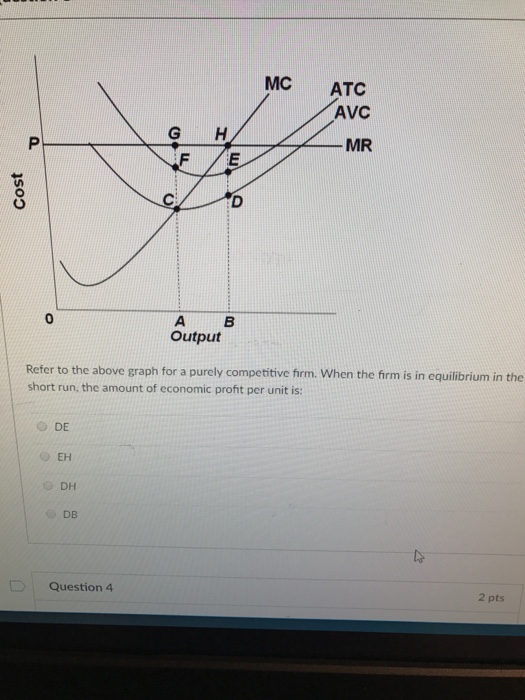
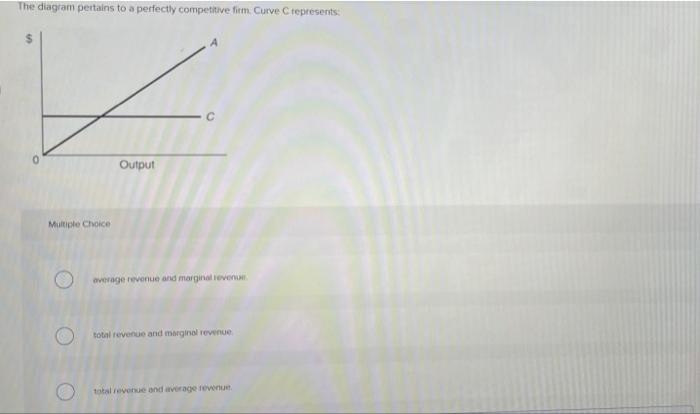
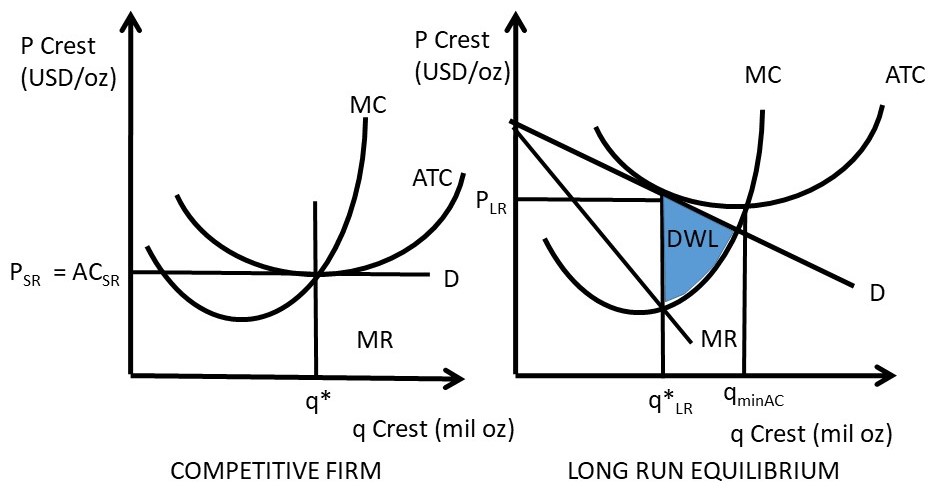
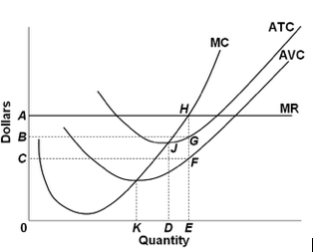
39 refer to the diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. curve c represents
successessays.comAssisting students with assignments online - Success Essays Get 24⁄7 customer support help when you place a homework help service order with us. We will guide you on how to place your essay help, proofreading and editing your draft – fixing the grammar, spelling, or formatting of your paper easily and cheaply. Managing The Environment - United States Environmental ... Even in this form, it still represents a "popula- tion;" dollars are born and die, migrate in and out of particular regions just like any other population. If I am adding to my money stock i aster than I arn spending it or diminishing it, it will grow. In a developed society barter is a miniscule part of the total volume of exchanges. Most people or economic units have an input of money which ...
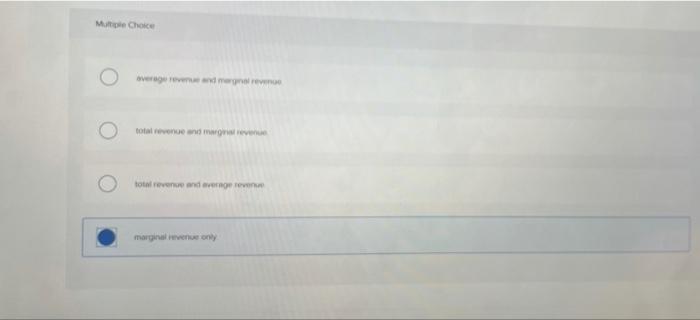
TEST 3 Flashcards | Chegg.com The marginal revenue curve of a purely competitive firm: A. lies below the firm's demand curve. B. is downsloping because price must be reduced to sell more 20. Refer to the above diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. Curve A represents: A. total revenue and marginal revenue.

Refer to the diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. curve c represents
supply and demand | Definition, Example, & Graph | Britannica The resulting price is referred to as the equilibrium price and represents an agreement between Please refer to the appropriate style manual or other sources if you have any questions. A demand curve is almost always downward-sloping, reflecting the willingness of consumers to purchase more... PDF Lab 12: Perfectly Competitive Market | minimum point of ATC curve). All the firms in a perfectly competitive market earn economic profit equal to zero. (Since economic profit is the profit after accounting for the implicit cost of a firm e. Shutdown point and break-even point are the same in the long run: the minimum point of ATC curve (compare to the shutdown point... › 38914977 › _Hodder_Education(PDF) [Hodder Education] Cambridge ... - Academia.edu Academia.edu is a platform for academics to share research papers.
Refer to the diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. curve c represents. silo.pub › modern-management-concepts-and-skillsModern Management: Concepts and Skills (12th Edition) - SILO.PUB It can also refer to a body of knowledge; in this context, management is a cumulative body of information that furnishes insights on how to manage. The term management can also refer to the individuals who guide and direct organizations or to a career devoted to the task of guiding and directing organizations. Perfect Competition | Boundless Economics A perfectly competitive firm faces a demand curve is a horizontal line equal to the equilibrium price of the entire market. Learning Objectives. In a perfectly competitive market individual firms are price takers. The price is determined by the intersection of the market supply and demand curves. favorite homework help service - Achiever Essays Your favorite homework help service. Who Works in Our Academic Writing Service? We have writers with varied training and work experience. A perfectly elastic demand curve implies that the firm... - Brainly.com In a purely competitive market, all the firms are selling the same product so there is a lot of competition. The market sets the price in this industry at the point where quantity When it comes to the demand curve for the individual firm however, it is elastic because price is not set by the firm.
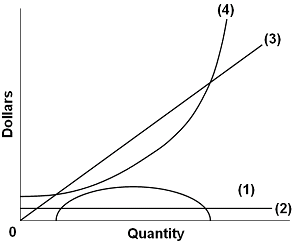
Помогите пожалуйста с тестами по английскому языку which type of... Помогите пожалуйста с тестами по английскому языку Which type of money are paid to professional people such architects and lawyers? Ответы а) currency б)fees в bonus г salary 2.The money paid for the use of house or flat Ответы a bills бrent в bonus г coins 3Choose the synonym of social security... Chapter 6: 1. A firm is a: A) Physical establishment which contributes A perfectly competitive firm does not try to sell more of its product by lowering its price below the market price because: A) its competitors would not Price is constant or "given" to the individual firm selling in a perfectly competitive market because: A) the firm's demand curve is downward sloping. Purely Competitive Market Demand Curve Economic Details: Pure competition, or perfect competition, refers to a market structure with a large number of competitors selling the same, or similar, products. Details: Purely Competitive Adjustment A. Suppose industry demand and supply yield an equilibrium price P at which a firm's economic profit is... Refer To The Diagram Which Pertains To A Purely Competitive... Curve a represents a. Each firm in an oligopoly depends on its own pricing strategy and that of its rivals. The demand curves are perfectly elastic for both a purely competitive firm and a purely competitive industry. Average revenue and marginal revenue.
Pareto Efficiency - Definition, Graphical Representation, Example Pareto Efficiency, a concept commonly used in economics, is an economic situationAggregate Supply and DemandAggregate supply and demand refers to the concept of supply and demand but applied at a macroeconomic scale. 34 Refer To The Diagram, Which Pertains To A Purely Competitive... Refer to the diagram for a purely competitive producer. New firms will enter this industry. Curve a represents a. Over which price range is the demand. Curve 2 horizontal line in the above diagram is a purely competitive firms marginal revenue curve a firm is producing an output such that the... › cryptopedia › glossaryCrypto Glossary - Cryptopedia - Gemini Bonding curve smart contracts represent a method for nurturing balanced supply and demand for a token. A bonding curve is a mathematical concept used to explain the relationship between the price and supply of an asset. Pre-Test Chapter 21 ed17 3. Refer to the above diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. Curve C represents: A. total revenue and marginal revenue. Prof Keep Econ Pr-Test Chap 21 ed 17 Page 2 of 9 7. Refer to the above information. For a purely competitive firm, marginal revenue: A. graphs as a straight...
Introduction to Marketing Coursera Quiz Answer Competitive Points of Difference. 4. When Steve Jobs updated his company name from Apple Computer to Apple in 2007, which part of the brand positioning was he changing? 8. According to the lectures, what should a company's long-term marketing strategy be?
Definition of competitive advantage and a discussion of its sources... A competitive advantage exists when the firm is able to deliver the same benefits as competitors but at a lower cost (cost advantage), or deliver benefits that exceed those of competing products (differentiation advantage). Capabilities refer to the firm's ability to utilize its resources effectively.
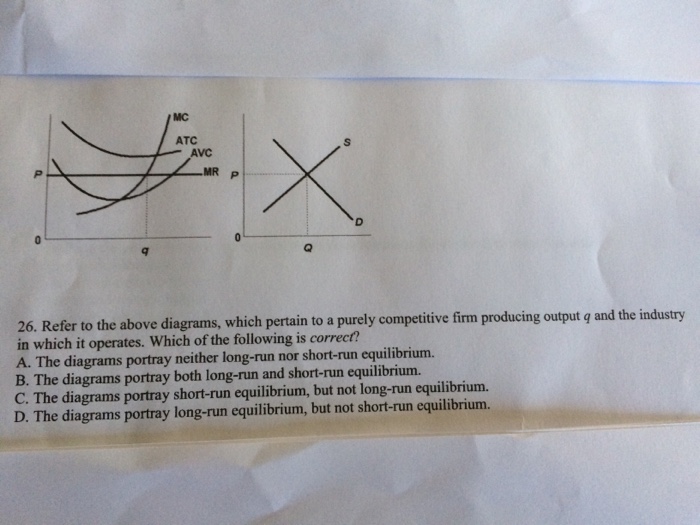
Карточки Chapter 11 Study Questions ( | Quizlet Refer to the diagrams, which pertain to a purely competitive firm producing output q and the industry in which it operates. In the long run we should expect Refer to the diagram showing the average total cost curve for a purely competitive firm.
fountainessays.comFountain Essays - Your grades could look better! 100% money-back guarantee. With our money back guarantee, our customers have the right to request and get a refund at any stage of their order in case something goes wrong.
BUSINESS ETHICS TEXT BOOK PROF DR C ... - Academia.edu This book primarily handles issues and contemporary practices aligned to business ethics with a brief perspective on the HR practices to make ethics in business stronger. Business ethics Overview Functional business areas Finance paradigm Human
ECON 1550 Introduction To EconomicsEND-OF-SEMESTER... 17. Refer to the above diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. Curve C represents: A) total revenue and marginal revenue. Use the following to answer question 22: 22. Which of the above diagrams correctly portray a nondiscriminating pure monopolist's demand (D) and marginal...
Types of Market Structures on the Basis of Competition A purely competitive market is one in which there are a large number of independent buyers and Figure-2 shows the average revenue curve under pure competition curve Refers to the main feature of monopoly.Under monopoly market conditions, there is a single seller or producer of products.
Join LiveJournal Password requirements: 6 to 30 characters long; ASCII characters only (characters found on a standard US keyboard); must contain at least 4 different symbols;
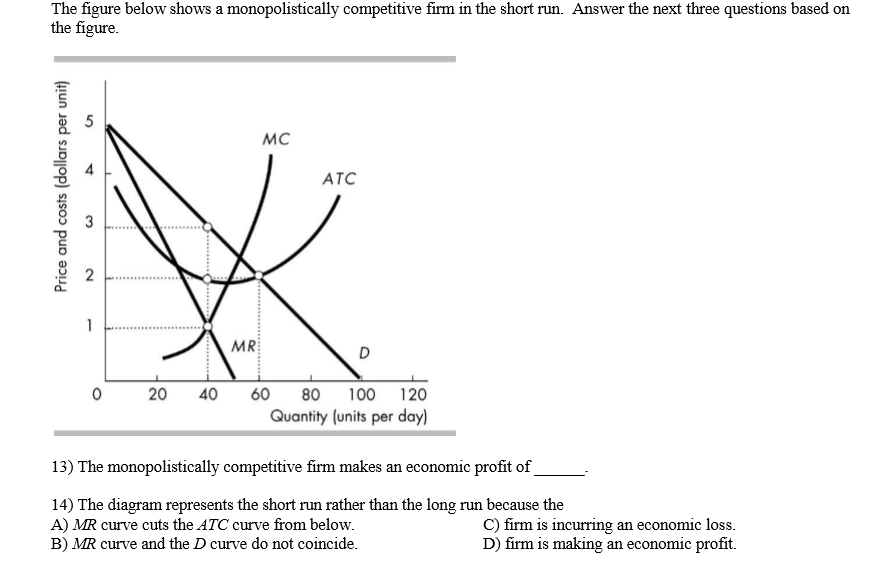
Chapter 9: Four Market Models | PURE COMPETITION 2. Refer to the above diagrams, which pertain to a purely competitive firm producing output q and the industry in which it operates. Monopolistic Competition - Quick Quiz. 1. Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium.
Demand Curve: Definition, Types, and How It Works The demand curve is a visual representation of how many units of a good or service will be bought at each possible price. If demand increases, the entire curve will move to the right. That means larger quantities will be demanded at every price.
Pure Competition Pure Competition. A perfectly competitive market is rare, but those that exist are very large, such as the A breakeven point is achieved when the total cost curve becomes less than total revenue for the first Because, for purely competitive firms, marginal revenue = price, maximum revenue is also...
University of Leeds 1137 Projects 1137 incoming 1137 knowledgeable 1137 meanings 1137 σ 1136 demonstrations 1136 escaped 1136 notification 1136 FAIR 1136 Hmm 1136 CrossRef 1135 arrange 1135 LP 1135 forty 1135 suburban 1135 GW 1135 herein 1135 intriguing 1134 Move 1134 Reynolds 1134 positioned 1134 didnt 1134 int 1133 Chamber 1133 termination 1133 overlapping 1132 newborn …
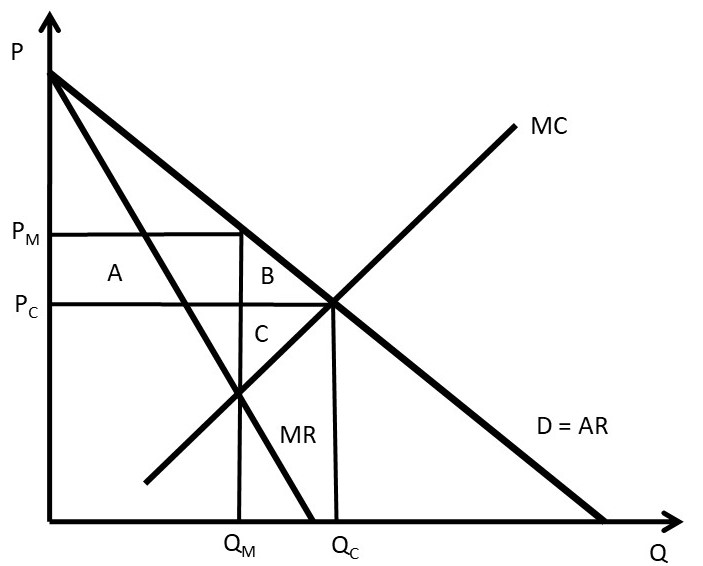
PDF Microsoft Word - CH 23_STUDY QUESTIONS.doc The demand curve facing a pure monopolist is downward sloping; that facing the purely competitive firm is horizontal, perfectly elastic. Bad feature: More income is transferred from consumers to the monopolist. 24-7 Assume a pure monopolist and a purely competitive firm have the same unit costs.
Multiple Choice Quiz | Online Resources Formulated prior to a review of the literature. Statements of predicted relationships between variables. B but not A. Both A and B. 3. A study of teaching professionals posits that their performance-related pay increases their motivation which in turn leads to an increase in their job satisfaction.
Demand curve - Wikipedia Demand curves are used to estimate behaviour in competitive markets and are often combined with supply curves to find the equilibrium price (the price at which sellers together are willing to Movement "along the demand curve" refers to how the quantity demanded changes when the price changes.
Aggregate Demand (AD) Curve The aggregate demand curve represents the total quantity of all goods (and services) demanded by the economy at different price levels. Suppose interest rates were to fall so that investors increased their investment spending; the aggregate demand curve would shift to the right.
What is the demand curve in a perfectly competitive market? - Quora In Perfectly competitive market, all firms sell homogeneous product and the number of sellers is also large. If a firm tries to increase their price then it will lose and demand for its product will be 0. Thus, the price elasticity of demand is in...
Chapter 10 | Business Quiz - Quizizz Refer to the diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. Curve C represents. answer choices. Refer to the diagram for a purely competitive producer. The lowest price at which the firm should produce (as opposed to shutting down) is.
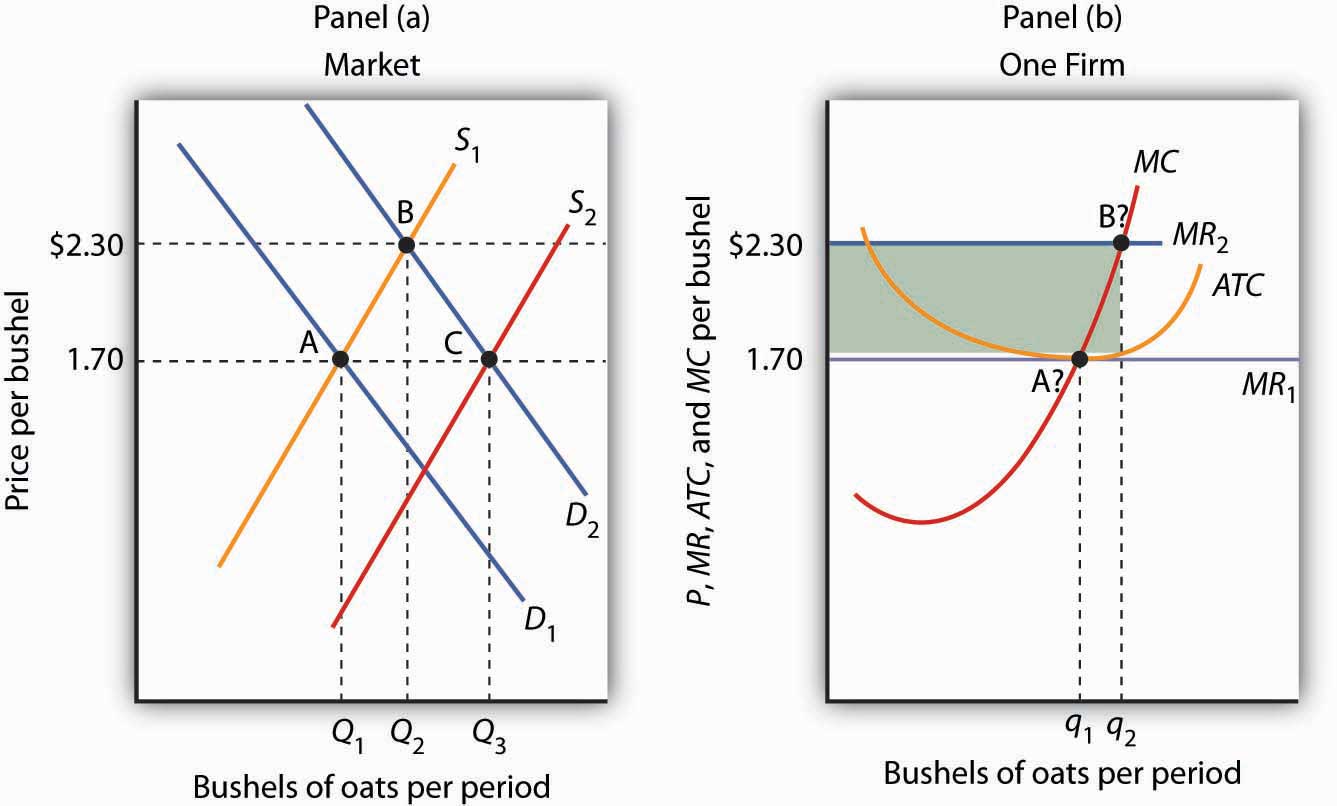
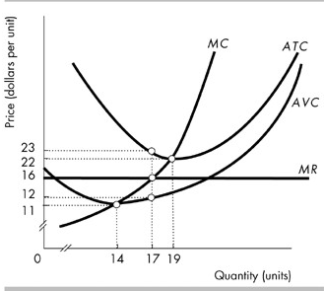
MicroEconomics Flashcards Refer to the diagram below, in which S1 and D1 represent the original supply and demand curves and S2 and D2 the new curves. Assume that in the short run a firm is producing 100 units of output, has average total costs of $200, and average variable costs of $150.
PDF sol_10.PDF | a. Calculate the firm's marginal revenue curve. Assuming the firm maximizes profits, a. What is the level of production, price, and total profit per week? The profit-maximizing output is found by setting marginal revenue equal to marginal cost. The supply curve is equivalent to the average expenditure curve.
Capitalism - Wikipedia Capitalism is an economic system based on the private ownership of the means of production and their operation for profit. Central characteristics of capitalism include capital accumulation, competitive markets, price system, private property, property rights recognition, voluntary exchange, and wage labor. In a capitalist market economy, decision-making and investments …
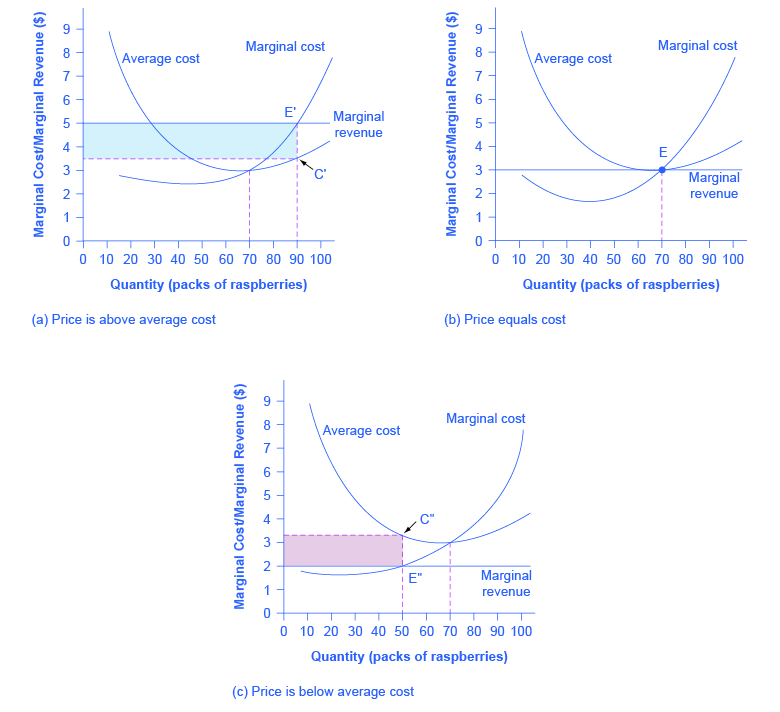
Refer to the above diagram which pertains to a purely competitive... Chapter 08 - Pure Competition in the Short Run 31. Firms seek to maximize: 32. A competitive firm in the short run can determine the profit-maximizing (or loss-minimizing) output by equating: 33. In the short run a purely competitive firm that seeks to maximize profit will produce: 8-8.
Which is the feature of a purely competitive market? - Answers The representative firm in a purely competitive industry? There are multiple characteristics which correspond to an ideally competitive market. These are a rule of law and contracts enforcement, competition through multiple merchants, market integrity against anti-competitive behaviors, and...
essaysassignment.comEssays Assignment - One assignment at a time, we will help ... One assignment at a time, we will help make your academic journey smoother.
› 38914977 › _Hodder_Education(PDF) [Hodder Education] Cambridge ... - Academia.edu Academia.edu is a platform for academics to share research papers.
PDF Lab 12: Perfectly Competitive Market | minimum point of ATC curve). All the firms in a perfectly competitive market earn economic profit equal to zero. (Since economic profit is the profit after accounting for the implicit cost of a firm e. Shutdown point and break-even point are the same in the long run: the minimum point of ATC curve (compare to the shutdown point...
supply and demand | Definition, Example, & Graph | Britannica The resulting price is referred to as the equilibrium price and represents an agreement between Please refer to the appropriate style manual or other sources if you have any questions. A demand curve is almost always downward-sloping, reflecting the willingness of consumers to purchase more...


















:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_Production_Possibility_Frontier_PPF_Apr_2020-01-b1778ce20e204b20bf6b9cf2a437c42e.jpg)
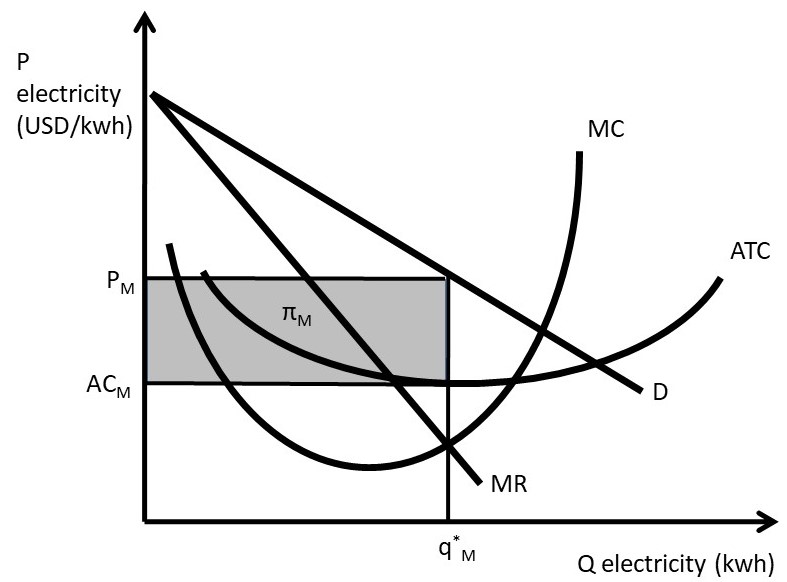
0 Response to "39 refer to the diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. curve c represents"
Post a Comment