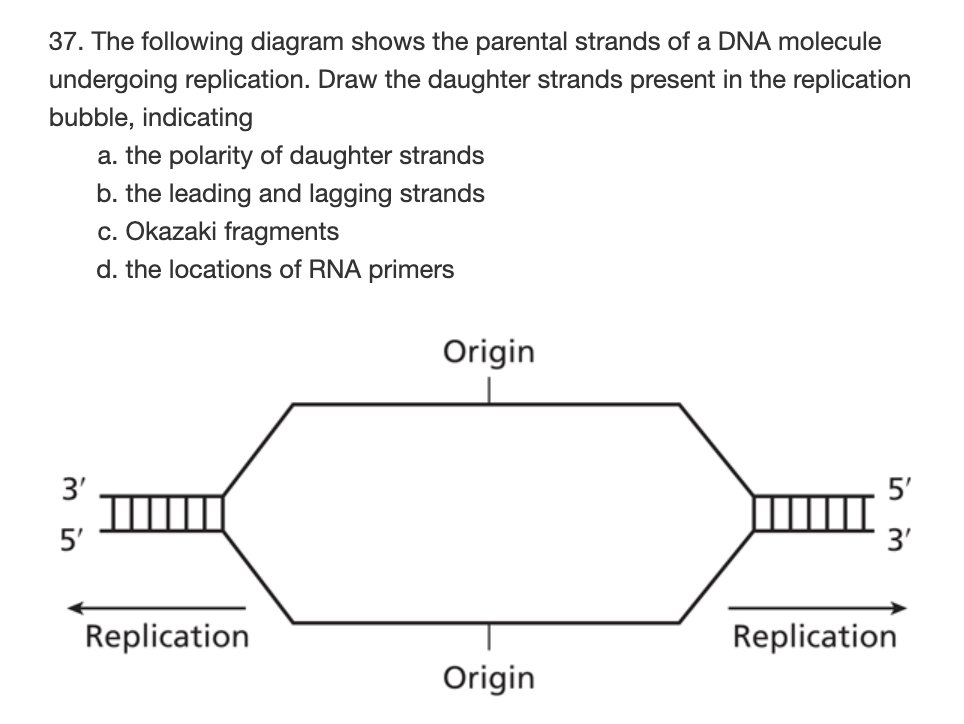
39 the diagram below shows a double-stranded dna molecule (parental duplex).
DNA Review Worksheet.doc - Name Period Date DNA Structure ... 19. The figure below shows DNA replicating. In the space provided, describe what is occurring in each step. Make sure the explanation includes all the enzymes involved in the process. Before DNA can be replicated, the double stranded molecule must turn into two single strands. PDF Cell, Vol. 12,1007-1020, December 1977, Copyright 8 1977 ... DNA segment with one double- to single-stranded transition like type II molecules; there was also, however, a single-stranded branch emerging from the duplex portion of the molecule, like type I molecules. Type I, type II and type l/II molecules accounted for 85-90% of the molecules that contained both single- and double-stranded DNA (excluding ob-
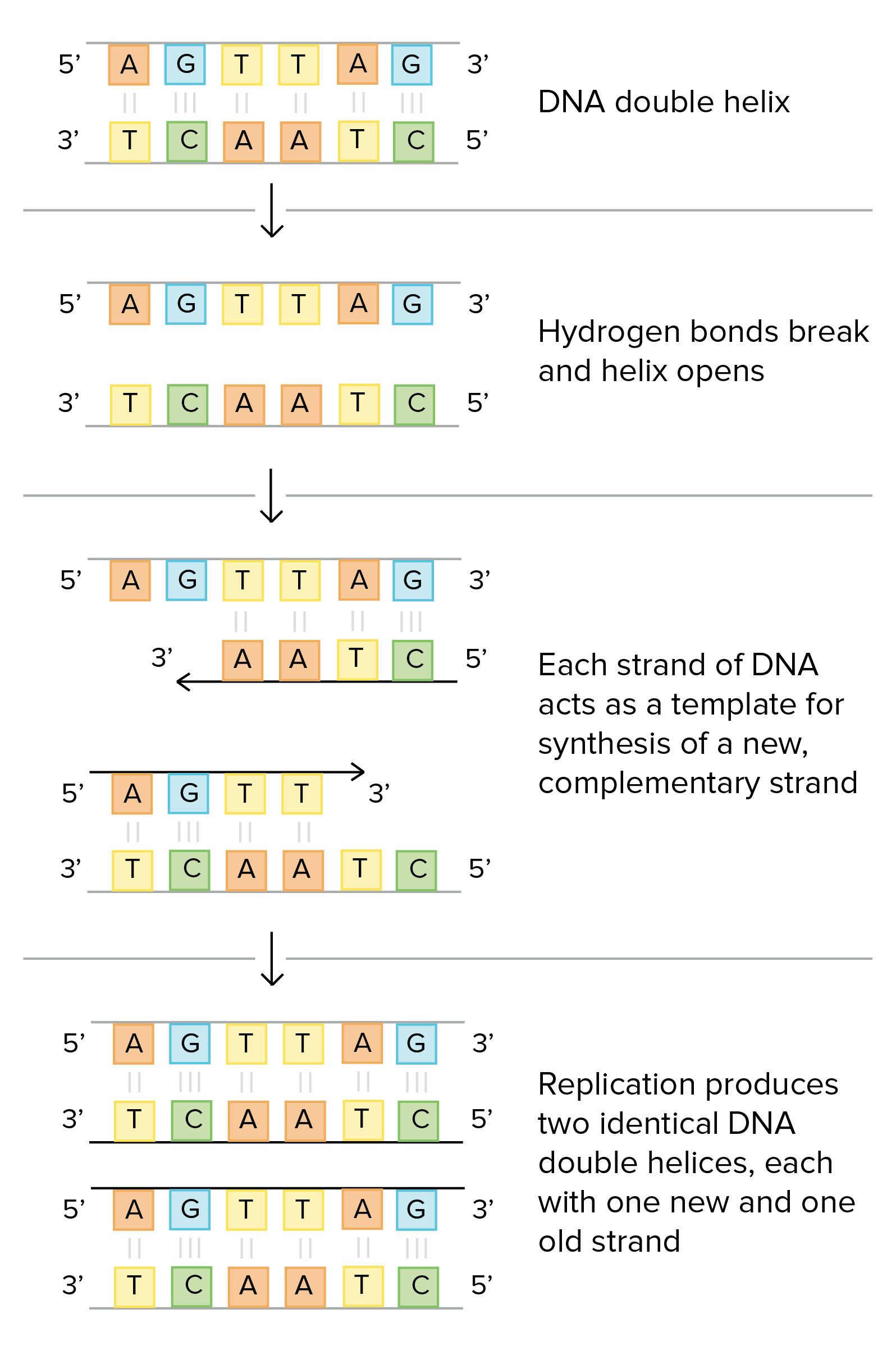
How DNA Replicates | Matthew Meselson | Franklin W. Stahl Based upon their model for the structure of DNA, Watson and Crick proposed that DNA replicates in a "Semi-Conservative" manner (Figure 2).In this model, the two strands of the DNA double helix unwind and separate, and each "parent" strand serves as a template for the synthesis of a new "daughter" strand.

The diagram below shows a double-stranded dna molecule (parental duplex).
Answered: A duplex DNA molecule contains a random… | bartleby While studying the structure of a small gene that was recently sequenced during the Human Genome Project, an investigator notices that one strand of the DNA molecule contains the following: 20 adenine (A) bases 30 cytosine (C) bases25 guanine (G) bases 22 thymine (T) bases How many of each base is found in the complete double-stranded molecule? Solved I am new with this. Please help DNA replication is ... The diagram below shows a double-stranded DNA molecule (parental duplex). Drag the correct labels to the appropriate locations in the diagram to show the composition of the daughter duplexes after one and two cycles of DNA replication. Nucleic acid double helix - Wikipedia In molecular biology, the term double helix refers to the structure formed by double-stranded molecules of nucleic acids such as DNA.The double helical structure of a nucleic acid complex arises as a consequence of its secondary structure, and is a fundamental component in determining its tertiary structure.The term entered popular culture with the publication in 1968 of The Double Helix: A ...
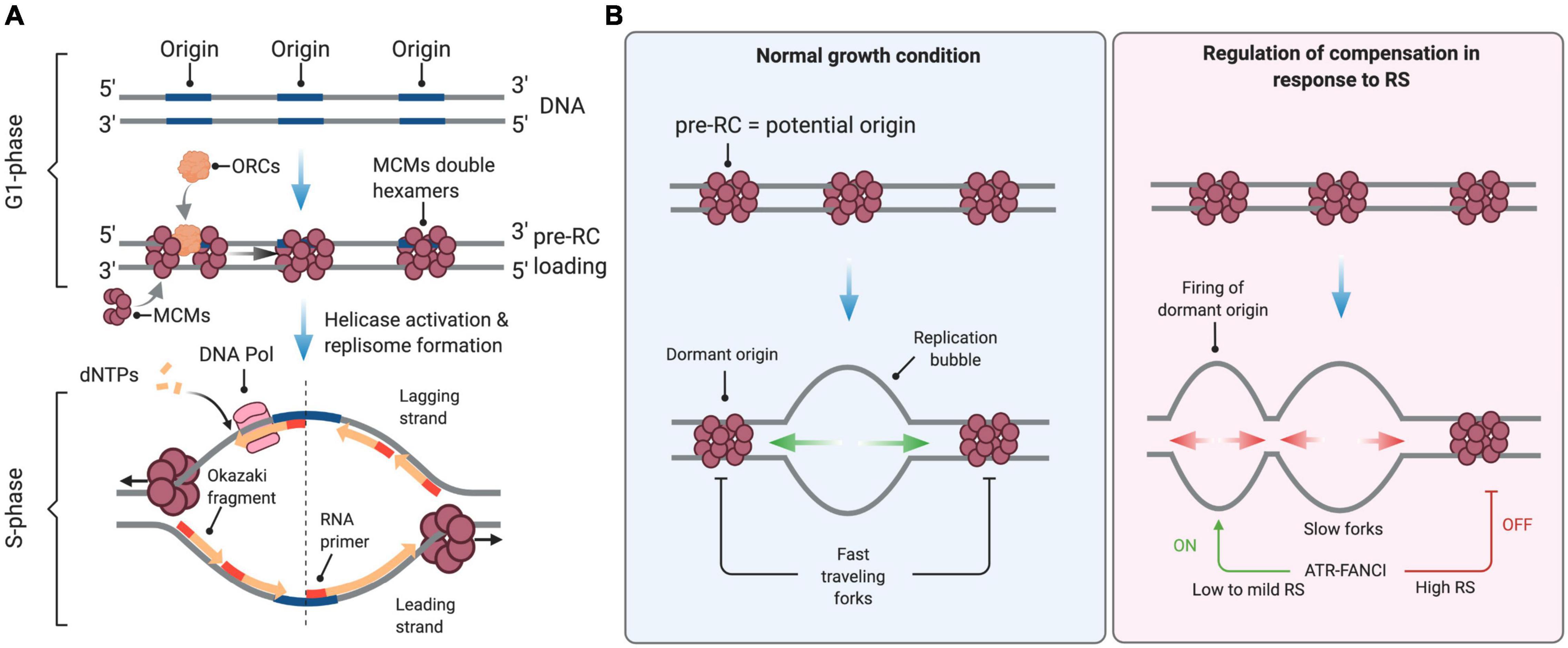
The diagram below shows a double-stranded dna molecule (parental duplex).. Chapter 5- DNA.pdf - Chapter 5 DNA Structure, Replication ... DNA Structure DNA is a polymer of nucleotides, covalently linked by 3′-to-5′ phosphodiester bonds. With the exception of a few viruses that contain single-stranded DNA (ssDNA), DNA exists as a double-stranded molecule (dsDNA), in which the two strands wind around each other, forming a double helix. The Central Dogma of Molecular Biology - CliffsNotes DNA is replicated when each strand of DNA specifies the sequence of its partner to make two daughter molecules from one parental double‐stranded molecule. DNA, RNA, and nucleotide structure DNA is a polymer—a very large molecule made up of smaller units of four components. PDF CHAPTER 8 Changing genes: site-directed mutagenesis and ... is available in single-stranded form, and cloning the gene in M13-based vectors makes this easy. However, DNA cloned in a plasmid and obtained in duplex form can also be converted to a partially single-stranded molecule that is suitable (Dalbadie-McFarland et al. 1982). The synthetic oligonucleotide primes DNA syn- DNA Replication, Definition, Steps, Enzymes, and ... Replication occurs in three major steps: the opening of the double helix and separation of the DNA strands, the priming of the template strand, and the assembly of the new DNA segment. During separation, the two strands of the DNA double helix uncoil at a specific location called the origin. Several enzymes and proteins then work together to ...
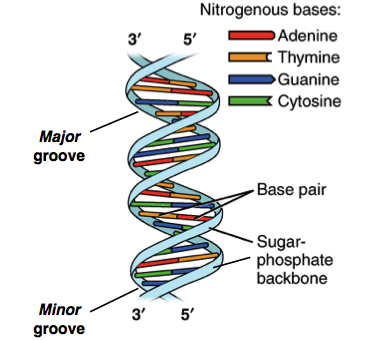
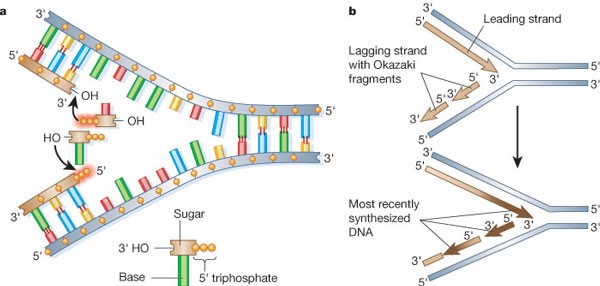
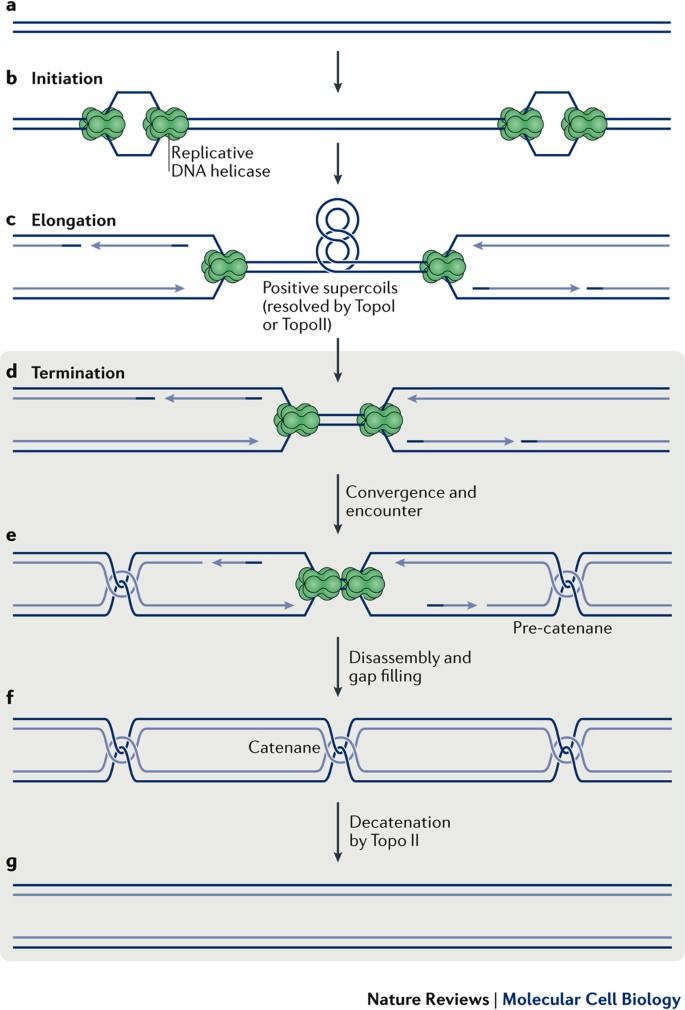
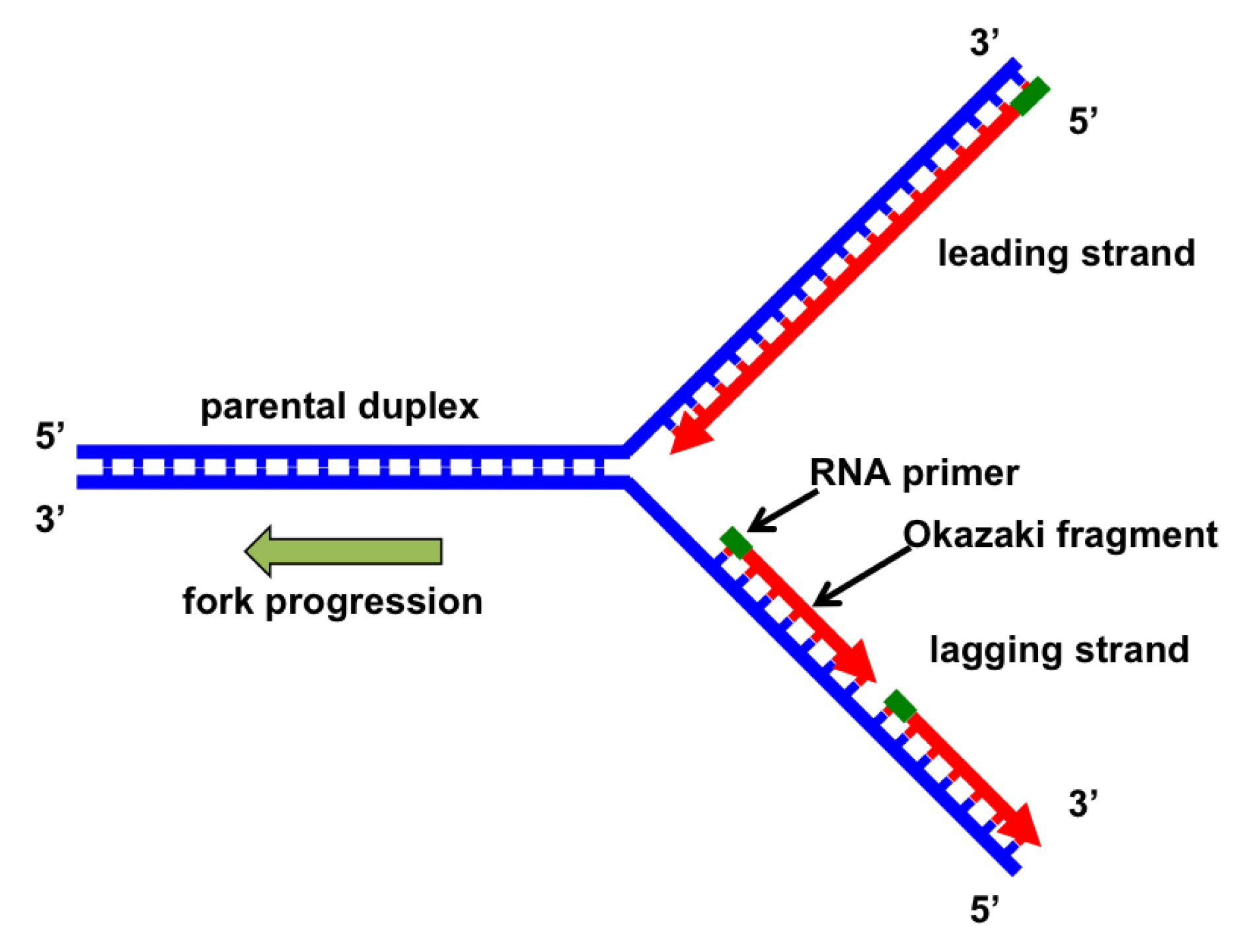
DNA Replication Mechanisms - Molecular Biology of the Cell ... Initially, the simplest mechanism of DNA replication seemed to be the continuous growth of both new strands, nucleotide by nucleotide, at the replication fork as it moves from one end of a DNA molecule to the other. But because of the antiparallel orientation of the two DNA strands in the DNA double helix (see Figure 5-2), this mechanism would require one daughter strand to polymerize in the 5 ... The Initiation and Completion of DNA Replication in ... DNA Synthesis Begins at Replication Origins. As discussed previously, the DNA double helix is normally very stable: the two DNA strands are locked together firmly by a large number of hydrogen bonds formed between the bases on each strand. To be used as a template, the double helix must first be opened up and the two strands separated to expose unpaired bases. DNA: Structure, Forms and Functions (With Diagram) The DNA of E. coli appears to consist of a single, enormous double-stranded DNA molecule with a molecular weight of about 2.8 x 10 9, a thickness of about 2.0 nm and a contour length of about 1,360µm. E. coli DNA contains 4 million deoxyribonucleotide pairs. Structure of HIRAN domain of human HLTF bound to duplex ... DNA replication is one of the most fundamental process for life to duplicate double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) during cell division. Both strands of DNA, the leading and lagging strands, are synthesized together at the replication fork, the three-way junction between newly separated parental strands and un-replicated parental DNA duplex.
The Diagram Below Shows A Bacterial Replication Fork And ... Part A The mechanism of DNA replication The diagram below shows a doublestranded DNA molecule (parental DNA)%(11). Mar 19, · The diagram below shows a bacterial replication fork and its principal proteins. Drag the labels to their appropriate locations in the diagram to describe the name or function of each structure. Mastering Biology Chapter 13 Flashcards - Quizlet The diagram below shows a double-stranded DNA molecule (parental DNA). Drag the correct labels to the appropriate locations in the diagram to show the composition of the daughter DNA molecules after one and two cycles of DNA replication. In the labels, the original parental DNA is blue and the DNA synthesized during replication is red. PDF Questions with Answers- Nucleotides & Nucleic Acids double- stranded form could assume a Z-DNA structure. b) If the single-stranded molecule has the sequence 5'-(GATC)10, then its double-stranded form could assume an H-DNA structure. c) If the single-stranded molecule has the sequence 5'-(CTGA)10, then its double-stranded form could assume a hairpin structure. DNA Helicase - CBM In bacteria, the unwinding of parental duplex DNA is carried out by the replicative DNA helicase (DnaB) that couples NTP hydrolysis to 50 to 30 translocation. The crystal structure of the DnaB hexamer in complex with GDP-AlF4 and ssDNA reported here reveals that DnaB adopts a closed spiral staircase quaternary structure around an A-form ssDNA ...
The diagram below shows a double-stranded dna molecule ... The diagram below shows a double-stranded DNA molecule (parental duplex). Drag the correct labels to the appropriate locations in the diagram to show the composition of the daughter duplexes after one and two cycles of DNA replication. In the labels, the original parental DNA is blue and the DNA synthesized during replication is red.
Mastering Biology Chapter 16 - RHS Homework The diagram below shows a double-stranded DNA molecule (parental DNA). Drag the correct labels to the appropriate locations in the diagram to show the composition of the daughter DNA molecules after one and two cycles of DNA replication. In the labels, the original parental DNA is blue and the DNA synthesized during replication is red.
PDF Moving one DNA double helix through another by a type II ... In (a), the general problem of separating the two parental strands is illustrated for a double-stranded DNA ring. In this two-line representation of the duplex DNA ring, each of the circular DNA strands is represented by a closed line. Because of the double helix geometry of DNA, the two strands are topologically linked; the degree
The parallel lines shown here represent the ... - Brainly.com Both strands of parental DNA serve as templates for newly synthesized daughter strands that inherits a new double helix DNA containing one old and one new daughter strands arising from the parental duplex. This mechanism would require one daughter strand to polymerize in the 5′-to-3′ direction and the other in the 3′-to-5′ direction ...
Chapter 11 Flashcards | Quizlet The diagram below shows a double-stranded DNA molecule (parental duplex). Drag the correct labels to the appropriate locations in the diagram to show the composition of the daughter duplexes after one and two cycles of DNA replication. In the labels, the original parental DNA is blue and the DNA synthesized during replication is red.
(Solved) The diagram below shows a double-stranded DNA ... The diagram below shows a double-stranded DNA molecule (parental DNA). Drag the correct labels to the appropriate locations in the diagram to show the composition of the daughter DNA molecules after one and two cycles of DNA replication. In the labels, the original parental DNA is blue and the DNA synthesized during replication is red.
The Figure Below Shows A Double-stranded DNA Molecule ... The figure below shows a double-stranded DNA molecule (parental duplex). Drag the correct labels to the appropriate locations in the diagram to show the structure of the daughter duplex after one and two cycles of DNA replication.
Can You Correctly Label Various Parts Of A Dna Molecule This DNA is right handed. Represent portions of a DNA molecule. In a double helix structure the strands of DNA run antiparallel meaning the 5 end of one DNA strand is parallel with the 3 end of the other DNA strand. DNA and RNA labeling techniques Oligonucleotides can be labeled at either the 3 or the 5 end. Add your answer.
Chapter 9: DNA Replication - Chemistry In the dispersive model, all resulting DNA strands have regions of double-stranded parental DNA and regions of double-stranded daughter DNA. Figure by Parker, N., et.al. (2019) Openstax Matthew Meselson and Franklin Stahl devised an experiment in 1958 to test which of these models correctly represents DNA replication (Figure 9.2).
Nucleic acid double helix - Wikipedia In molecular biology, the term double helix refers to the structure formed by double-stranded molecules of nucleic acids such as DNA.The double helical structure of a nucleic acid complex arises as a consequence of its secondary structure, and is a fundamental component in determining its tertiary structure.The term entered popular culture with the publication in 1968 of The Double Helix: A ...
Solved I am new with this. Please help DNA replication is ... The diagram below shows a double-stranded DNA molecule (parental duplex). Drag the correct labels to the appropriate locations in the diagram to show the composition of the daughter duplexes after one and two cycles of DNA replication.
Answered: A duplex DNA molecule contains a random… | bartleby While studying the structure of a small gene that was recently sequenced during the Human Genome Project, an investigator notices that one strand of the DNA molecule contains the following: 20 adenine (A) bases 30 cytosine (C) bases25 guanine (G) bases 22 thymine (T) bases How many of each base is found in the complete double-stranded molecule?


















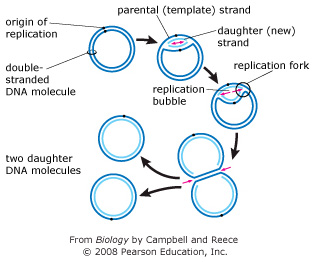

0 Response to "39 the diagram below shows a double-stranded dna molecule (parental duplex)."
Post a Comment