40 heteronuclear molecular orbital diagram
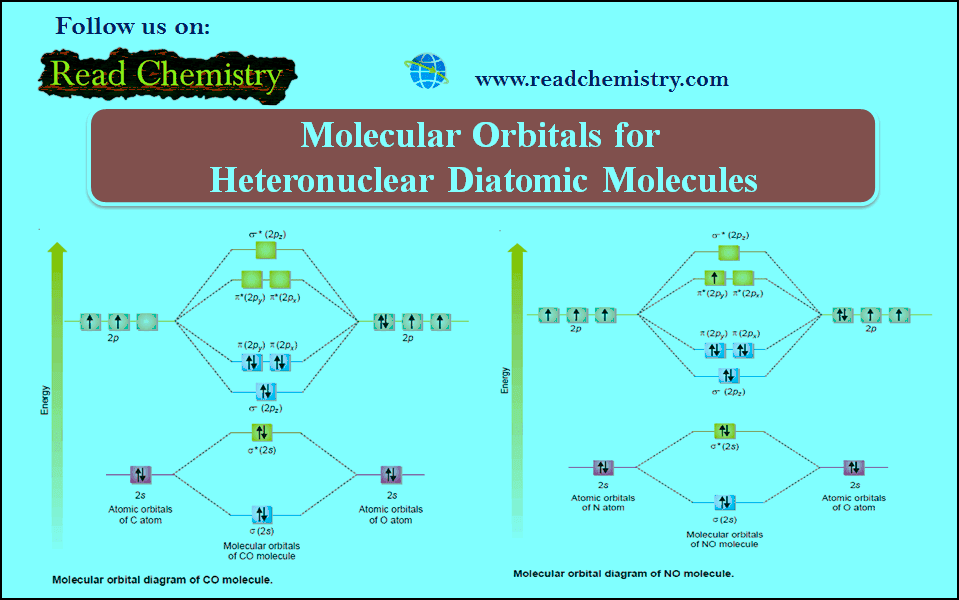
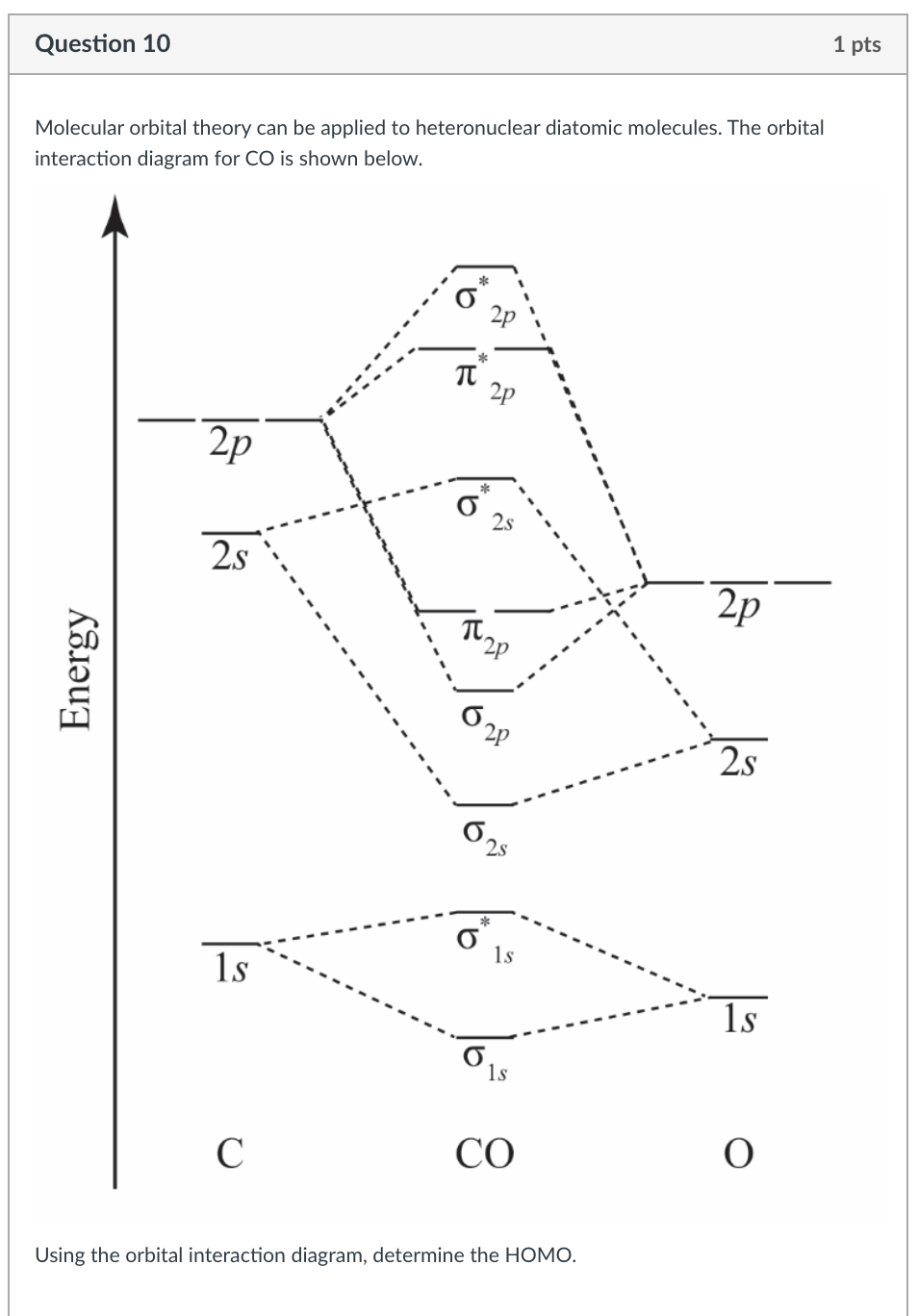
D6.5 MOs for Heteronuclear Diatomic Molecules - Chemistry ... Diatomic molecules with two non-identical atoms are called heteronuclear diatomic molecules, examples include CO, NO and HCl. Molecular orbital diagrams for these molecules have one more layer of complexity, but they also serve to explain many bond and molecular properties we will encounter later on in the course. Let's consider CO as an example. Molecular Orbital Theory Heteronuclear Diatomic (Cyanide ... Dr. Shields shows you how to draw the MO correlation diagram for cyanide (CN-), calculate the MO bond order, and write the MO electron configuration with an ...
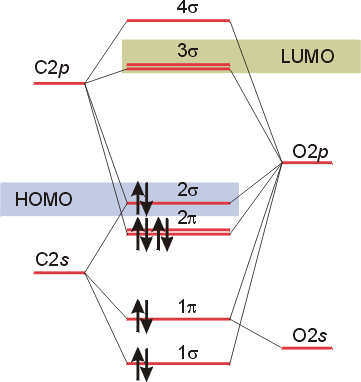
Hf Molecular Orbital Diagram - Summarized by Plex.page ... Heteronuclear Diatomic Molecules Diatomicconsisting of two atoms heteronuclearhaving different types of atoms nuclei in heteronuclear diatomic molecules, atomic orbitals only mix when electronegativity values are similar. In carbon monoxide, oxygen 2s orbital is much lower in energy than carbon 2s orbital, the degree of mixing is low.
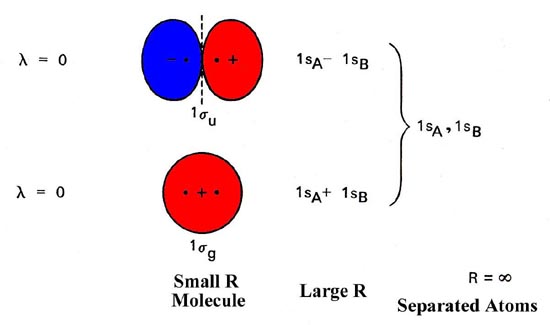
Heteronuclear molecular orbital diagram
8 - Drawing Molecular Orbital Diagrams — Flux Science Nov 12, 2021 · Molecular Orbital Diagram. As we’ve established (link to last lesson), bonding and antibonding interactions are the key to molecular orbital theory. In fact, the idea of molecular orbitals, the distribution of electrons across a molecule, arises from how electrons distribute themselves energetically. ... Heteronuclear Molecular Orbitals ... Solved Question 7 3 points Save A Draw the molecular ... Question 7 3 points Save A Draw the molecular orbital diagram (MO diagram) for the heteronuclear diatomic species CF to answer the following questions. Only show the valence Atomic orbitals and valence Molecular orbitals. The order of MO energy levels for CF will be the same as for the O2 homonuclear diatomic molecule. (PDF) Inorganic Chemistry 4th edition ... - Academia.edu Academia.edu is a platform for academics to share research papers.
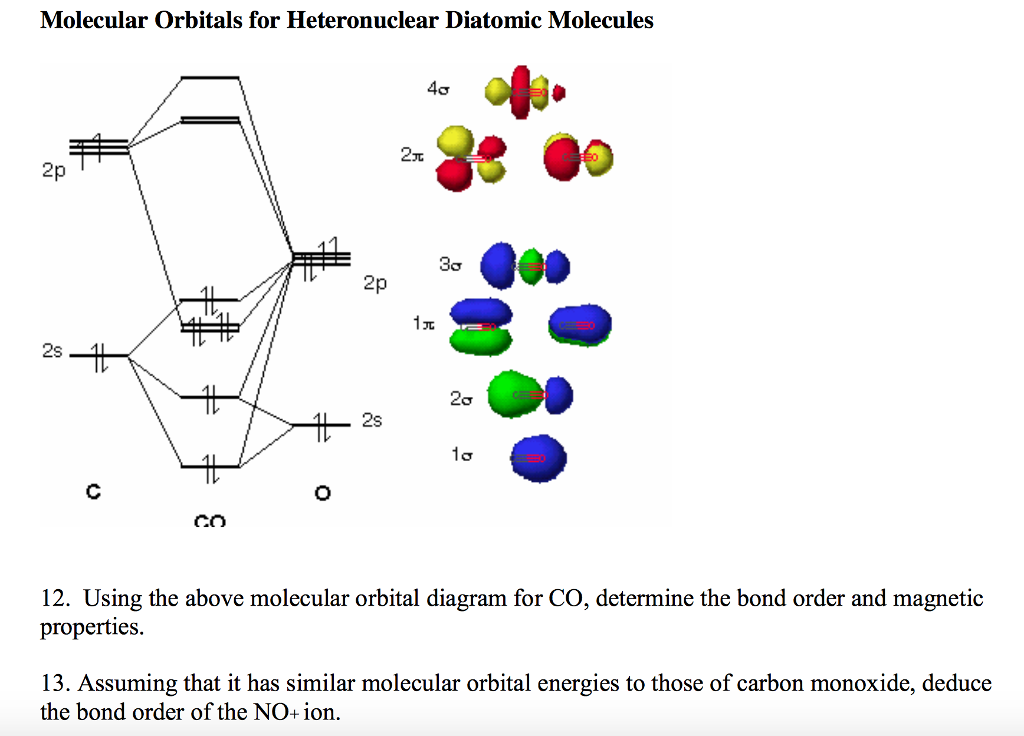
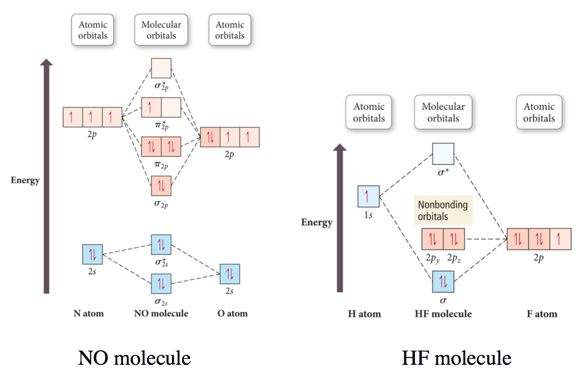
Heteronuclear molecular orbital diagram. Solved Molecular Orbitals for Heteronuclear Diatomic ... Molecular Orbitals for Heteronuclear Diatomic Molecules Using the above molecular orbital diagram for CO, determine the bond order and magnetic properties. Assuming that it has similar molecular orbital energies to those of carbon monoxide, deduce the bond order of the NO+ ion. Difference Between Homonuclear and Heteronuclear Diatomic ... Key Difference - Homonuclear vs Heteronuclear Diatomic Molecules Diatomic molecules are substances composed of two atoms per molecule. These molecules are composed of two atoms bonded to each other via covalent chemical bonds.The atoms can be bonded via single bonds, double bonds or triple bonds. Depending on the types of atoms present in the diatomic molecule, there are two types of ... Bioprofe | Chemistry | Molecular Orbital Theory This method, called molecular orbital theory, begins with a simple description of the molecules, but quickly becomes complex in the details. Theory assigns the electrons of a molecule to a series of orbitals that belong to the complete molecule, which are the so-called molecular orbitals. In the same way as atomic orbitals, molecular orbitals ... MO Theory: Heteronuclear Diatomic Molecules - Chemistry ... Molecular Orbital Diagrams of Heteronuclear Diatomics. Concept #1: Molecular Orbital Diagrams of Heteronuclear Diatomics ... Report issue. Example #1: Construct the Molecular Orbital Diagram for carbon monoxide, CO. Report issue. Practice: Apply Molecular Orbital Theory to determine the MO orbital diagram for the CF + ion.
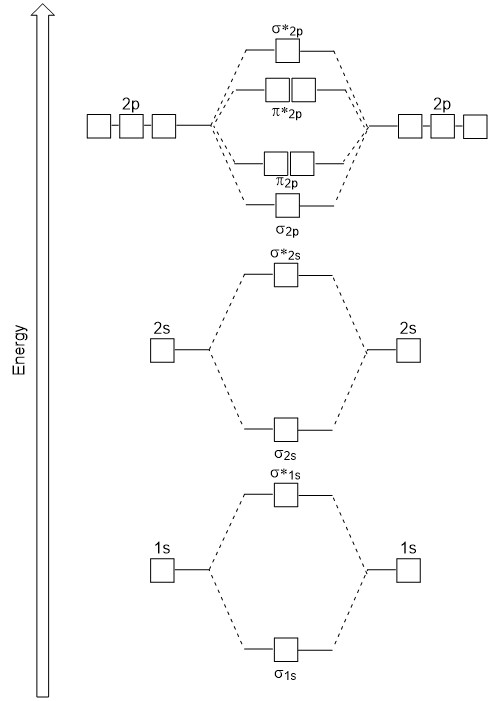
What is the bond order of the heteronuclear diatomic ... What is the bond order of the heteronuclear diatomic molecule no? Because 10 electrons are sufficient to fill all the bonding molecular orbitals derived from 2p atomic orbitals, the 11th electron must occupy one of the degenerate π * orbitals. The predicted bond order for NO is therefore (8-3) ÷ 2 = 2 1/2 . Click to see full answer. Molecular orbital diagram - Wikipedia A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine … (PDF) Inorganic Chemistry by Miessler ~ 5th Edition ... This book is ideal for who want to use a strong molecular-orbital approach to explain structure and reactivity in inorganic chemistry. . × Close Log In. Log in with Facebook Log in with Google. or. Email. Password. Remember me on this computer. or reset password. Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link. ... MO Diagrams for Diatomic Molecules Summary MO Theory • LCAO-MO Theory is a simple method for predicting the approximate electronic structure of molecules. • Atomic orbitals must have the proper symmetry and energy to interact and form molecular orbitals. • Photoelectron spectroscopy provides useful information on the energies of atomic orbitals. • Next we'll see that symmetry will help us treat larger molecules in
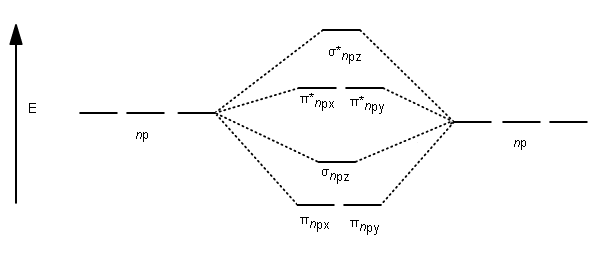
Molecular Orbitals - Molecular Orbitals for Heteronuclear ... The molecular orbitals which describe the motion of a single electron in a molecule containing two unequal nuclear charges will not exhibit the g and u symmetry properties of the homonuclear diatomic case. The molecular orbitals in the heteronuclear case will in general be concentrated more around one nucleus than the other. 03 Molecular Orbitals of Heteronuclear Diatomics | Susan ... 03 Molecular Orbitals of Heteronuclear Diatomics. Exercise 3.1: LCAO of Heteronuclear Diatomics. 100 KB. Exercise 3.1: LCAO of Heteronuclear Diatomics (Answers) 110 KB. Exercise 3.2: Molecular Orbital Diagrams of Heteronuclear Diatomics. 139 KB. Exercise 3.2: Molecular Orbital Diagrams of Heteronuclear Diatomics (Answers) 173 KB. Diatomic Molecule: Definition & Example - Video & Lesson ... Oct 26, 2021 · A diatomic molecule is one that is composed of two atoms of the same element and is either homonuclear or heteronuclear. Discover more about the definition and countless examples of diatomic ... PDF The molecular orbital - Darbhanga College of Engineering 2. Individual atomic orbitals (AO) are arranged on the far left and far right of the diagram. 3. Overlapping atomic orbitals produce molecular orbitals located in the middle of the diagram. These MO overlap with either a sigma or pi bond and are designated in bonding, nonbonding, or antibonding orbitals with respect to their phases. 4.
molecular orbital theory - How to know whether s-p mixing ... The general description is that there are two equivalent O-H s p X 3 sigma bonds and two equivalent lone pairs, also in s p X 3 orbitals. The lone pair - lone pair repulsion is greater than the sigma bond - sigma bond repulsion, so the lone pair-O-lone pair angle opens up slightly and the H − O − H angle closes down to the observed 104.5 degrees.
9.8: Molecular Orbital Theory - Chemistry LibreTexts Feb 20, 2022 · Molecular Orbital Diagrams. This scheme of bonding and antibonding orbitals is usually depicted by a molecular orbital diagram such as the one shown here for the dihydrogen ion H 2 +. Atomic valence electrons (shown in boxes on the left and right) fill the lower-energy molecular orbitals before the higher ones, just as is the case for atomic ...
Molecule - Wikipedia A molecule is a group of two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions which satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and biochemistry, the distinction from ions is dropped and molecule is often used when referring to polyatomic ions.. In the kinetic theory of gases, the term molecule is …
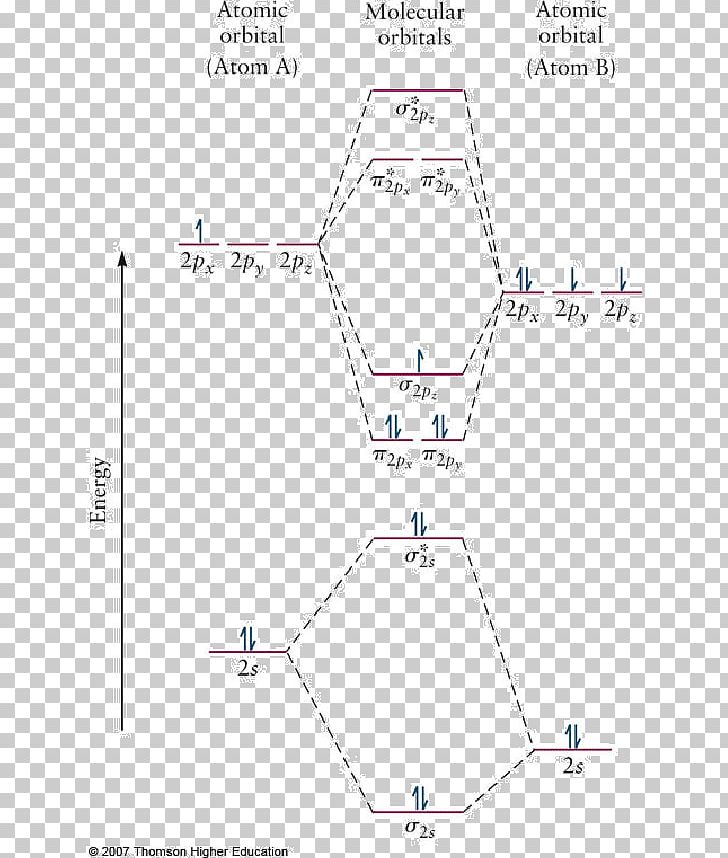
4.10: Second-Row Diatomic Molecules - Chemistry LibreTexts Figure 4.10.4: Molecular Orbital Energy-Level Diagram for a Heteronuclear Diatomic Molecule AB, Where χ B > χ A. The bonding molecular orbitals are closer in energy to the atomic orbitals of the more electronegative B atom. Consequently, the electrons in the bonding orbitals are not shared equally between the two atoms.
Molecular Orbitals - Introductory Chemistry - 1st Canadian ... Heteronuclear Diatomic Molecules. In heteronuclear diatomic molecules, where two different molecules are bonded, the energy levels of the individual atoms' atomic orbitals may differ. However, the molecular orbital diagram we see in Figure 9.25 ("Molecular orbital energy diagram for homonuclear diatomic molecules made from atoms of atomic ...
Molecular orbitals of heteronuclear diatomic molecules and ... By definition, electrons in nonbonding orbitals have no effect on bond order, so they are not counted in the calculation of bond order. Thus, the predicted bond order of HCl is (2 − 0) ÷ 2 = 1. Because the σ bonding molecular orbital is closer in energy to the Cl 3 p z than to the H 1 s atomic orbital, the electrons in the σ orbital are concentrated closer to the chlorine atom than to ...
How do you use molecular orbital diagrams? FUNDAMENTAL STEPS IN DERIVING MO DIAGRAMS Find the valence electron configuration of each atom in the molecule. Decide if the molecule is homonuclear of heteronuclear. Fill molecular orbitals using energy and bonding properties of the overlapping atomic orbitals. Use the diagram to predict properties of the molecule.
PDF Heteronuclear Molecules Diagram with MO shapes 2-59 Hybridization • Molecular Orbital Theory: -> Electrons are delocalized over entire molecule (including core shell electrons!)
Heteronuclear Molecular orbital diagram - Summarized by ... In heteronuclear diatomic molecules, atomic orbitals only mix when the electronegativity values are similar. A s orbital on hydrogen could be involved in a molecular orbital picture of HF, as seen by a s orbital on fluorine in a molecular orbital picture of HF.
PDF Molecular Orbitals of Heteronuclear Diatomics The molecular orbitals of heteronuclear diatomics (HF, CO, CN-, etc.) can be predicted using the same principles that we used to construct the molecular orbitals of homonuclear diatomics: i) Ignore the coreelectrons ii) Remember that the total number of MOs = total number of AOs iii) Only AOs of similar energycombine.
PCl5 Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry, Hybridization ... Apr 15, 2022 · Molecular Orbital Theory and MO diagram of PCl5. Molecular Orbital theory makes use of Molecular Orbital diagrams to showcase a clear picture of the state of electrons in an atom. While the Valence Bond theory and VSPER give an idea of an atom’s properties, it is not useful in the case of certain molecules.
How To Draw Molecular Orbital Diagram For Heteronuclear ... How to draw molecular orbital diagram for heteronuclear molecules. Now, mo diagrams are only simple for elements of the second row of the periodic table ($\ce{li}$ through $\ce{ne}$). You have now 2 electrons left,. It is a linear molecule. Consider the h 2 molecule, for example. The lewis structure shows that the beryllium in beh 2 makes 2 ...
Molecular Orbital Theory Diatomic molecules Heteronuclear ... Chem 59 -250 Molecular Orbital Theory Polyatomic molecules The steps you can use to build a MO diagram for any polyatomic molecule are: 1. Determine the symmetry of the molecule and figure out which atoms are symmetry related. e. g. Be. H 2 su sg 2.
Gibb's Phase Rule Questions and Answers - Sanfoundry Select the wrong statements from the following statements with respect to a phase diagram. a) Gives information about concentration b) Gives information about solubility ... Valence Bond Theory Hybridisation Molecular Orbital Theory Heteronuclear Molecules. Structure & Stereostructure of Molecules.
Heteronuclear Diatomic Molecules | Introduction to Chemistry In heteronuclear diatomic molecules, atomic orbitals only mix when the electronegativity values are similar. In carbon monoxide (CO), the oxygen 2s orbital is much lower in energy than the carbon 2s orbital, so the degree of mixing is low. The g and u subscripts no longer apply because the molecule lacks a center of symmetry.
inorganic chemistry - Molecular orbitals of heteronuclear ... Now, MO diagrams are only simple for elements of the second row of the periodic table ( L i through N e ). Involving heavier atoms makes it harder to guess at molecular orbital diagrams, and there is need for quantum chemistry calculations. Thus, the rule becomes: the further to the right your element is, the lower its energy levels are.
Molecular orbital theory. Heteronuclear diatomics. CO ... 12-12 This video describes the molecular orbital theory diagram of CO, placing emphasis on how MO theory differs for homo and heteronuclear diatomics
(PDF) Inorganic Chemistry 4th edition ... - Academia.edu Academia.edu is a platform for academics to share research papers.
Solved Question 7 3 points Save A Draw the molecular ... Question 7 3 points Save A Draw the molecular orbital diagram (MO diagram) for the heteronuclear diatomic species CF to answer the following questions. Only show the valence Atomic orbitals and valence Molecular orbitals. The order of MO energy levels for CF will be the same as for the O2 homonuclear diatomic molecule.
8 - Drawing Molecular Orbital Diagrams — Flux Science Nov 12, 2021 · Molecular Orbital Diagram. As we’ve established (link to last lesson), bonding and antibonding interactions are the key to molecular orbital theory. In fact, the idea of molecular orbitals, the distribution of electrons across a molecule, arises from how electrons distribute themselves energetically. ... Heteronuclear Molecular Orbitals ...



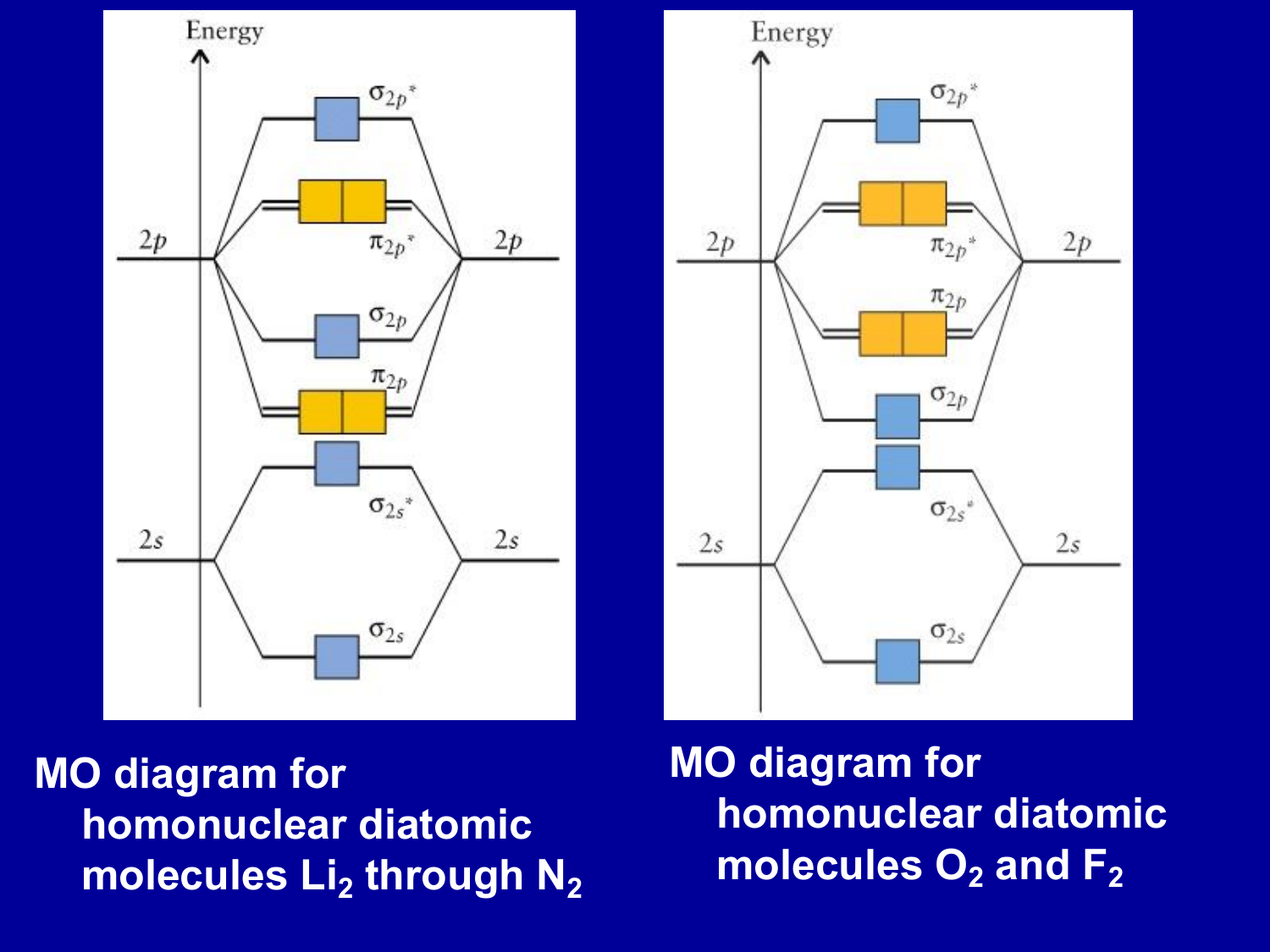

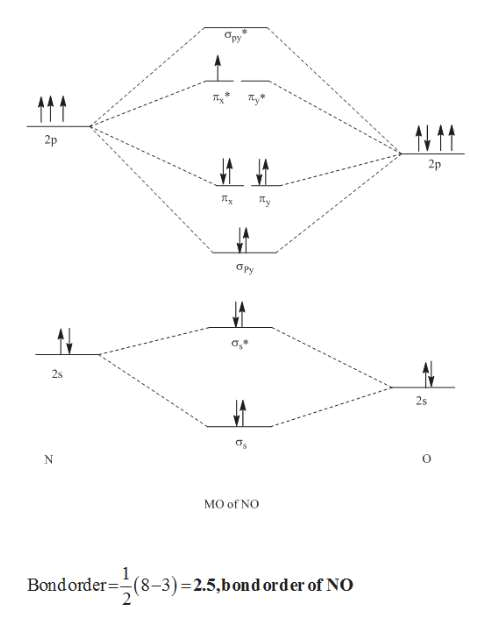


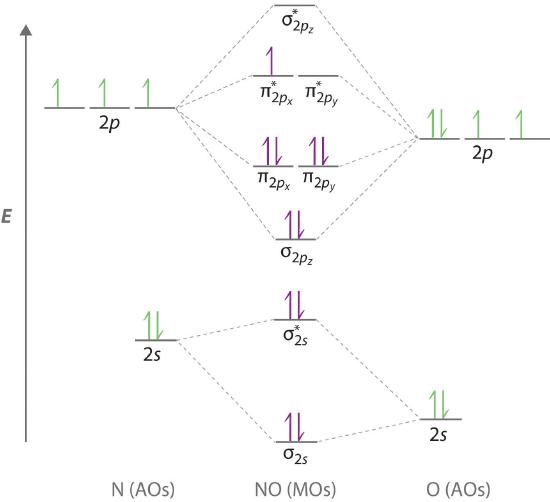



![SOLVED:5.0 [20 pts] Consider the heteronuclear diatomic ...](https://cdn.numerade.com/ask_images/1d261a94a8c543ecb38c77d0d5a38b69.jpg)






0 Response to "40 heteronuclear molecular orbital diagram"
Post a Comment