38 law of reflection diagram
› reviews › Reflection-andReflection and Mirrors Review - Answers #1 Answer: D. The angle of incidence is the angle between the incident ray and the normal. As this angle approaches 90 degrees, the reflected ray also approaches a 90 degree angle with the normal; thus, the angle between the incident and reflected ray approach 180 degrees. reflection - Louisiana State University 1) Students should be able to state the law of reflection and draw a ray diagram to illustrate it. 2) Students should be able to apply the law of reflection to predict the position of images formed by objects in front of a planar mirror. Material required: 1) Full length mirror hung horizontally
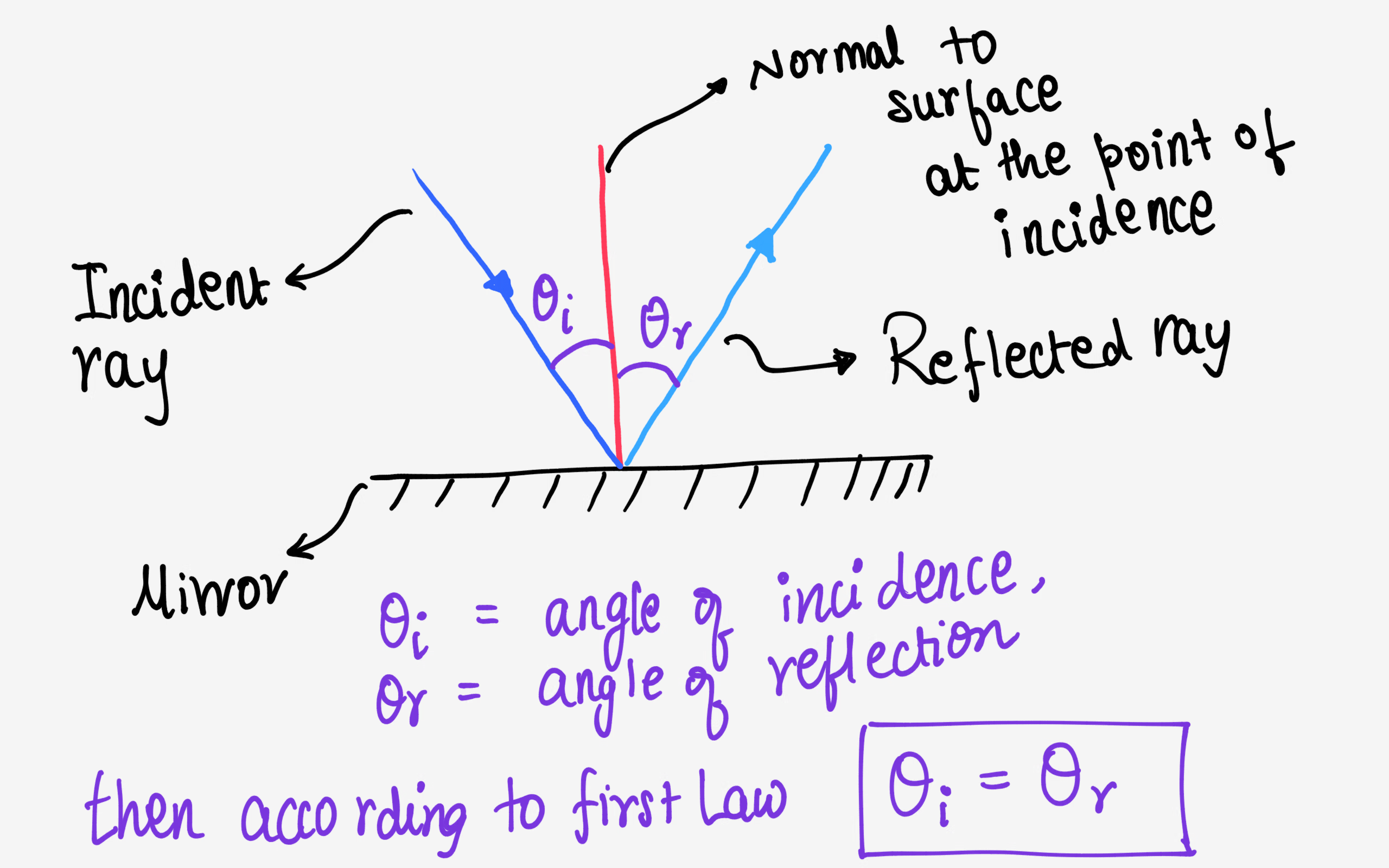
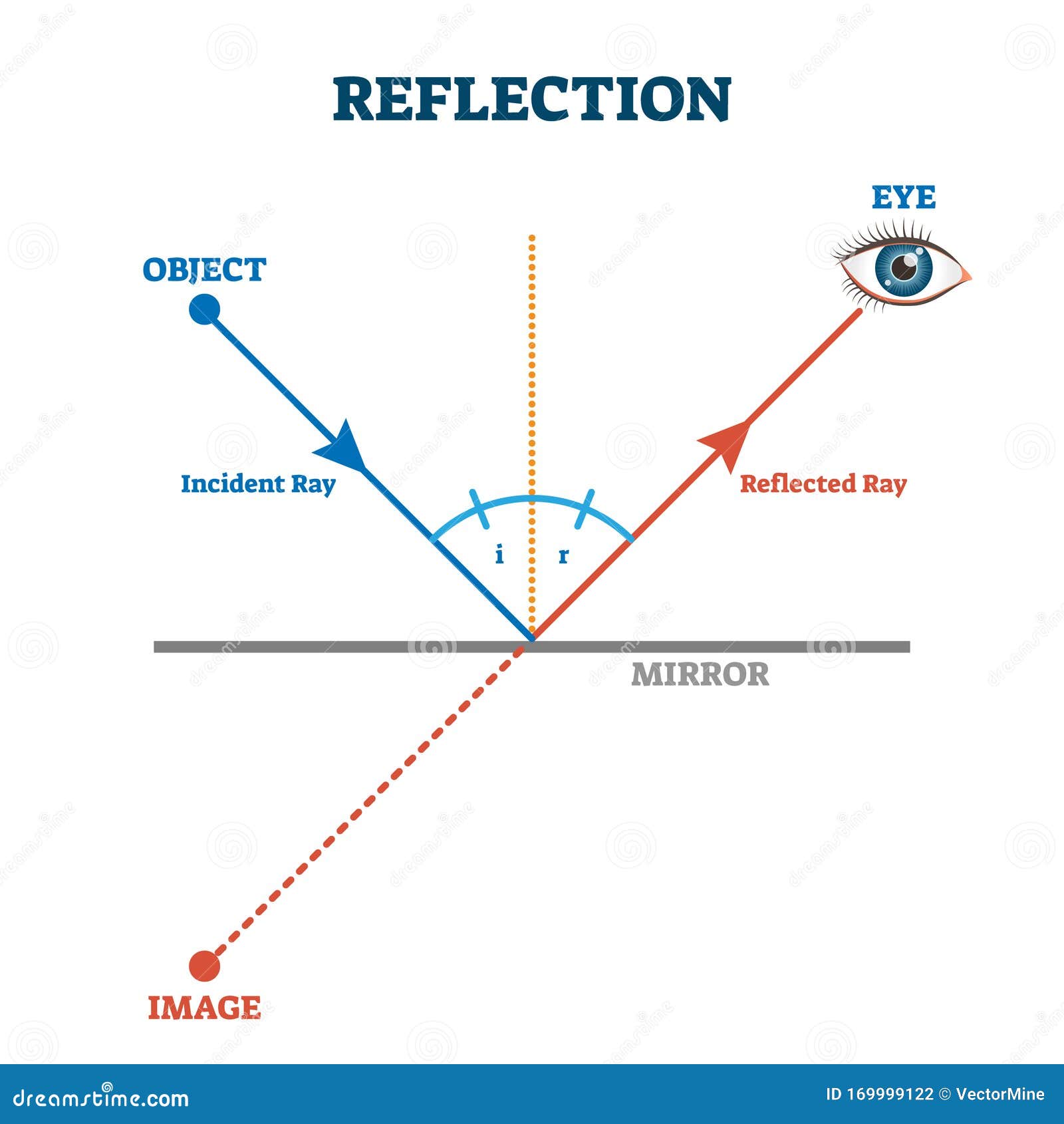
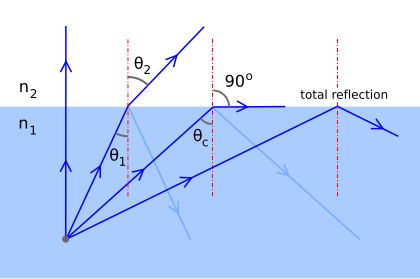
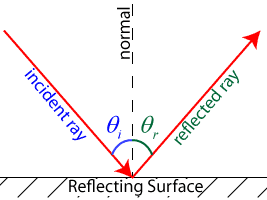
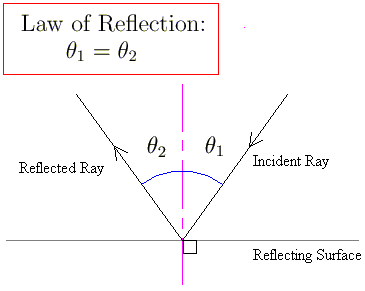
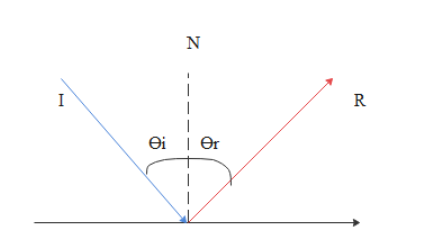
state the law of reflection of light with diagram - Brainly.in The diagram below illustrates the law of reflection. In the diagram, the ray of light approaching the mirror is known as the incident ray (labeled I in the diagram). ... The law of reflection states that when a ray of light reflects off a surface, the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. search. rotate.

Law of reflection diagram
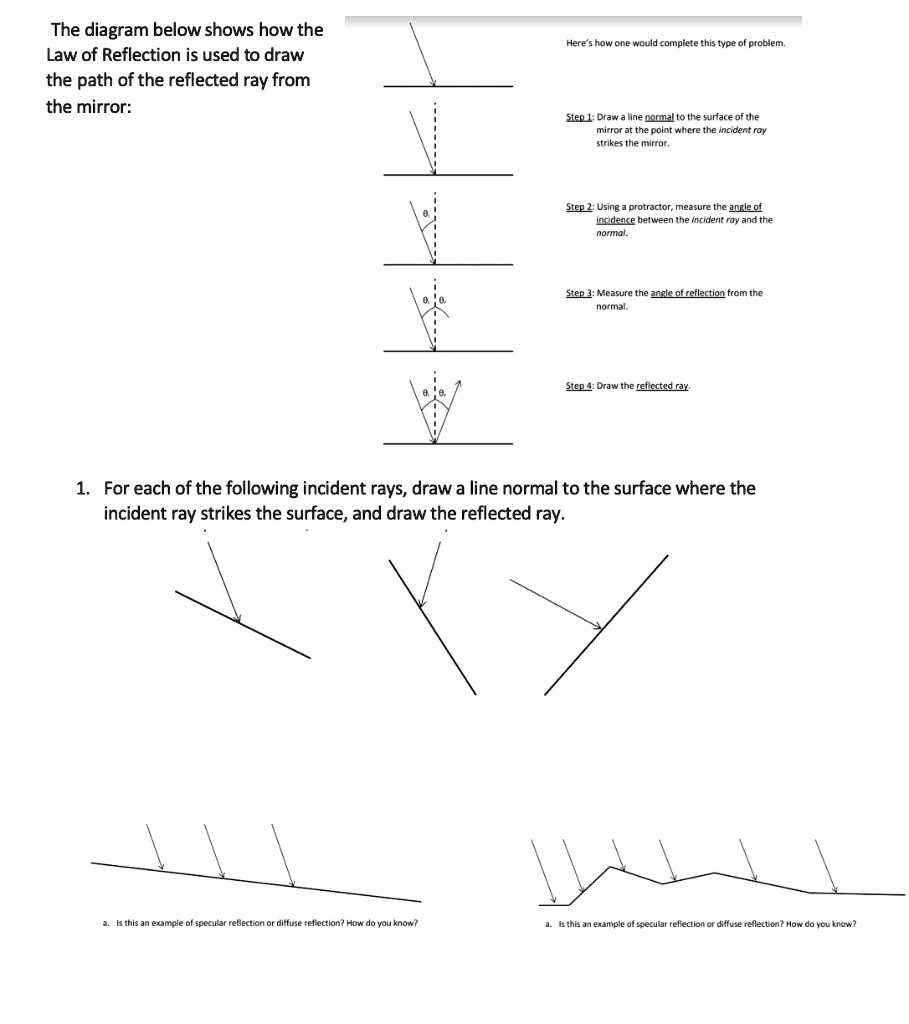
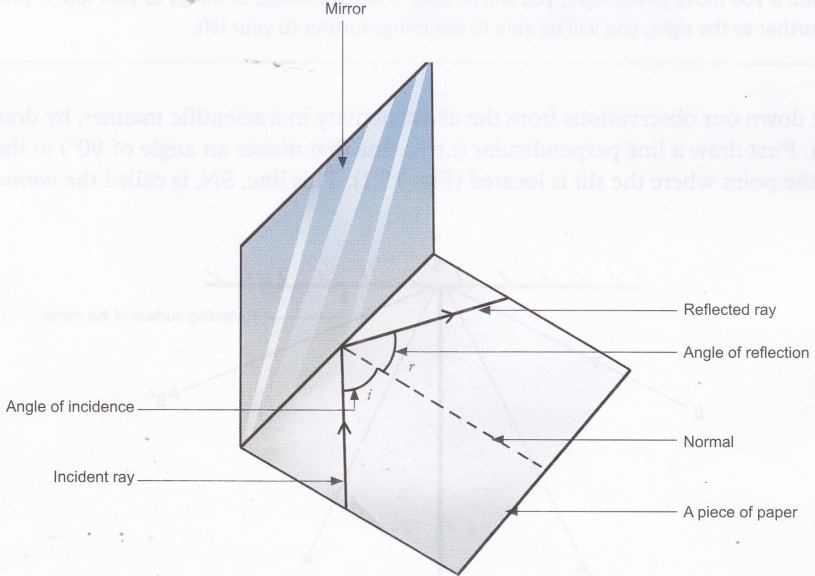
PDF Light Reflection - Physics Classroom 2. These diagrams are intended to represent the path of light from an object to an eye as the eye sights at the image of the object. Each diagram is incorrect. Discuss what makes them incorrect. a. Discussion: b. Discussion: 3. State the law of reflection in the space below. Consider the diagram at the right in answering the next three ... Physics Tutorial: The Law of Reflection The diagram below illustrates the law of reflection. In the diagram, the ray of light approaching the mirror is known as the incident ray (labeled I in the diagram). The ray of light that leaves the mirror is known as the reflected ray (labeled R in the diagram). Light and Reflection Diagram Skills E STI 500 Mirrot Flat ... The law of reflection allows to find the results for the questions about ray reflection in a plane mirror are: a) Attachment we see a diagram of the incident and reflected rays, incident and reflected angles are equal. b) The extension of the reflected rays is what forms the image.
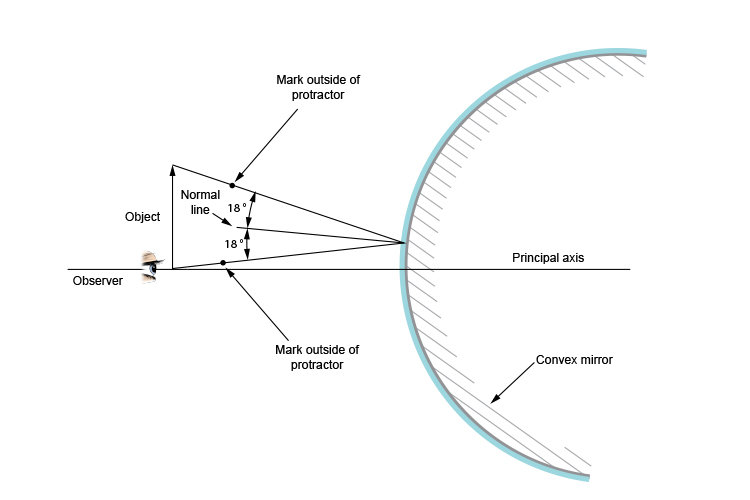
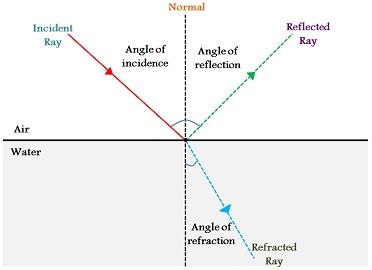
Law of reflection diagram. byjus.com › physics › concave-convex-mirrorsConcave Mirrors And Convex Mirrors - Image Formation, Ray Diagram A ray passing through the center of curvature of the spherical mirror will retrace its path after reflection. Image Formation By Concave Mirror By changing the position of the object from the concave mirror, different types of images can be formed. Reflection - Light waves - KS3 Physics Revision - BBC Bitesize The law of reflection states that the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection, i = r. It works for any angle. For example: the angle of reflection is 30° if the angle of incidence is 30 ... Huygens' Principle: Proving the Law of Reflection | Study.com The law of reflection tells us that the incident angle ( θi) of a light ray striking a surface is equal to the reflected angle ( θr) of the ray bouncing off of it. Here we see the two light rays... What is law of reflection short definition? - Runyoncanyon ... The three laws of reflection are. 1. The angle between the incident ray and the normal is equal to the angle between the reflected ray and the normal. 2. The incident ray, the normal and the reflected ray are all in the same plane. 3. Incident ray and refracted ray are on different sides of the normal. How can the law of reflection be explained?
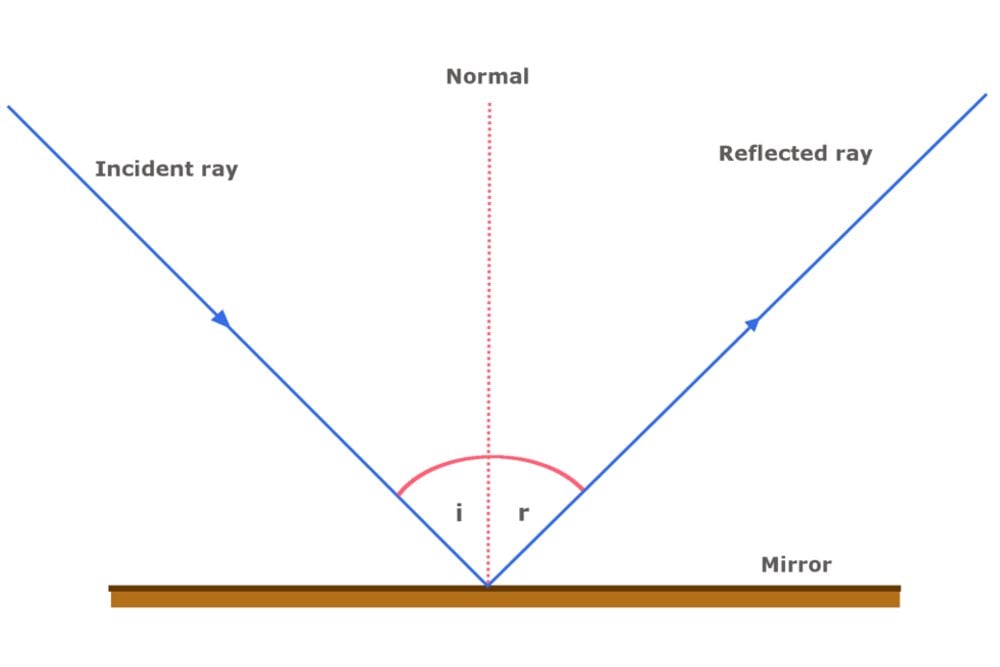
What is Law of Reflection | what is Ray Diagram ... Laws of Reflection #reflectionlaws #Raydiagram #optics #Physics what is Law of Reflection?what is Ray Diagram?In this video the Reflection of light is exp... Sample Problems for The Law of Reflection When light is reflected from a surface, the angle of incidence is always equal to the angle of reflection, where both angles are measured from the path of the light to the normal to the surface at the point at which light strikes the surface. This equality is known as the law of reflection. Sample Problem 1: State the laws of reflection. Draw a diagram to show ... First, we consider reflection, as shown in the diagram below for a light wave striking a surface. We identify the incoming ray as the incident ray and the outgoing ray as the reflected ray. Concomitantly, the angleθ i that the incoming ray makes with a line (dashed in the diagram) normal to the surface is called the angle of incidence. The three laws of reflection - Mammoth Memory The three laws of reflection are 1. The angle between the incident ray and the normal is equal to the angle between the reflected ray and the normal 2. The incident ray, the normal and the reflected ray are all in the same plane 3. Incident ray and refracted ray are on different sides of the normal Law 1 explained
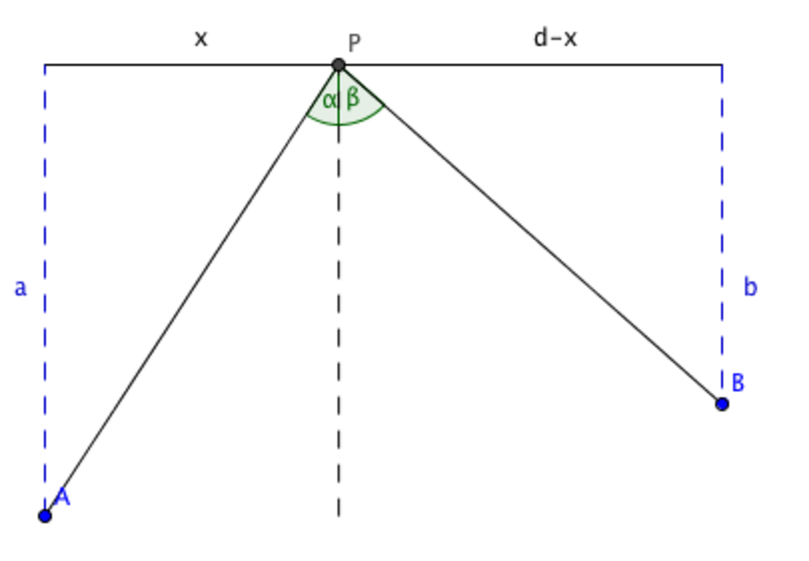
byjus.com › physics › electrical-forceElectrical Force - Definition, Diagram, Examples, Coulomb's Law Coloumb’s law is an experimental law that quantifies the amount of force between two stationary electrically charged particles. The electric force between stationary charged body is conventionally known as the electrostatic force or Coloumb’s force. Coulomb’s law describes the amount of electrostatic force between stationary charges. PhysicsLAB: Reflection The ray diagram below shows the reflection of one of the rays that strikes the parabolic mirror. Notice that the law of reflection is obeyed, and the angle of incidence (from the normal, the dashed line) equals the angle of reflection (from the normal). Complete the diagram by drawing the reflected rays of the other three rays that are shown. Law of reflection - Reflection and refraction of light ... the angle of reflection, r, is the angle between the normal and reflected ray. The law of reflection states that: angle of incidence i = angle of reflection r. For example, if a light ray hits a... The reflection of light - Boston University The first is the parallel ray; it is drawn from the tip of the object parallel to the principal axis. It then reflects off the mirror and either passes through the focal point, or can be extended back to pass through the focal point. The second ray is the chief ray.
The Law of Reflection | Physics - Lumen Learning The law of reflection states that the angle of reflection equals the angle of incidence— θr = θi. The angles are measured relative to the perpendicular to the surface at the point where the ray strikes the surface.
› Concept-BuildersBalanced vs. Unbalanced Forces Interactive Each interactive concept-builder presents learners with carefully crafted questions that target various aspects of a discrete concept. There are typically multiple levels of difficulty and an effort to track learner progress at each level.
Law of Reflection (Diagram) Diagram | Quizlet Angle of Reflection The angle measured between the reflected ray and the normal. Mirror Smooth, shiny surfaces make the best mirrors. The flat side on the diagram is the shiny side. Law of Reflection (plane mirror) Angle of incidence = Angle of Reflection Sets with similar terms Light and wave terms 13 terms Caleb_Sowah
What is the Law of Reflection: Definition and A Simple ... This is basically what the law of reflection is all about. Here's a diagram to help you visualize the law of reflection a bit better: Angle of incidence and angle of reflection In the diagram above, the light ray approaching the mirror is known as the incident ray, while the one that bounces off the mirror is called the reflected ray.
Mirrors, Law of Reflection, and Ray Diagrams Quiz - Quizizz Q. In the given figure, which of the following holds TRUE? answer choices. The angle of incidence is 10°. The angle of incidence is 80°. The angle of reflection is 10°. The angle of reflection is 90°. The angle of incidence is 10°.. alternatives.
State the laws of Reflection along with a suitable diagram. There are two basic laws of reflection of light - (i) The incident ray the reflected ray and the normal to the reflecting surface at the point of incidence lie in the same plane ; (ii) The angle of incidence is always equal to angle of reflection i.e ∠ i = ∠r Was this answer helpful? 0 0
Using the law of reflection - Ray diagram rules Using the law of reflection - Ray diagram rules When we observe an object in a convex mirror there are three ways to try to work out how the light rays from an object focus into the eye of an observer. Use the ray diagram flat/plane mirror rules Use the laws of reflection Use new ray diagram rules and create a virtual image
The Laws of Reflection and Refraction First, we consider reflection, as shown in the diagram below for a light wave striking a surface. We identify the incoming ray as the incident ray and the outgoing ray as the reflected ray. Concomitantly, the angle ?i that the incoming ray makes with a line (dashed in the diagram) normal to the surface is called the angle of incidence.
What is Reflection of Light? - Definition, Laws, Types & Video The law of reflection states that The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal all lie in the same plane The angle of incidence = Angle of reflection 2,63,148 Types of Reflection of Light Different types of reflection of light are briefly discussed below: Regular reflection is also known as specular reflection Diffused reflection
Laws Of Reflection: Definition, Types, Diagrams ... According to the Law of Reflection, θ = θ r Hence, Angle of Reflection = 60° Q2: A light ray strikes a reflective plane surface at an angle of 54° with the surface. (i) Calculate the angle of incidence. (ii) Calculate the angle of reflection. (iii) Calculate the angle made by the reflected ray and the surface.
Law of Reflection Lab.docx - Law of Reflection Lab In this ... Law of Reflection Lab In this lab we will review a ray diagram for mirrors. Materials: Laser CPO Optics bench Graph Paper Mirror Protractor Procedure: 1. Set up the CPO Light and Optics base on a table/desk and connect the AC adapter. 2. Connect the laser to any socket on the side of the CPO Light and Optics base.
Laws of Reflection - First and Secons Law with Examples According to the law of light, the angle of reflection where the reflected ray hits an object. The angle of reflection is created when the ray hits the object and bounces back to the opposite direction. The angle of reflection is only created by the reflected ray. There can be a single angle of reflection for a single reflected ray of light. 4.
Law of Reflection | Physics Quiz - Quizizz Question 3. SURVEY. 30 seconds. Q. The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. answer choices. law of light. law of reflection. law of refraction.
PhysicsLAB: Video: Law of Reflection Sample Diagram The Law of Reflection states that when waves are reflected from an interface, the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. The purpose of this lab is to experimentally verify this outcome. Given below are a sample screen capture and an accompanying image showing an example of the corresponding ray and angle constructions.
Light and Reflection Diagram Skills E STI 500 Mirrot Flat ... The law of reflection allows to find the results for the questions about ray reflection in a plane mirror are: a) Attachment we see a diagram of the incident and reflected rays, incident and reflected angles are equal. b) The extension of the reflected rays is what forms the image.
Physics Tutorial: The Law of Reflection The diagram below illustrates the law of reflection. In the diagram, the ray of light approaching the mirror is known as the incident ray (labeled I in the diagram). The ray of light that leaves the mirror is known as the reflected ray (labeled R in the diagram).
PDF Light Reflection - Physics Classroom 2. These diagrams are intended to represent the path of light from an object to an eye as the eye sights at the image of the object. Each diagram is incorrect. Discuss what makes them incorrect. a. Discussion: b. Discussion: 3. State the law of reflection in the space below. Consider the diagram at the right in answering the next three ...













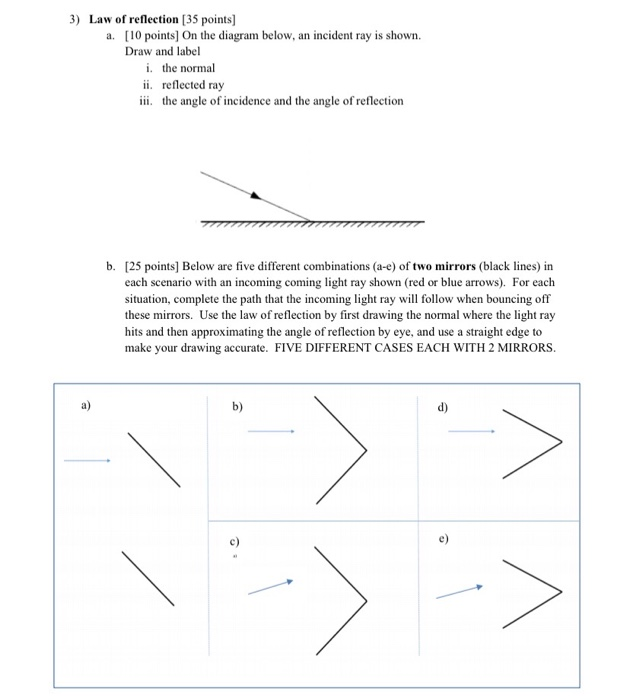
![Solved 2) Law of reflection [35 points] a. [10 points] On ...](https://media.cheggcdn.com/media%2F1eb%2F1ebb8037-d34b-45a6-a7dd-e7d711b040c5%2FphpB6Fcqx.png)






0 Response to "38 law of reflection diagram"
Post a Comment