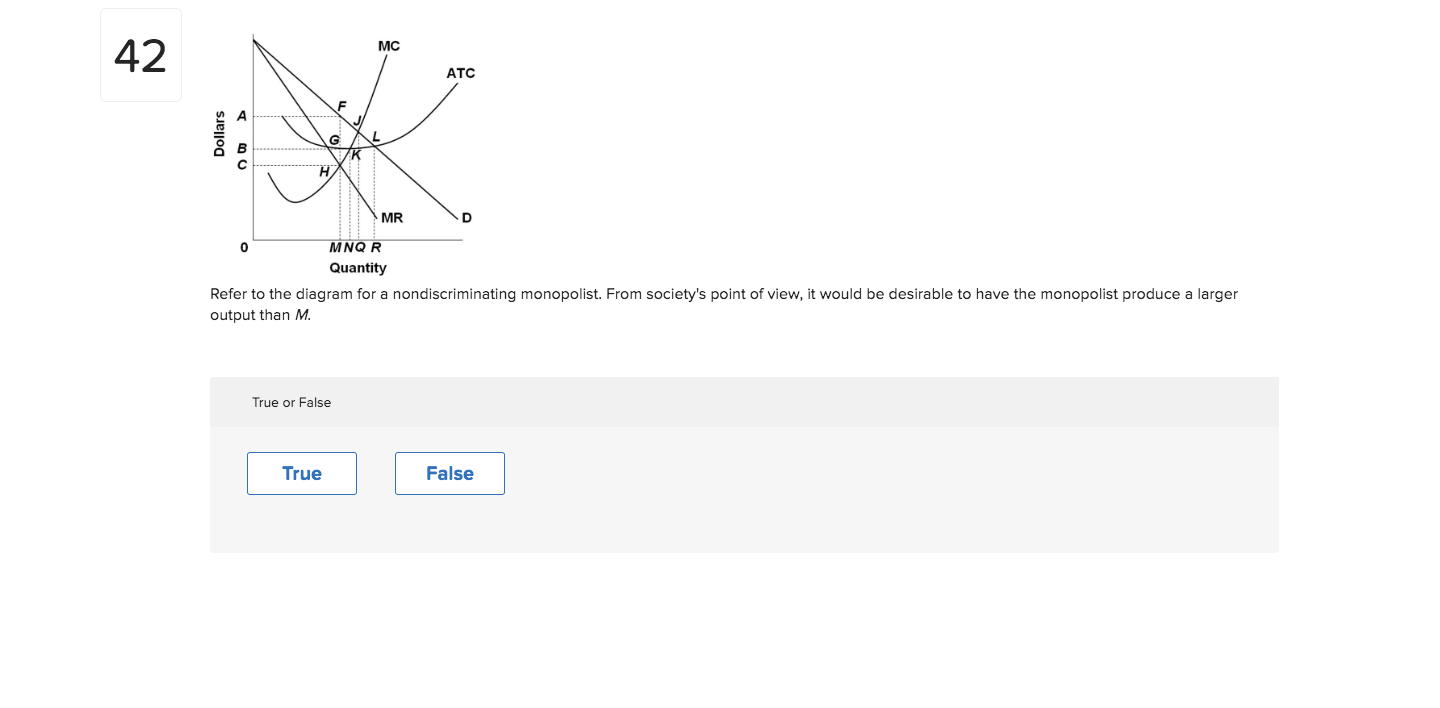
42 refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. the profit-seeking monopolist will
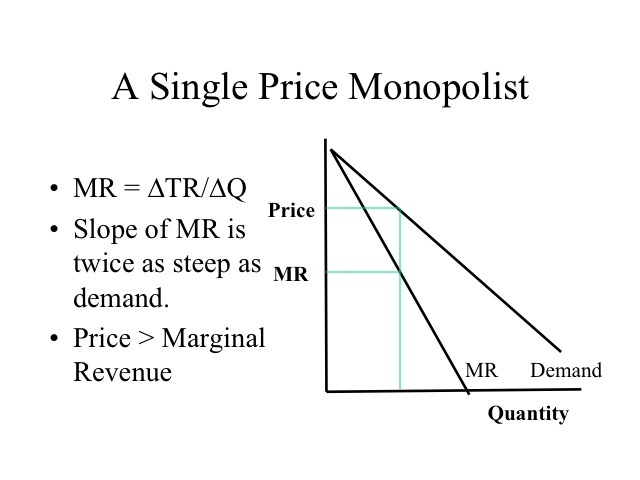
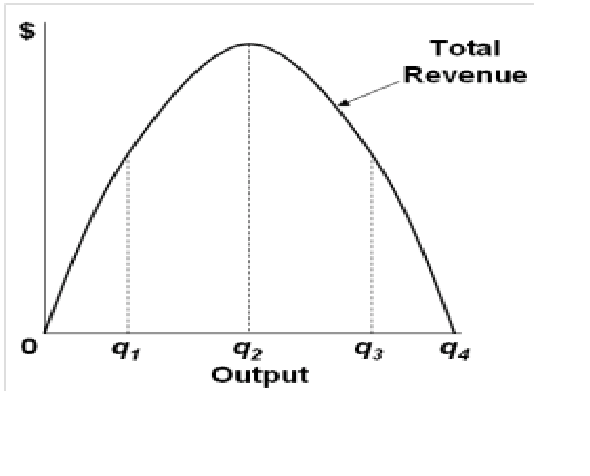
Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. the profit-seeking monopolist will; At its profit-maximizing output, a pure nondiscriminating monopolist achieves; For a pure nondiscriminating monopolist, marginal revenue is less than price because; If a pure monopolist is operating in a range of output where demand is elastic: Refer to ... Monopolist optimizing price: Dead weight loss. AP.MICRO: PRD‑3 (EU) , PRD‑3.B.6 (EK) Transcript. A monopolist might be pretty happy about its extraordinary profits, but these come at a cost for society. In this video we explore the welfare implications of a monopoly market. Created by Sal Khan.
The profit-maximizing output for this firm is M. A. True B. False12: Refer to the above diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. If the government regulates the monopolist so that it charges the socially optimal price, the monopolist will produce output Q. A. True B. False13: Refer to the above diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist.

Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. the profit-seeking monopolist will
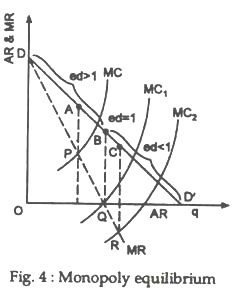
Economics questions and answers. Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. Demand is elastic: Question 41 options: in the q1q3 output range. only for outputs greater than q4. for all levels of output less than q2. for all levels of output greater than q2. Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. The profit-seeking monopolist will: C. never produce an output larger than q 2. 6. Assume a pure monopolist is currently operating at a price-quantity combination on the inelastic segment of its demand curve. If the monopolist is seeking maximum profits, it should: 5. Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. The profit-seeking monopolist will: C. never produce an output larger than q 2. 6. Assume a pure monopolist is currently operating at a price-quantity combination on the inelastic segment of its demand curve. If the monopolist is seeking maximum profits, it should: D. charge a higher ...
Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. the profit-seeking monopolist will. 57. Refer to the above diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. The profit-maximizing output for this firm is M. True False 58. Refer to the above diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. At the profit-maximizing output the firm's economic profit will beBAFG. True False 59. Refer to the above diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. (Supposed to be a graph) Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. The profit-seeking monopolist will a.) always produce at output q2. b.) always produce more than q2. c.) never produce an output larger than q2. d.) never produce an output larger than q1. Refer to the above diagram. If price is reduced from P1 to P2, total revenue will: Answer . decrease by C minus A. increase by A minus C. decrease by A minus C. increase by C minus A. 55) Refer to the above data for a nondiscriminating monopolist. At its profit-maximizing output, this firm's total profit will be: Answer . zero. $27. $82. $54 than with nondiscriminating monopoly; others, a lower price. Good features: greater output and improved allocative efficiency. Bad feature: More income is transferred from consumers to the monopolist. 24-7 Assume a pure monopolist and a purely competitive firm have the same unit costs. Contrast the
53. Refer to the above diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. Marginal revenue will be zero at output: A. q1. B. q2. C. q3. D. q4. 54. Refer to the above diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. The profit-seeking monopolist will: A. always produce at output q2. B. always produce more than q2. C. never produce an output larger than q2. Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. The profit-seeking monopolist will: asked Aug 17, 2018 in Economics by Kaywee. principles-of-economics; If a nondiscriminating pure monopolist decides to sell one more unit of output, the marginal revenue associated with that unit will be: 45. If a nondiscriminating pure monopolist decides to sell one more unit of output, the marginal revenue associated with that unit will be: A. equal to its price. B. the price at which that unit is sold less the price reductions which apply to all other units of output. C. the price at which that unit is sold plus the price increases which apply to all other units of output. In seeking the profit-maximizing output the pure monopolist underallocates resources to its production. Confronted with the same unit cost data, a monopolistic producer will charge: A. the same price and produce the same output as a competitive firm.
Draw a diagram showing the relevant demand, marginal revenue, average total-cost, and marginal cost curves and the equilibrium price and output for a nondiscriminating monopolist. Use the same diagram to show the equilibrium position of a monopolist that is able to practice perfect price discrimination. Refer to the diagram. The profit-maximizing level of output for this firm: ... If a profit-seeking competitive firm is producing its profit-maximizing output and its total fixed costs fall by 25 percent, the firm should: ... realize a smaller economic profit than a nondiscriminating monopolist. The profit seeking monopolist will Never produce an output larger than Q2 In a monopoly the marginal revenue will be lower than… View the full answer Transcribed image text : value: 1.00 points Total Revenue 42 Output 3 94 Refer to the above diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. Type: G Topic: 3 E: 444 MI: 200 54. Refer to the above diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. The profit-seeking monopolist will: A) B) Answer: C always produce at output q2. always produce more than q2. C) D) never produce an output larger than q2. never produce an output larger than q1. Type: A Topic: 3 E: 444 MI: 200 55.
Refer to the above diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. The profit-seeking monopolist will: A. always produce at output q 2. B. always produce more than q 2. C. never produce an output larger than q 2. D. never produce an output larger than q 1.
Refer to the data for a nondiscriminating monopolist. At its profit-maximizing output, this firm's price will exceed its marginal cost by ____ and its average total cost by ____. asked Aug 17, 2018 in Economics by Dorothy
Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. the profit-seeking monopolist will General. Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. the profit-seeking monopolist will. 518 students attemted this question. Bookmark. Add Comment.
Refer to the above diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. The profit-seeking monopolist will: A. always produce at output q 2. B. always produce more than q 2. C. never produce an output larger than q 2. D. never produce an output larger than q 1.
54. Refer to the above diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. The profit-seeking monopolist will: A) always produce at output q2. C) never produce an output larger than q2. B) always produce more than q2. D) never produce an output larger than q1.
A profit maximizing monopolist will always produce an output that is less than the output that maximizes sales revenue. 3) What is the effect of a lump sum tax on a monopolist? 4) Can the government find a price at which to regulate a natural monopoly that is lower than the monopolistʹs price but generates the same profit? 5) True/False. ...
Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. The profit-seeking monopolist will never produce an output larger than q 2 . Suppose a pure monopolist is charging a price of $12 and the associated marginal revenue is $9. We thus know that total revenue is increasing.
Diagram of Monopoly 28 July 2019 by Tejvan Pettinger Monopoly Graph A monopolist will seek to maximise profits by setting output where MR = MC This will be at output Qm and Price Pm. Compared to a competitive market, the monopolist increases price and reduces output Red area = Supernormal Profit (AR-AC) * Q
5. Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. The profit-seeking monopolist will: C. never produce an output larger than q 2. 6. Assume a pure monopolist is currently operating at a price-quantity combination on the inelastic segment of its demand curve. If the monopolist is seeking maximum profits, it should: D. charge a higher ...
Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. The profit-seeking monopolist will: C. never produce an output larger than q 2. 6. Assume a pure monopolist is currently operating at a price-quantity combination on the inelastic segment of its demand curve. If the monopolist is seeking maximum profits, it should:
Economics questions and answers. Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. Demand is elastic: Question 41 options: in the q1q3 output range. only for outputs greater than q4. for all levels of output less than q2. for all levels of output greater than q2.






















0 Response to "42 refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. the profit-seeking monopolist will"
Post a Comment