38 pacemaker cell action potential diagram
File:Pacemaker potential.svg - Wikipedia Pacemaker cell action potential diagram. Licensing. I, the copyright holder of this work, hereby publish it under the following license: Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2 or any later version published by the Free Software Foundation; with no ... Action Potential in Cardiac Pacemaker Cells- TeachMePhysiology Fig 2 - Diagram showing the action potential in cardiac pacemaker cells and the main ion movements at each stage. Control by the Autonomic Nervous System The autonomic nervous system (ANS) alters the slope of the pacemaker potential, in order to alter heart rate.
Cardiac Action Potentials - Human Physiology Nodal Cell Action Potential Profile. This diagram illustrates the action potential profile of a nodal cell within the heart, with time plotted against membrane potential. From this diagram, several characteristics of a nodal cell can be noted. ... Pacemaker cells do not compete, they go at the fastest rate. In a healthy human, this is the SA node.

Pacemaker cell action potential diagram
Action Potential | Definition, Steps, Phases, Role & Summary However, there is a clear distinction between the cells that are capable of producing an action potential and cells that can only conduct it (i.e. ventricular myocytes). Cells that generate the action potential are called pacemaker cells and are found in the right atrium at the sinoatrial node. They exhibit automaticity. Cardiac Myocyte Action Potential • LITFL • BSCC Examination Professor providing a more detailed explanation (with transcript) Draw and explain the action potential in a cardiac myocyte Examinee response: Drawing and explanation in real-time video/audio Examiner Explanation Transcript Basic Science in Clinical Context more Physiology Philes Deanne Chiu Emergency Physician, FACEM. PDF Cardiac Action Potential - Yola • Initiation of action potential in autorhythmic cells: 1. Pacemaker Potential due to influx of sodium and reduced efflux of 2. Depolarizationpotassium. and reversal of the membrane potential due to 3. Repolarizationinflux of calcium. due to efflux of potassium. • Initiation of action potential in contractile cells: 1.
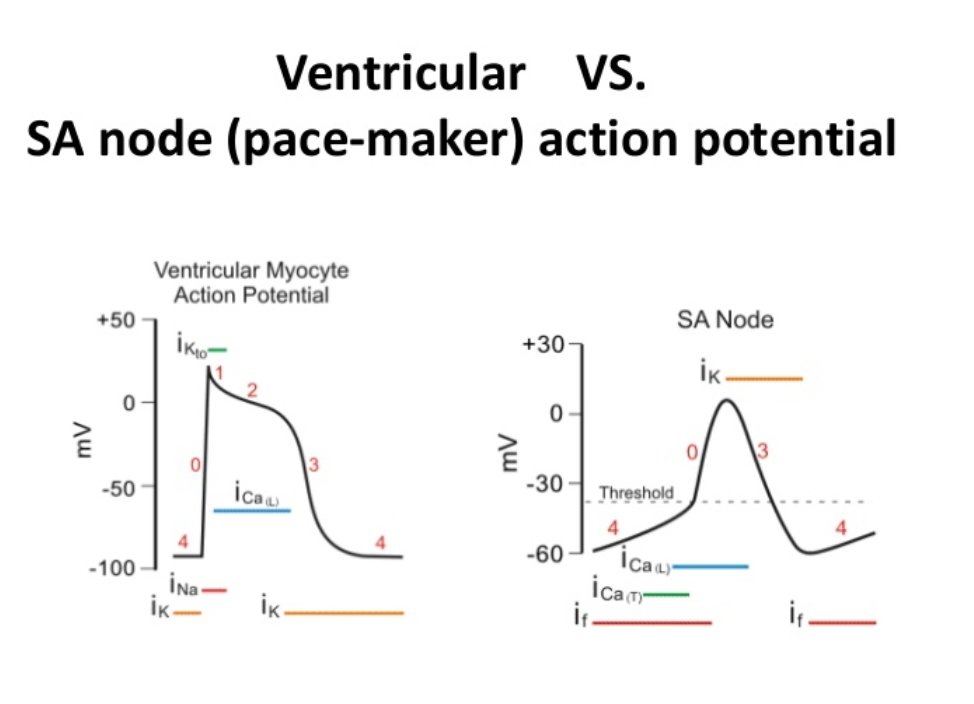
Pacemaker cell action potential diagram. Pacemaker and Action Potentials of Typical Cardiac ... Start studying Pacemaker and Action Potentials of Typical Cardiac Pacemaker Cells. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Sinoatrial Node Action Potentials - CV Physiology SA nodal action potentials are divided into three phases. Phase 4 is the spontaneous depolarization (pacemaker potential) that triggers the action potential once the membrane potential reaches threshold between -40 and -30 mV). Phase 0 is the depolarization phase of the action potential. This is followed by phase 3 repolarization. Pacemaker Cell action potential Flashcards - Quizlet Start studying Pacemaker Cell action potential. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Cardiac action potential - All About Cardiovascular System ... Action potential of ventricular myocardial cell. Action potential of pacemaker cells. Action potential of the pacemaker cell is different from that of ventricular myocardial cell. It is characterized by lower slope of phase 0 (lower Vmax) and the presence of diastolic depolarization mediated by the funny current (I f), also known as pacemaker ...
Pacemaker potential - Wikipedia Pacemaker potential. In the pacemaking cells of the heart (e.g., the sinoatrial node ), the pacemaker potential (also called the pacemaker current) is the slow, positive increase in voltage across the cell 's membrane (the membrane potential) that occurs between the end of one action potential and the beginning of the next action potential. Action Potentials Made Easy: Cardiac Myocyte ... - EZmed An action potential is a change in voltage across a cell membrane, specifically a rise in voltage followed by a fall. Action potentials are used to send information throughout the body, and they are also necessary for some types of cells to function as they trigger intracellular processes (such as contraction of muscle cells). Cardiac action potential | Psychology Wiki | Fandom The standard model used to understand the cardiac action potential is the action potential of the ventricular myocyte. The action potential has 5 phases (numbered 0-4). Phase 4 is the resting membrane potential, and describes the membrane potential when the cell is not being stimulated. Cardiac Action Potential, Animation. - YouTube (USMLE topics, cardiology) Cardiac action potential in pacemaker cells and contractile myocytes, electrophysiology of a heartbeat. Purchase PDF (script of th...
BIO 2982 Action Potentials of Cardiac Pacemaker Cells ... BIO 2982 Action Potentials of Cardiac Pacemaker Cells STUDY Learn Write Test PLAY Match Created by mkrach7694 PLUS Terms in this set (6) Pacemaker potential--due to slow influx of Na+ and closing of K+ channels. ... Depolarization--point at which action potential begins, as it reaches threshold; due to influx of Ca++ ... Cardiac Electrophysiology Notes: Diagrams & Illustrations ... Figure 17.2 Graph depicting the action potential of a pacemaker cell. ACTION POTENTIALS IN MYOCYTES osms.it/myocyte-action-potentials Myocytes Receive signal from from pacemaker cells causing them to contract Able to depolarize, spread action potentials Action potential phases: Phase 0 (depolarization phase): rapid influx of sodium into cell (inward current); responsible for rapid ... Conduction System of the Heart: Step-By-Step ... - EZmed The pacemaker cells within the SA node generate action potentials at 60-100 beats per minute. The action potential travels from the SA node through the right atrium via the internodal pathway, and to the left atrium via Bachmann's bundle. As the action potential travels through the atria, the atria depolarize and contract. AV Node Cardiac electrophysiology: action potential, automaticity ... The action potential in the sinoatrial node and in contractile myocardial cells. Phase 4 of the action potential in the sinoatrial node is called 'pacemaker potential', because it is responsible for the spontaneous repetitive depolarization. The depolarization spreads from the sinoatrial node to the atrial and ventricular myocardium.
PDF Cardiac Action Potential - interactivephysiology.com 1. Pacemaker Potential • An autorhythmic cell has the unique ability to depolarize spontaneously, resulting in a pacemaker potential. 2. Depolarization and Reversal of the Membrane Potential • Once threshold is reached, an action potential is initiated, which begins with further depolarization and leads to reversal of the membrane potential ...
Phases - PhysiologyModels.info The three sections of the pacemaker action potential are labeled and color coded on the graph. The y-axis of the graph shows the membrane potential in millivolts (mV) and the x-axis is time. how the membrane potential changes over time. Depolarization is also called phase 0, repolarization is called phase 3and
PDF Cardiac Action Potential - Yola • Initiation of action potential in autorhythmic cells: 1. Pacemaker Potential due to influx of sodium and reduced efflux of 2. Depolarizationpotassium. and reversal of the membrane potential due to 3. Repolarizationinflux of calcium. due to efflux of potassium. • Initiation of action potential in contractile cells: 1.
Cardiac Myocyte Action Potential • LITFL • BSCC Examination Professor providing a more detailed explanation (with transcript) Draw and explain the action potential in a cardiac myocyte Examinee response: Drawing and explanation in real-time video/audio Examiner Explanation Transcript Basic Science in Clinical Context more Physiology Philes Deanne Chiu Emergency Physician, FACEM.
Action Potential | Definition, Steps, Phases, Role & Summary However, there is a clear distinction between the cells that are capable of producing an action potential and cells that can only conduct it (i.e. ventricular myocytes). Cells that generate the action potential are called pacemaker cells and are found in the right atrium at the sinoatrial node. They exhibit automaticity.

0 Response to "38 pacemaker cell action potential diagram"
Post a Comment