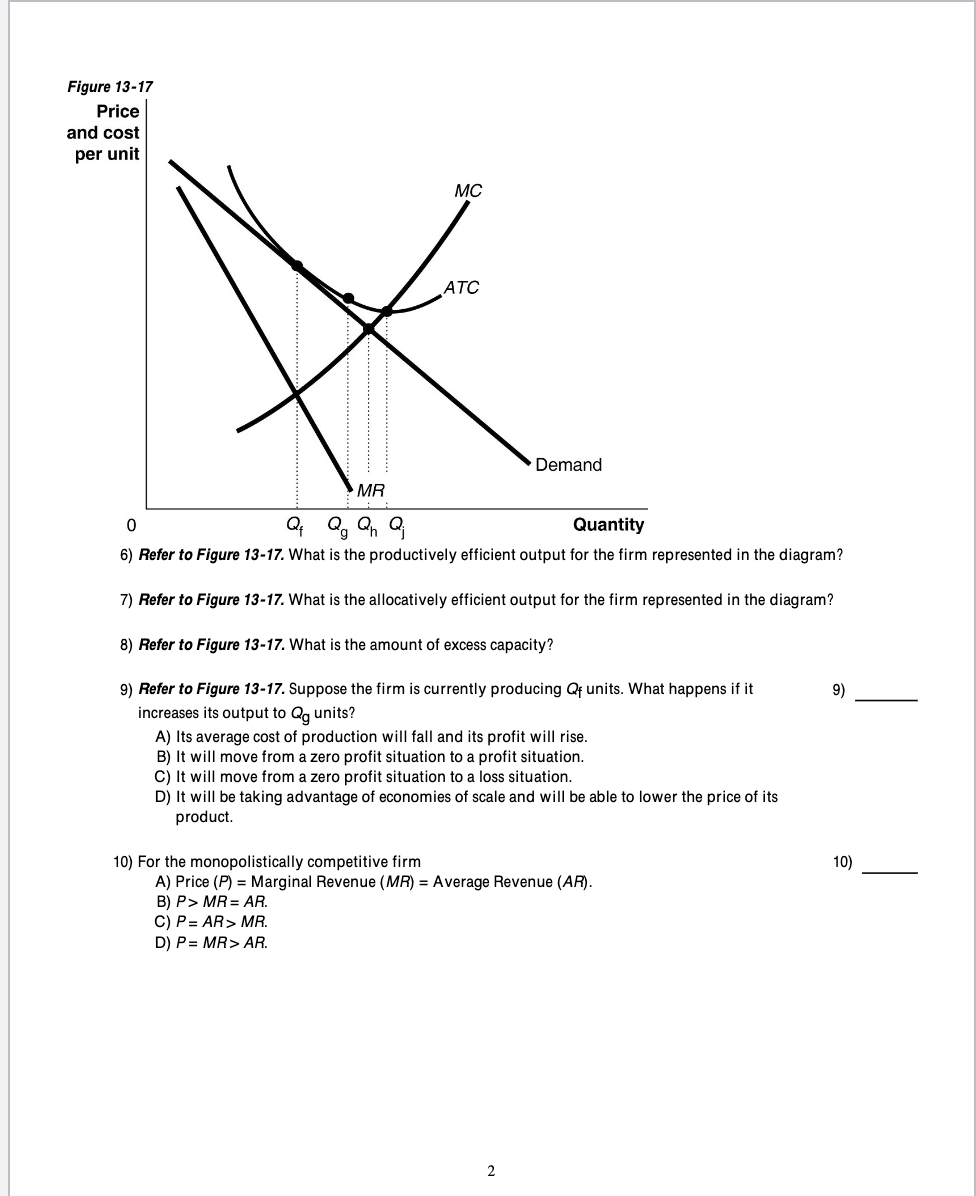
Answered: Refer to the diagram to the right.… | bartleby Refer to the diagram to the right. Suppose the firm is currently producing Q, units. What happens if it expands output to Q, units? TC TR O A. It incurs a loss. O B. It will be moving toward its profit maximizing output. Oc. It makes less profit. O D. Its profit increases by the size of the vertical distance df. a 1,000 Qo Q, Q2 Q3 Quantity d Solved MC 3 ATC 0 MR Q, Qa2 Quantity Refer to the diagram ... Transcribed image text: MC 3 ATC 0 MR Q, Qa2 Quantity Refer to the diagram. By producing at output level Q O productive efficiency is achieved. but allocative efficiency ls not. D neither productive nor allocetive etficiency s achieved O aflocative efficiency is achieved, but productive efficiency is not O both productive and allocative ... PDF Chapter 8 Profit Maximization and Competitive Supply 60 = 2Q, or Q = 30. b. What will the profit level be? Profit is equal to total revenue minus total cost: π = (60)(30) - (100 + 302) = $800. c. At what minimum price will the firm produce a positive output? A firm will produce in the short run if the revenues it receives are greater than its variable costs.
Refer to the diagram. by producing at output level q,. ECO 211 Microeconomics Yellow Pages ANSWERS Unit 3 3. Refer to the above diagram. To maximize profit or minimize losses this firm will produce: 1. K units at price C. 2. D units at price J. 3. E units at price A. 4. E units at price B. 4. Refer to the above diagram. At the profit-maximizing output, total revenue will be: 1. 0AHE. 2. 0BGE. 3. 0CFE. 4. ABGE. 5. Refer to the above diagram. Chapters 6, 7, 8 - Microeconomics Quiz questions - StuDocu 15) Refer to the Figure above. The diagram above contains __ cost curves. A) short run B) intermediate run C) long run D) both short run and long run. Answer: A. 16) Refer to the Figure above. At output level Q A) average fixed cost is increasing. B) average variable cost equals average fixed cost. C) marginal cost is negative. Refer to the above diagram At output level Q total cost is ... 60. Refer to the above diagram. At output level Q: A. marginal product is falling. B. marginal product is rising. C. marginal product is negative. D. one cannot determine whether marginal product is falling or rising. Chapter 11 | Business Quiz - Quizizz Q. The primary force encouraging the entry of new firms into a purely competitive industry is answer choices normal profits earned by firms already in the industry. economic profits earned by firms already in the industry. government subsidies for start-up firms. a desire to provide goods for the betterment of society. Question 2 120 seconds Q.
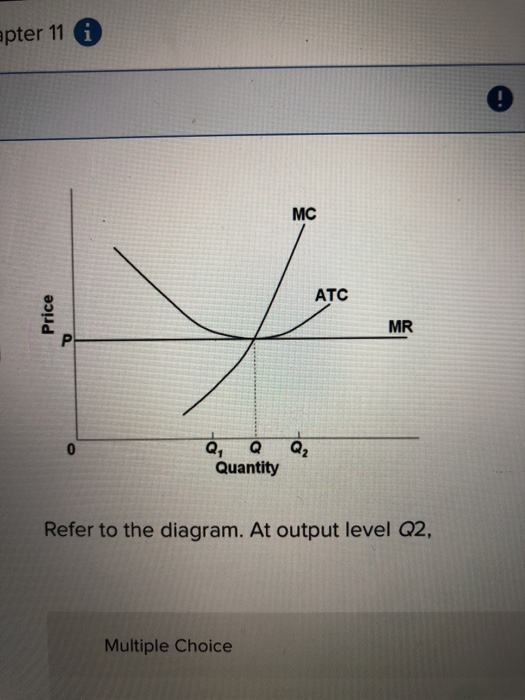
DOC Chapter 9: Four Market Models Economists use the term imperfect competition to describe: 1. all industries which produce standardized products. 2. any industry in which there is no nonprice competition. 3. a pure monopoly only. 4. those markets which are not purely competitive. 5. In which of the following industry structures is the entry of new firms the most difficult? OneClass: Refer to the above diagram. At output level Q, the ... Oct 06, 2020 · Refer to the diagram. By producing at output level Q. A. productive efficiency is achieved but allocative efficiency ls not. B. neither productive nor allocative efficiency is achieved. C. allocative efficiency is achieved, but productive efficiency is not. D. both productive and allocative efficiency is achieved. DOC Microeconomics, 7e (Pindyck/Rubinfeld) 35) Refer to Figure 7.1. At output level Q1 . A) marginal cost is falling. B) average total cost is falling. C) average variable cost is less than average fixed cost. D) marginal cost is less than average total cost. E) all of the above . Answer: E. Diff: 2. Section: 7.2. 36) Refer to Figure 7.1. At output level Q2 . A) average fixed cost is ... Chapter 11 ND 12 Flashcards - Quizlet The long-run supply curve for a purely competitive increasing-cost industry will be upsloping. 11. A constant-cost industry is one in which: if 100 units can be produced for $100, then 150 can be produced for $150, 200 for $200, and so forth. 12.
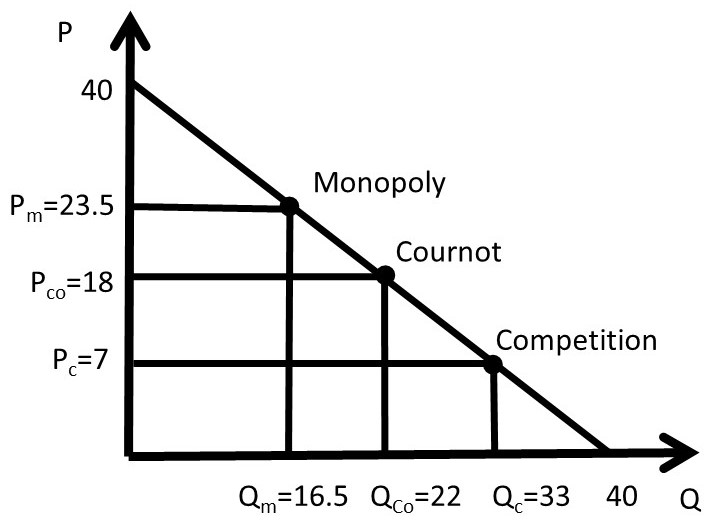
ECON 202 Blanchard Exam 2 - Subjecto.com ECON 202 Blanchard Exam 2 - Subjecto.com ECON 202 Blanchard Exam 2 Looking for Expert Opinion? Let us have a look at your work and suggest how to improve it! Get a Consultant « Previous Flashcard Next Flashcard » Like the Tone? PDF AP Unit 6 60. Refer to the above diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. At output Q production will be unprofitable. True False 61. Refer to the above diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. The profit-maximizing price for this firm is J. True False 62. Refer to the above diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. At output M total variable ... 5.1 Externalities - Principles of Microeconomics Consider our diagram of a negative externality again. Let's pick an arbitrary value that is less than Q 1 (our optimal market equilibrium). Consider Q 2.. Figure 5.1b. If we were to calculate market surplus, we would find that market surplus is lower at Q 2 than at Q 1 by triangle e.. The market surplus at Q 2 is equal to area a+b. [(a+b+c) - (c)]. Chapter 11 Study Questions ( Flashcards - Quizlet Refer to the diagram. By producing at output level Q: a. neither productive nor allocative efficiency is achieved. b. both productive and allocative efficiency are achieved. c. allocative efficiency is achieved, but productive efficiency is not. d. productive efficiency is achieved, but allocative efficiency is not.
Refer to the diagram. By producing at output level Q - OneClass 11 Dec 2019 Refer to the diagram. By producing at output level Q A. productive efficiency is achieved but allocative efficiency ls not. B. neither productive nor allocative efficiency is achieved. C. allocative efficiency is achieved, but productive efficiency is not. D. both productive and allocative efficiency is achieved. Show full question
Microeconomics (ECON-2302) Flashcards | Quizlet Refer to Figure 15-4. If the monopoly firm is currently producing Q3 units of output, then a decrease in output will necessarily cause profit to ~ decrease. ~ increase as long as the new level of output is at least Q2. ~ remain unchanged. ~ increase as long as the new level of output is at least Q1.
Econ Practice 11 Flashcards - Quizlet Gravity 1. Which of the following is true concerning purely competitive industries? Click card to see definition 👆 C. In the short run, firms may incur economic losses or earn economic profits, but in the long run they earn normal profits. Click again to see term 👆 1/20 YOU MIGHT ALSO LIKE... 20 Principles of Microeconomics TextbookMediaPremium
Question 8 of 50 10 Points Refer to the diagram By producing ... Refer to the diagram. By producing at output level Q: A. neither productive nor allocative efficiency is achieved. B. both productive and allocative efficiency are achieved. C. allocative efficiency is achieved, but productive efficiency is not. D. productive efficiency is achieved, but allocative efficiency is not.
Refer to the above diagram At output level Q 1 A neither ... Refer to the above diagram. At output level Q 1 : A. resources are overallocated to this product and productive efficiency is not realized. B. resources are underallocated to this product and productive efficiency is not realized. C. productive efficiency is achieved, but resources are underallocated to this product.
Microeconomics: Trivia Questions On Production ... - ProProfs Scenario 2: The production function for earthquake detectors (Q) is given as follows:Q = 4K 1/2 L 1/2 , where K is the amount of capital employed and L is the amount of labor employed.The price of capital, P K, is $18 and the price of labor, P L, is $2Refer to Scenario 2.Suppose that in order to produce Q=48 detectors 16 units of labor and 9 units of capital were being used.
Microeconomics Midterm 1 Flashcards - Quizlet In the diagram, total product will be a maximum at: A) Q1 units of labor. B) Q3 units of labor. C) Q2 units of labor. D) some point that cannot be determined with the above information. B Other things equal, if the fixed costs of a firm were to increase by $100,000 per year, which of the following would happen?
PDF Chapter 8 Profit Maximization and Competitive Supply 60 = 2Q, or Q = 30. b. What will the profit level be? Profit is equal to total revenue minus total cost: π = (60)(30) - (100 + 302) = $800. c. At what minimum price will the firm produce a positive output? A firm will produce in the short run if the revenues it receives are greater than its variable costs.
Solved MC 3 ATC 0 MR Q, Qa2 Quantity Refer to the diagram ... Transcribed image text: MC 3 ATC 0 MR Q, Qa2 Quantity Refer to the diagram. By producing at output level Q O productive efficiency is achieved. but allocative efficiency ls not. D neither productive nor allocetive etficiency s achieved O aflocative efficiency is achieved, but productive efficiency is not O both productive and allocative ...
Answered: Refer to the diagram to the right.… | bartleby Refer to the diagram to the right. Suppose the firm is currently producing Q, units. What happens if it expands output to Q, units? TC TR O A. It incurs a loss. O B. It will be moving toward its profit maximizing output. Oc. It makes less profit. O D. Its profit increases by the size of the vertical distance df. a 1,000 Qo Q, Q2 Q3 Quantity d



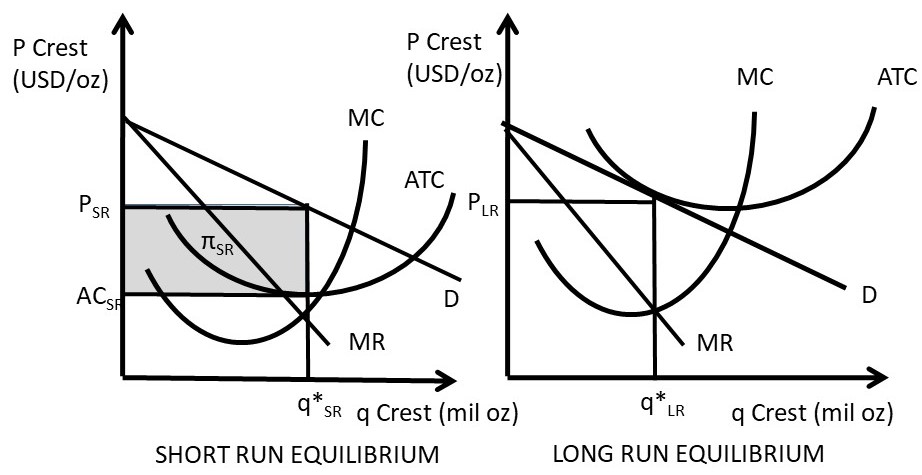


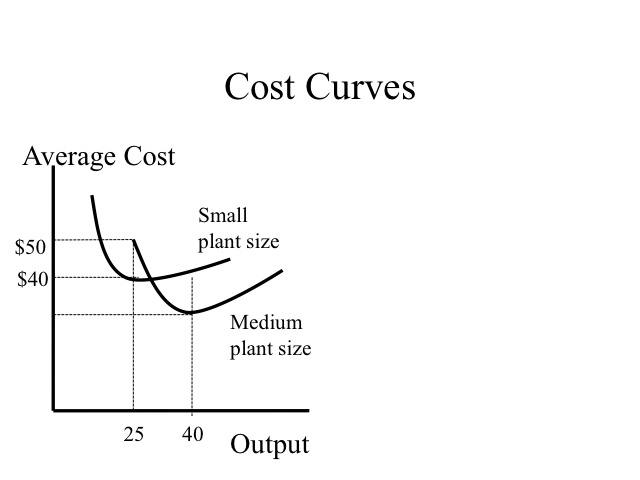










/MinimumEfficientScaleMES2-c9372fffba0a4a1ab4ab0175600afdb6.png)
0 Response to "40 refer to the diagram. by producing at output level q,"
Post a Comment