41 orbital diagram for p
Atomic orbital - Wikipedia The p z orbital is the same as the p 0 orbital, but the p x and p y are formed by taking linear combinations of the p +1 and p −1 orbitals (which is why they are listed under the m = ±1 label). Also, the p +1 and p −1 are not the same shape as the p 0, since they are pure spherical harmonics. PDF Orbital Diagram Lab - New Providence School District Orbital Diagram Lab Background. The electrons in an atom occupy distinct principal energy levels. To be located in ... p, d, and f. Within each sublevel there is a specific number of orbitals. The orbitals within a given sublevel have the same energy requirements for electrons. Each orbital can "hold" ... The Aufbau diagram below ...
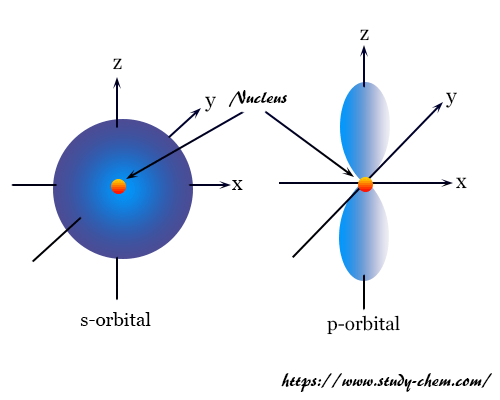
Orbitals Chemistry (Shapes of Atomic Orbitals) - Shape of ... Each p orbital consists of two sections better known as lobes which lie on either side of the plane passing through the nucleus. The three p orbitals differ in the way the lobes are oriented whereas they are identical in terms of size shape and energy.

Orbital diagram for p
PDF Electron Configurations and Orbital Diagrams key 1. Describe the two differences between a 2p x orbital and a 3p y orbital. The 2px orbital lies on the x-axis. The 3py orbital lies on the y-axis and is larger than the 2px orbital. 2. The lobes of a p orbital disappear at the nucleus. What does this tell us about electrons in p orbitals? How do yo write the orbital diagram for oxygen? | Socratic The electron configuration for oxygen is: 1s^2 2s^2 2p^4 This video will walk you through the step of writing orbital diagram. The video uses Kr as an example, but the process is exactly as the same as what you need to do for oxygen. Hope this helps! Carbon Orbital diagram, Electron configuration, and ... The orbital diagram for Carbon is drawn with 3 orbitals. The orbitals are 1s, 2s, and 2p. The Carbon orbital diagram contains 2 electrons in 1s orbital, 2 electrons in 2s orbital, and the rest two electrons in 2p orbital. Orbital diagram for a ground-state electron configuration of Carbon atom is shown below-
Orbital diagram for p. › flux › mods8 - Drawing Molecular Orbital Diagrams — Flux Science Nov 12, 2021 · Well, s-p mixing doesn’t occur with diatomic oxygen, creating a molecular orbital diagram like the first in this article. This is because, as more electrons are added to a system, the higher the energy becomes, due to their electrostatic repulsion. If the energy of the 2s and 2p orbitals are too far apart, mixing won’t occur. How to Draw Orbital Diagrams - YouTube Orbital diagrams are a visual way to show where the electrons are located within an atom. Orbital diagrams must follow 3 rules: The Aufbau principle, the Pau... Orbital Box Diagram Phosphorus - schematron.org The p orbital can hold up to six electrons. We'll put six in the 2p orbital and then put the next two electrons in the 3s. Since the 3s if now full we'll move to the 3p where we'll place the remaining three electrons. Therefore the Phosphorus electron configuration will be 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 3. A molecular orbital diagram or MO diagram for ... Orbital Diagram of All Elements (Diagrams given Inside) Orbital diagram of Hydrogen (H) 2: Orbital diagram of Helium (He) 3: Orbital diagram of Lithium (Li) 4: Orbital diagram of Beryllium (Be) 5: Orbital diagram of Boron (B) 6: Orbital diagram of Carbon (C) 7: Orbital diagram of Nitrogen (N) 8: Orbital diagram of Oxygen (O) 9: Orbital diagram of Fluorine (F) 10: Orbital diagram of Neon (Ne) 11 ...
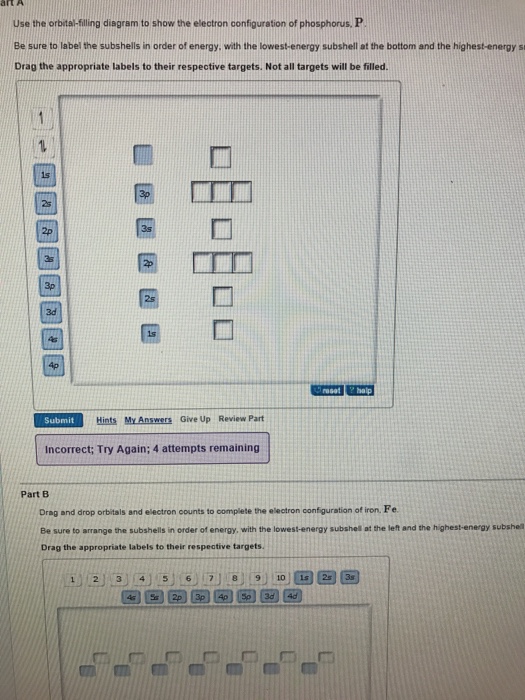
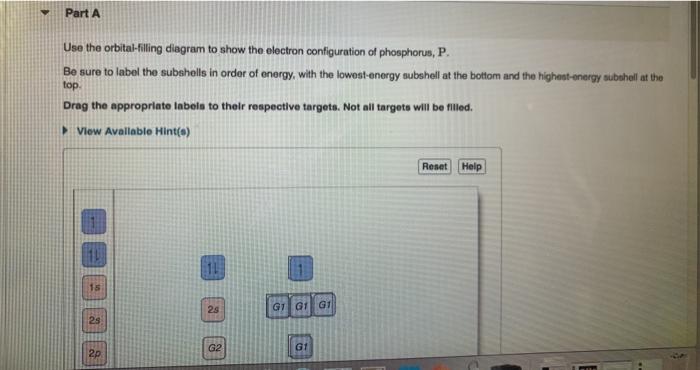
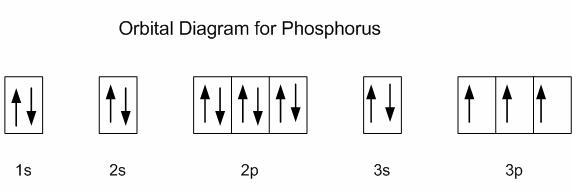
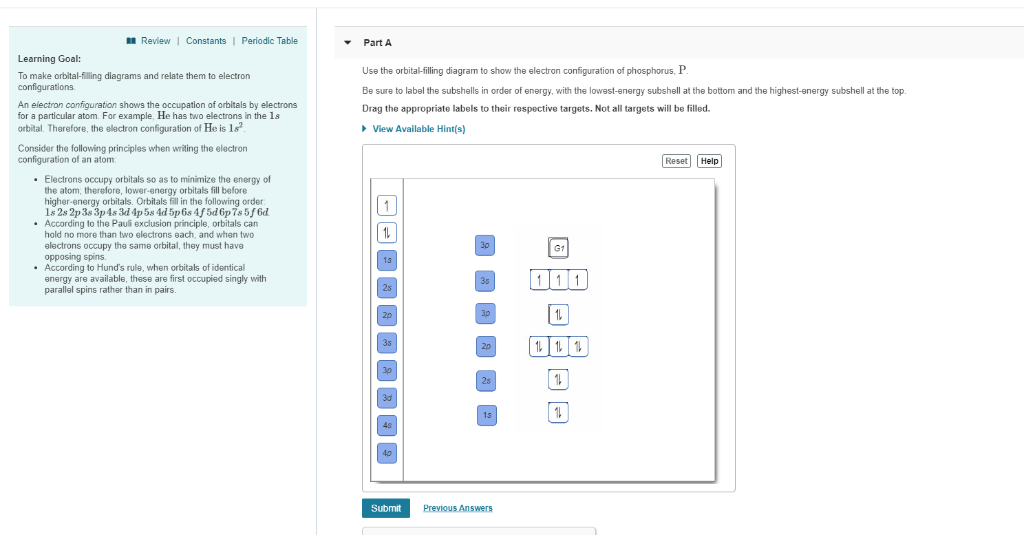
Electron Configuration for Phosphorus (P) - UMD The p orbital can hold up to six electrons. We'll put six in the 2p orbital and then put the next two electrons in the 3s. Since the 3s if now full we'll move to the 3p where we'll place the remaining three electrons. Therefore the Phosphorus electron configuration will be 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 3. Video: Phosphorus Electron Configuration Notation Orbital - Definition, Diagram, Meaning - Study Chemistry Shape of p-orbitals. For p-orbital l = 1 and m = +1, 0, -1. Three values of magnetic quantum number (m) define the three orientations along x, y, z-direction in space. Therefore, p-orbitals are designated as p x, p y, and p z. In the absence of a magnetic or electric field, these three orbitals are equivalent in energy and said to be three-fold ... Krypton Orbital Diagram What does this tell us about electrons in p orbitals? An orbital diagram is similar to electron configuration, except that instead of indicating the atoms by total numbers, each orbital is shown with up and down arrows to represe nt the electrons in each orbital. Refer to the related link to see an illustration of an orbital diagram for aluminum. Bromine Orbital Diagram - Wiring Diagrams Answer to Write the electron configuration and give the orbital diagram of a bromine (Br) atom (Z = 35). Note that in linear diatomic molecules, the p_z orbital always points along the internuclear axis, so it has to contribute to one of the sigma bonds. I've drawn the overlaps below in the MO diagrams.
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Orbital_elementsOrbital elements - Wikipedia Orbital elements are the parameters required to uniquely identify a specific orbit. In celestial mechanics these elements are considered in two-body systems using a Kepler orbit . There are many different ways to mathematically describe the same orbit, but certain schemes, each consisting of a set of six parameters, are commonly used in ... 7.7 Molecular Orbital Theory - Chemistry Fundamentals The relative energy levels of atomic and molecular orbitals are typically shown in a molecular orbital diagram (Figure 7.7.9). For a diatomic molecule, the atomic orbitals of one atom are shown on the left, and those of the other atom are shown on the right. Each horizontal line represents one orbital that can hold two electrons. valenceelectrons.com › sodium-electron-configurationSodium(Na) electron configuration and orbital diagram Sodium(Na) is the 11th element in the periodic table and its symbol is ‘Na’. This article gives an idea about the electron configuration of sodium and orbital diagram, period and groups, valency and valence electrons of sodium, bond formation, compound formation, application of different principles. What Are The 3 Rules For Orbital Diagrams An s-orbital is spherical with the nucleus at its centre, a p-orbitals is dumbbell-shaped and four of the five d orbitals are cloverleaf shaped. The fifth d orbital is shaped like an elongated dumbbell with a doughnut around its middle. The orbitals in an atom are organized into different layers or electron shells. What does 2s orbital look like?
www1.lasalle.edu › ~prushan › IC-articlesPolyatomic Molecular Orbital Theory - La Salle University Molecular Orbital Theory – Walsh diagram The Walsh diagram shows what happens to the molecular orbitals for a set of molecules which are related in structure. In this case, the difference is the H-X-H bond angle which decreases from 180 o to 90 o Molecular Orbital Theory – Walsh diagram Water 104.5 ° X H H H O H
valenceelectrons.com › cobalt-electron-configurationCobalt(Co) electron configuration and orbital diagram The p-orbital can have a maximum of six electrons. So, the next six electrons enter the 2p orbital. The second orbit is now full. So, the remaining electrons will enter the third orbit. Then two electrons will enter the 3s orbital of the third orbit and the next six electrons will be in the 3p orbital. The 3p orbital is now full.
Molecular Orbital Theory - Chemistry However, for atoms with three or fewer electrons in the p orbitals (Li through N) we observe a different pattern, in which the σ p orbital is higher in energy than the π p set. Obtain the molecular orbital diagram for a homonuclear diatomic ion by adding or subtracting electrons from the diagram for the neutral molecule.
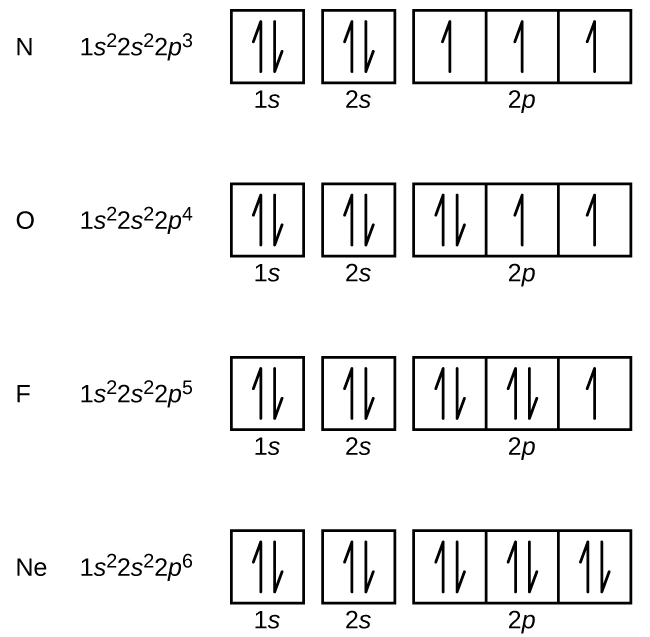
Hund's Rule and Orbital Filling Diagrams | Chemistry for ... Orbital filling diagram for carbon. Oxygen has four 2 p electrons. After each 2 p orbital has one electron in it, the fourth electron can be placed in the first 2 p orbital with a spin opposite that of the other electron in that orbital. Figure 4. Orbital filling diagram for oxygen. Summary
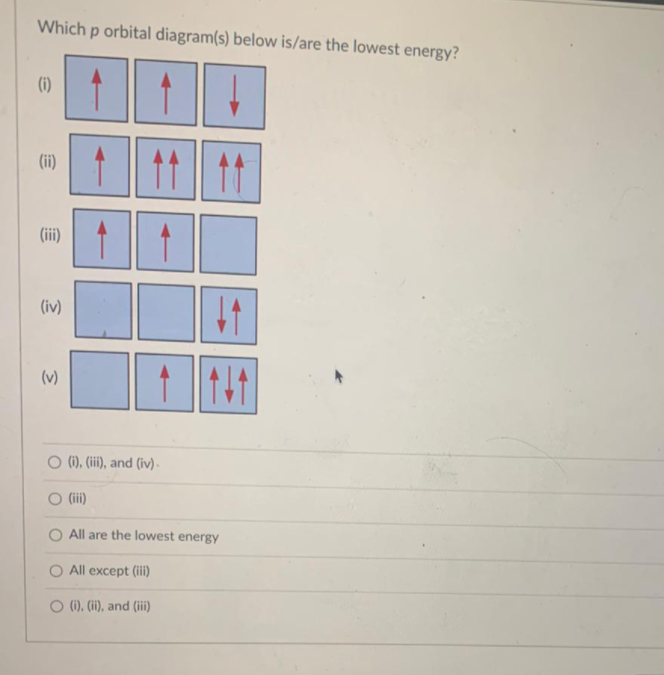
Orbital Diagrams - Concept - Chemistry Video by Brightstorm Orbital diagrams are pictorial descriptions of the electrons in an atom. Three rules are useful in forming orbital diagrams. According to the Auf Bau Principle, each electron occupies the lowest energy orbital. The Pauli Exclusion Principle says that only two electrons can fit into an single orbital.
s,p,d,f Orbitals - Chemistry | Socratic The p orbitals at the second energy level are called 2px, 2py and 2pz. There are similar orbitals at subsequent levels: 3px, 3py, 3pz, 4px, 4py, 4pz and so on. All levels except the first have p orbitals. d ORBITALS
Phosphorus(P) electron configuration and orbital diagram Phosphorus (P) orbital diagram 1s is the closest and lowest energy orbital to the nucleus. Therefore, the electron will first enter the 1s orbital. According to Hund's principle, the first electron will enter in the clockwise direction and the next electron will enter the 1s orbital in the anti-clockwise direction.
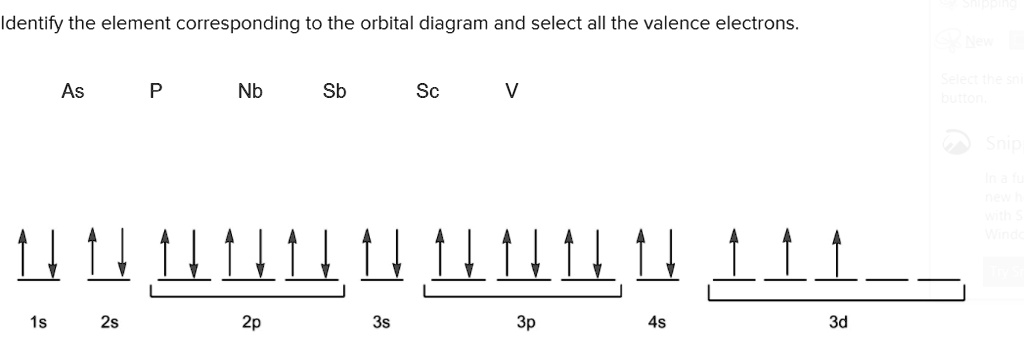
Orbital Diagram For Arsenic - schematron.org Orbital Diagram For Arsenic. Because the 4p section has 3 orbitals, but Arsenic ends with 4p3. It'll want to leave as few orbitals empty, so you have three arrows pointing up. The orbital diagram of arsenic can be written as 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s23p6 4s2 3d10 4p3. Arsenic has 33 electrons, including 3 in itsoutermost shell. schematron.org!
Oxygen(O) electron configuration and orbital diagram The Aufbau principle is that the electrons present in the atom will first complete the lowest energy orbital and then gradually continue to complete the higher energy orbital. These orbitals are named s, p, d, f. The electron holding capacity of these orbitals is s = 2, p = 6, d = 10 and f = 14.
S P D F orbitals Explained - 4 Quantum Numbers, Electron ... This video explains s, p, d, and f orbitals, sublevels, and their shapes. It discusses the 4 quantum numbers n, l, ml, and ms. n represents the energy leve...
How To Draw Molecular Orbital Diagram Of Co - Drawing ... A) draw a molecular orbital (mo) diagram for co and show the filling of electrons. Let's take [co (nh3)6]3+ as an example. For the homonuclear diatomic #o_2#, we simply have two copies of this atomic orbital diagram far apart at first. Electronic configuration of co molecule is: Draw the orbital diagram for the ion co2+.
Orbital Diagrams Chemistry Tutorial - AUS-e-TUTE An orbital diagram, or orbital box diagram, is a way of representing the electron configuration of an atom. A box, line, or circle, is drawn to represent each orbital in the electron configuration (using the Aufau Principle to order the orbitals and hence the boxes, lines or circles, as shown below) 1s → 2s → 2p x 2p y 2p z → 3s → 3p x 3p y 3p z →
Orbital filling diagrams - The Cavalcade o' Chemistry The orbital filling diagram of boron. I skipped past beryllium because I was getting bored. The electron configuration of boron is 1s²2s²2p¹, which means that there are two electrons in the 1s orbital, two electrons in the 2s orbital, and one electron in the 2p orbitals. This gives us an orbital filling diagram of:
Sodium Orbital diagram, Electron configuration, and ... Orbital diagram:-A orbital diagram is simply a pictorial representation of the arrangement of electrons in the orbital of an atom, it shows the electrons in the form of arrows, also, indicates the spin of electrons.Electron configuration:- Electron configuration is the arrangement of electrons in atomic orbitals.It shows the electrons in numbers, It doesn't show the details on the spin of ...
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Molecular_orbital_diagramMolecular orbital diagram - Wikipedia A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of ...
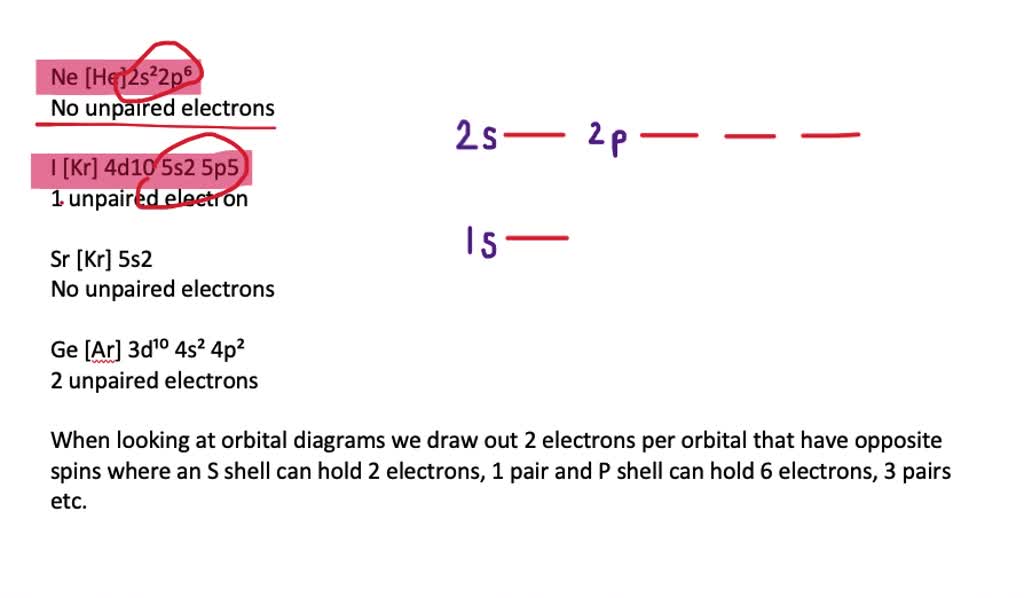
write orbital diagrams for the valence electrons and indicate the number of unpaired electrons for 2
Carbon Orbital diagram, Electron configuration, and ... The orbital diagram for Carbon is drawn with 3 orbitals. The orbitals are 1s, 2s, and 2p. The Carbon orbital diagram contains 2 electrons in 1s orbital, 2 electrons in 2s orbital, and the rest two electrons in 2p orbital. Orbital diagram for a ground-state electron configuration of Carbon atom is shown below-
How do yo write the orbital diagram for oxygen? | Socratic The electron configuration for oxygen is: 1s^2 2s^2 2p^4 This video will walk you through the step of writing orbital diagram. The video uses Kr as an example, but the process is exactly as the same as what you need to do for oxygen. Hope this helps!
PDF Electron Configurations and Orbital Diagrams key 1. Describe the two differences between a 2p x orbital and a 3p y orbital. The 2px orbital lies on the x-axis. The 3py orbital lies on the y-axis and is larger than the 2px orbital. 2. The lobes of a p orbital disappear at the nucleus. What does this tell us about electrons in p orbitals?










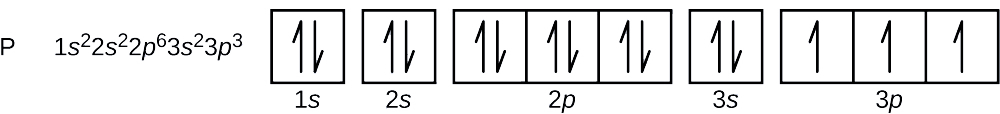



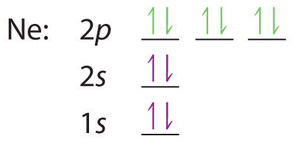








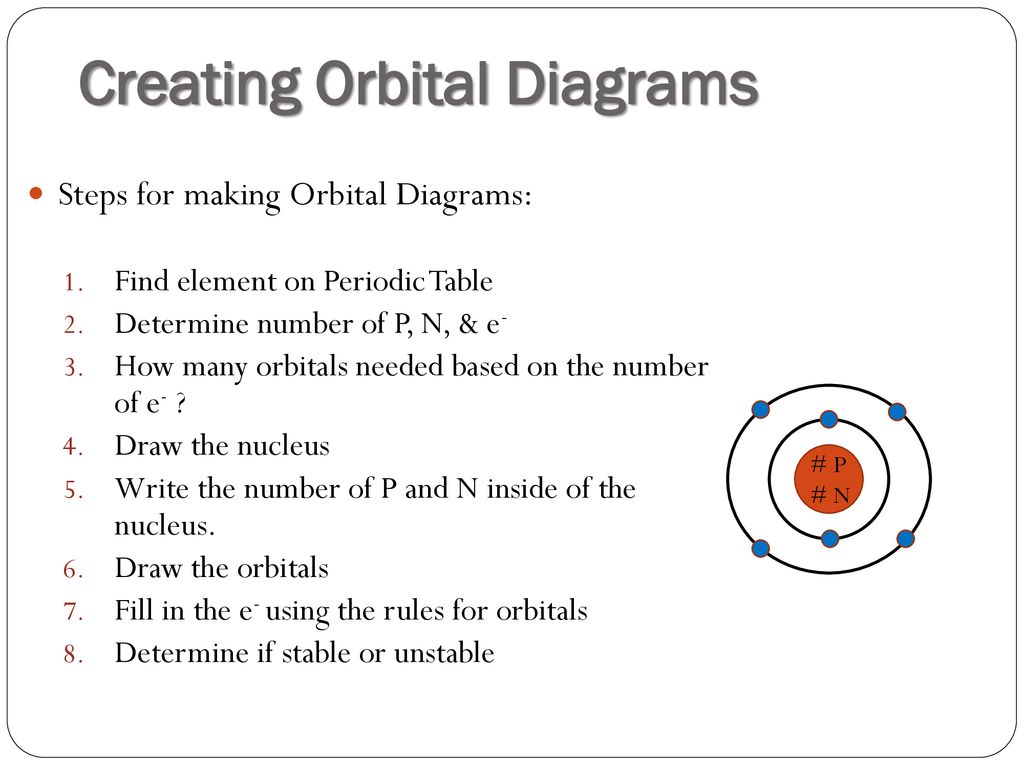


0 Response to "41 orbital diagram for p"
Post a Comment