37 free body diagram terminal velocity
For the first free-body diagram, at the instant where the cof fee filter has just been released, the . only force acting on the coffe e filter is the force due to gravity, or mg. A fter the coffee filter has . reached terminal velocity, the mg will equal the drag force. For this reason, the arrows in the free. body diagram for mg and drag force ... Physics of Sky Diving
Free Body Diagrams. The Free Body Diagrams Interactive is a skill-building tool that allows the learner to interactively construct free-body diagrams for 12 physical situations. Each situation is described and the learner clicks/taps on-screen buttons to select forces that are directed upward, downward, rightward and leftward.
Free body diagram terminal velocity
Harvard Instructional Physics Labs · Course Links and Lab Handouts · Staff Notes · Contact Info · Our mission is to provide support for instructional laboratories in the physical sciences. In addition to maintaining the infrastructure for the labs, we develop new experiments and serve as ... Worksheet #1 Free Body or Force diagrams Drawing Free-Body Diagrams ... 16. The object is falling at constant (terminal) velocity. 18. A rocket is accelerating straight upward 20.A big block of mass M is attached via a string to a smaller block of mass m. A student An Easy Guide to Understand Free Body Diagrams in Physics. Every macroscopic and microscopic body or object in the universe exerts different forces on the surroundings, as well as experiences the effect of various forces on it. It is possible to study such physical entities with the help of a free body diagram.
Free body diagram terminal velocity. "The terminal velocity of a falling human being with arms and legs outstretched is about 120 miles per hour (192 km per hour) — slower than a lead balloon, but a good deal faster than a feather!" 53 m/s: The terminal velocity of a falling body occurs during free fall when a falling body experiences zero acceleration. This is because of the ... Figure 6.33 Free-body diagram of an object falling through a resistive medium. We can find the object’s velocity by integrating the differential equation for v. First, we rearrange terms in this equation to obtain When an object attains terminal velocity, the upward force of air resistance is equal and opposite to the ... Be sure to include a free body diagram.1 answer · 1 vote: “Undergoes” is the wrong word. An object attains terminal velocity when it undergoes drag ... Answer: 1 📌📌📌 question A ball is falling at terminal velocity. Terminal velocity occurs when the ball is in equilibrium and the forces are balanced. Which free body diagram shows the ball falling at terminal velocity? - the answers to estudyassistant.com
Find my revision workbooks here: https://www.freesciencelessons.co.uk/workbooksIn this video, we explore how the forces acting on a skydiver change with the Your free body diagram is correct, The object isnt at constant velocity though, because it is being accelerated by gravity. The net force on the object is gravity. If there is no net force, or the net force = 0, then the velocity is constant. Im sorry I can't explain this better to you. Construct free-body diagrams for the various situations described below. 1. A book is at rest on a table top. Diagram the forces acting on the book. 2. A girl is suspended motionless from a bar which hangs from the ceiling by two ropes. Diagram the forces acting on the girl. 3. An egg is free-falling from a nest in a tree. Neglect air ... September 1, 2015 - When you drop a ball in the air, often the air resistance force is ignored. How high would you have to drop something so that the air resistance is significant?
The free-body diagrams are shown below for the instant in time in which they have reached terminal velocity. As learned above , the amount of air resistance depends upon the speed of the object. A falling object will continue to accelerate to higher speeds until they encounter an amount of air resistance that is equal to their weight. August 17, 2021 - Terminal velocity, steady speed achieved by an object freely falling through a gas or liquid. An object dropped from rest will increase its speed until it reaches terminal velocity; an object forced to move faster than it terminal velocity will, upon release, slow down to this constant velocity. Figure 5.32 (a) The free-body diagram for isolated object A. (b) The free-body diagram for isolated object B. Comparing the two drawings, we see that friction acts in the opposite direction in the two figures. Because object A experiences a force that tends to pull it to the right, friction must act to the left. Because object B experiences a component of its weight that pulls it to the left ... The Physics Classroom serves students, teachers and classrooms by providing classroom-ready resources that utilize an easy-to-understand language that makes learning interactive and multi-dimensional. Written by teachers for teachers and students, The Physics Classroom provides a wealth of ...
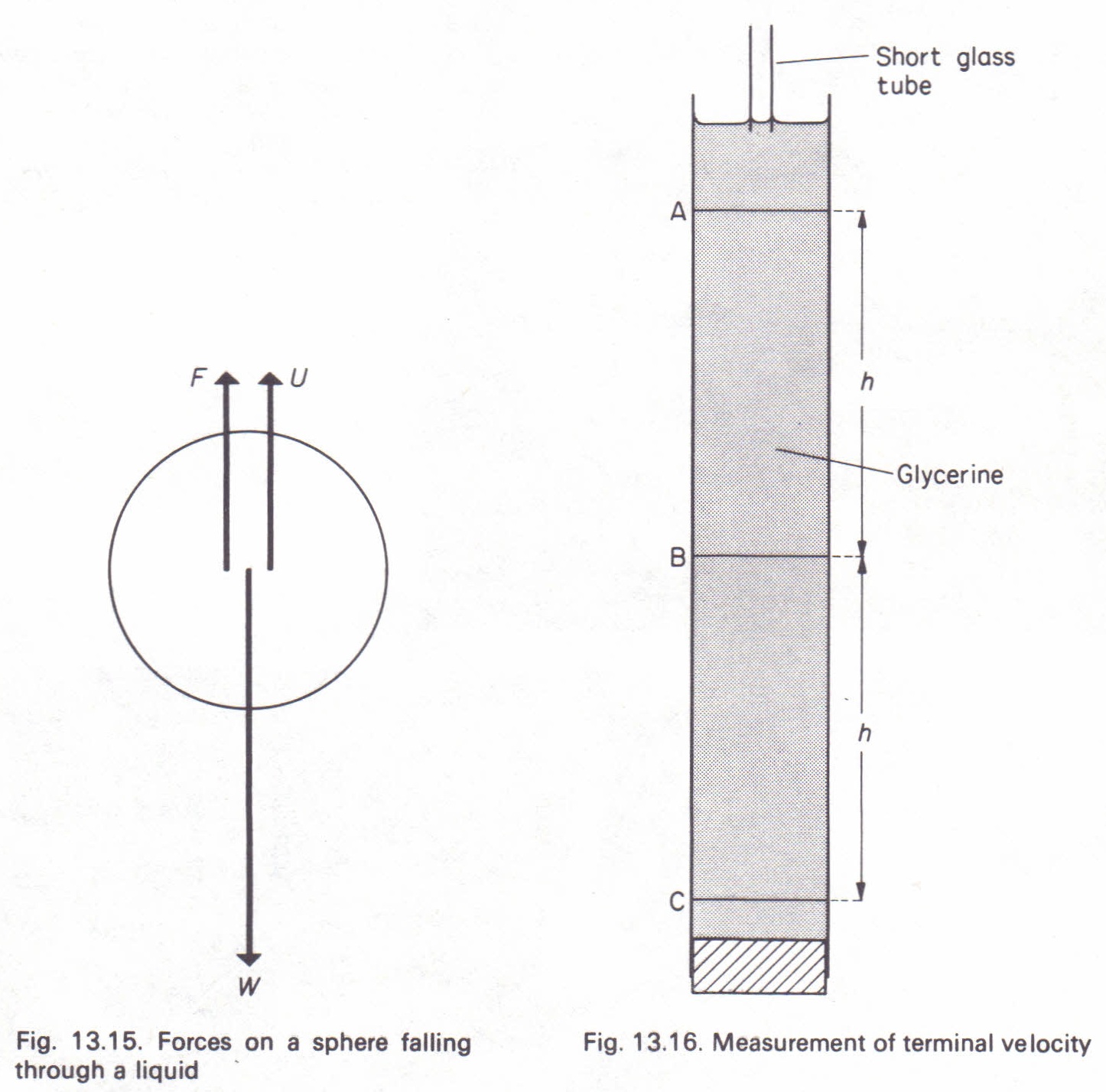
September 19, 2016 - As v increases, the frictional force –bv increases until it matches mg. At this point, there is no acceleration and the velocity remains constant at the terminal velocity ... Figure 6.33 Free-body diagram of an object falling through a resistive medium.
She has reached TERMINAL VELOCITY (air resistance =gravity) :acceleration and force Physics 12/16/04 * In order to understand this motion, we need to use a free body diagram 12/16/04 * Terminal Velocity of a human~180mph 12/16/04 :acceleration and force Physics 12/16/04 * In order to understand this motion, we need to use a free body diagram 12 ...
Which free body diagram shows the ball falling at terminal velocity? A free body diagram with one force pointing downward labeled F Subscript g Baseline 20 N. A free body diagram with 2 forces: the first pointing downward labeled F Subscript g Baseline 20 N and the second pointing upward labeled F Subscript air Baseline 20 N.
Fluid Friction Physics Homework Help Physics Assignments And Projects Help Assignments Tutors Online
Terminal velocity and free fall are two related concepts that tend to get confusing because they depend on whether or not a body is in empty space or in a fluid (e.g., an atmosphere or even water). Take a look at the definitions and equations of the terms, how they are related, and how fast a body falls in free fall or at terminal velocity under different conditions.
August 6, 2017 - This section the course textbook and reading assignments.
Draw Free Body Diagram (FBD) for the falling object: (Note: don't forget to label all forces exerted on the object) a) Neglect air resistance b) Do not neglect air resistance Q2: In general, what is the direction of acceleration? (Recall: Newton's Second Law) Q3: What does is mean that an object is falling with is terminal velocity? Explain.
Learn about Newton’s three laws, terminal velocity, contact and non-contact forces and free body diagrams with GCSE Bitesize Combined Science.
10. A parachuter that weighs 760 N is falling to Earth at terminal velocity. Recall that terminal velocity means that the freely-falling object has a constant velocity. 11. An apple that weighs 5 N at its start of a fall to Earth and is experiencing 1 N of air resistance (i.e., terminal velocity has not been reached). 12.
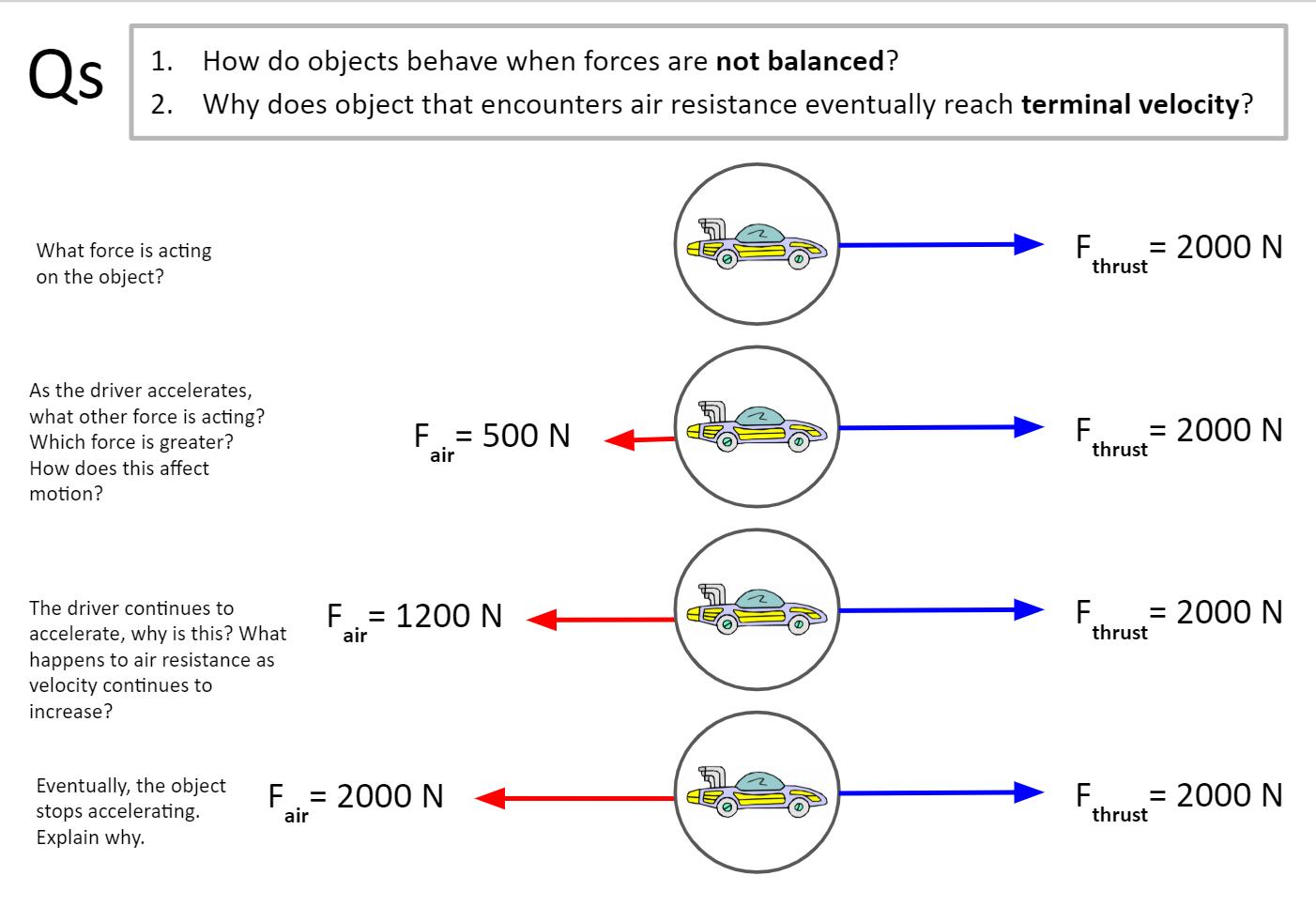
Ben Sudjaitham On Twitter Dualcoding Free Body Diagrams Newton S 1st Amp 2nd Law Teacher Guided Explanations Terminal Velocity For Horizontal And Vertical Motions Big Q Why Does Object That Encounters Air
The diagrams below represent the free-body diagrams for different skydivers at various moments during their fall. What is the acceleration of each skydiver and which Skydiver has reached terminal velocity? 1. Skydiver B 2: A) a=-1.6 B) a=0 C) a=1.26 D) a=.89.
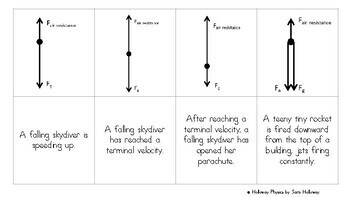
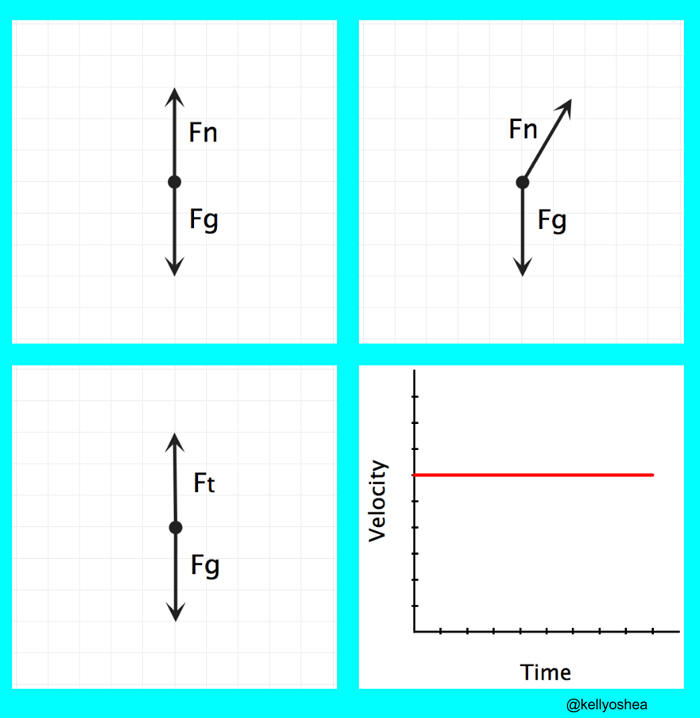
Free body diagrams of a person with 90 kg mass during a skydive. The initial speed is zero, so drag force is zero. As speed increases, the drag force grows, eventually cancelling out the person’s weight. At that point acceleration is zero and terminal velocity is reached. Dynamic Equilibrium
Free-Body Exercises: Circular Motion Draw free-body diagrams showing forces acting on the rock, and in each case, indicate the centripetal force. Please note that the rock is not in equilibljum if it is moving in a circle. The centripetal force depends on angular velocity and there may not be any indication of exactly how big that force should ...
Draw a free body diagram of a meteor that is falling towards earth at terminal velocity. F air F gravity Net Force = 0 N The meteor is falling down, but its net force is 0 N! There is no acceleration!
Solved Calculate The Reynolds Number For Each Of The Steel Balls Estimate The Viscosity Of Antibacterial Soap At The Temperature Measured From The Terminal Velocity And The Free Body Diagram Which Type Of
Graph of velocity versus time of ... terminal velocity. Based on wind resistance, for example, the terminal speed of a skydiver in a belly-to-earth (i.e., face down) free fall position is about 195 km/h (120 mph; 54 m/s). This speed is the asymptotic limiting value of the speed, and the forces acting on the body balance each ...
Construct free-body diagrams for the following physical situations. Label all forces (e.g, Fgrav, Fnorm, Fapp, Ffrict, Fair, Ftens, etc. ). a. A physics book rests upon a level table. b. A skydiver is falling and has reached a terminal velocity. c. A large crate is being pushed leftward at a constant velocity. d. A sledder has reached
Answer: "Undergoes" is the wrong word. An object attains terminal velocity when it undergoes drag due to air resistance. When an object attains terminal velocity, the upward force of air resistance is equal and opposite to the downward force of gravity. Find or draw your own free body diagram. O...
Refer to the following information for the next four questions. True or False: The magnitude of the normal, , is smaller than the object's weight. True. False. A 5 kg mass is being pushed across a rough table at a constant velocity by a constant force, F = 15 N, which acts at an angle θ = 37º to the horizontal.
velocity of the sphere relative to the fluid, and d is the diameter of the sphere. Using this equation, along with other well-known principle of physics, we can write an expression that describes the rate at which the sphere falls through a quiescent, viscous fluid. To be begin we must draw a free body diagram (FBD) of the sphere. That is we must
Click Images to Large View Parachuting Parachute Terminal Velocity Free Body Diagram. Pin By Juan On Skydiving In 2021 Physics Lessons Middle. Click Images to Large View Pin By Juan On Skydiving In 2021 Physics Lessons Middle. Ppt Gravity Air Resistance Terminal Velocity And.
PhysicsLAB: Freebody Diagrams. In each case, a rock is acted on by one or more forces. On a sheet of paper, draw an accurate vector diagram showing all forces acting on the rock, and no other forces. Use a ruler, and do it in pencil so you can correct mistakes. Refer to the following information for the next two questions.
November 5, 2020 - Figure \(\PageIndex{4}\): Free-body diagram of an object falling through a resistive medium. We can find the object’s velocity by integrating the differential equation for \(v\). First, we rearrange terms in this equation to obtain
Drawing Free-Body Diagrams. Free-body diagrams are diagrams used to show the relative magnitude and direction of all forces acting upon an object in a given situation. A free-body diagram is a special example of the vector diagrams that were discussed in an earlier unit. These diagrams will be used throughout our study of physics.
The terminal velocity is the same as the limiting velocity, which is the velocity of the falling object after a (relatively) long time has passed. Similarly, the limiting distance of the boat is the distance the boat will travel after a long amount of time has passed. ... Draw a free-body diagram of the forces to see what the angle . should be.)
Learn about and revise terminal velocity, Newton's Laws and braking forces with GCSE Bitesize Combined Science.
When it is going fast enough that the air resistance force is equal to the weight, the free body diagram will look like this: What the acceleration be at this time? (zero). This is called terminal velocity (because it will no longer speed up) Procedure There is a reason that coffee filters are used.
A free body diagram with 2 forces: the first pointing downward labeled F Subscript g Baseline 20 N and the second pointing upward labeled F Subscript air Baseline 20 N. Explanation: This is because at terminal velocity, the ball stops accelerating and the net force on the ball is zero.
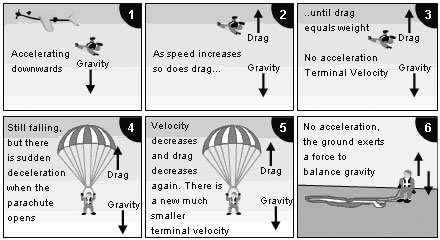
The maximum velocity reached by a falling object is called the '''terminal velocity'''. Opening a parachute further increases the drag force, causing the sky diver to decelerate (slow down). As the skydiver slows down, the drag force decreases until it balances the weight force once more and ...
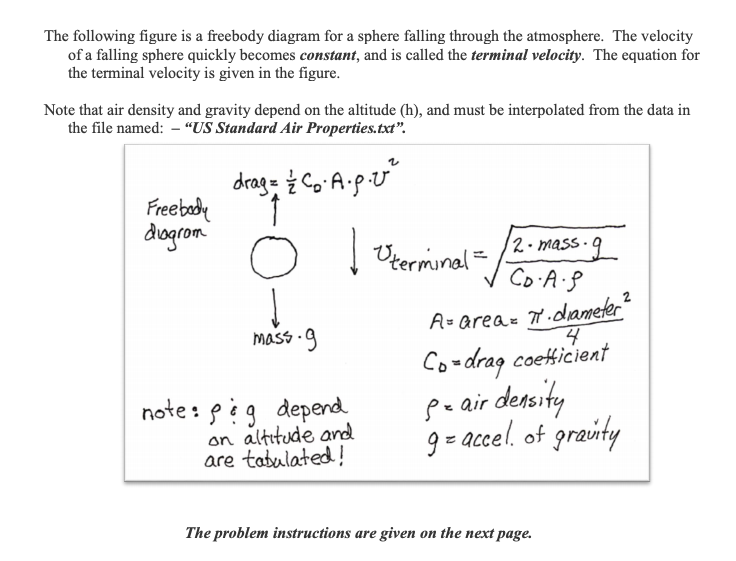
May 4, 2018 - An object which is falling through the atmosphere is subjected to two external forces. One force is the gravitational force, expressed as the weight of the object. The other force is the air resistance, or drag of the object. If the mass of an object remains constant, the motion of the object ...
Draw a free body diagram for the wire when it has reached terminal velocity. Wire Falling Down Rails 010 (part 1 of 5) 10.0 points A straight, horizontal wire falls vertically along parallel vertical conducting rails, as shown. The rails are connected at the bot- tom by a horizontal rail so that the wire and rails form a closed rectangular loop.
A free-body diagram is a representation of an object with all the forces that act on it. The external environment (other objects, the floor on which the object sits, etc.), as well as the forces that the object exerts on other objects, are omitted in a free-body diagram. Below you can see an example of a free-body diagram:
An Easy Guide to Understand Free Body Diagrams in Physics. Every macroscopic and microscopic body or object in the universe exerts different forces on the surroundings, as well as experiences the effect of various forces on it. It is possible to study such physical entities with the help of a free body diagram.
Worksheet #1 Free Body or Force diagrams Drawing Free-Body Diagrams ... 16. The object is falling at constant (terminal) velocity. 18. A rocket is accelerating straight upward 20.A big block of mass M is attached via a string to a smaller block of mass m. A student
Harvard Instructional Physics Labs · Course Links and Lab Handouts · Staff Notes · Contact Info · Our mission is to provide support for instructional laboratories in the physical sciences. In addition to maintaining the infrastructure for the labs, we develop new experiments and serve as ...

Terminal Velocity Arizona State University Ranked 1 Velocity Acirc Euro Cent The Object Acirc Euro Trade S Velocity Kinematics Kinetics Linear Angular Linear Angular Positioin Free Body Pdf Document


















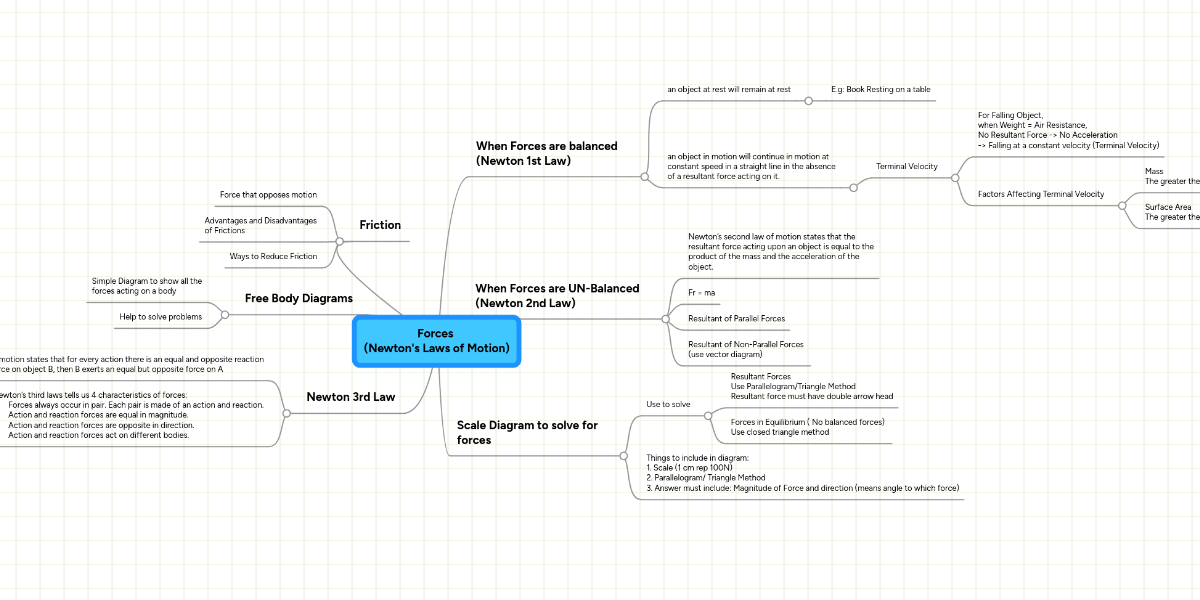
0 Response to "37 free body diagram terminal velocity"
Post a Comment