41 if the competitive firm depicted in this diagram produces output q, it will
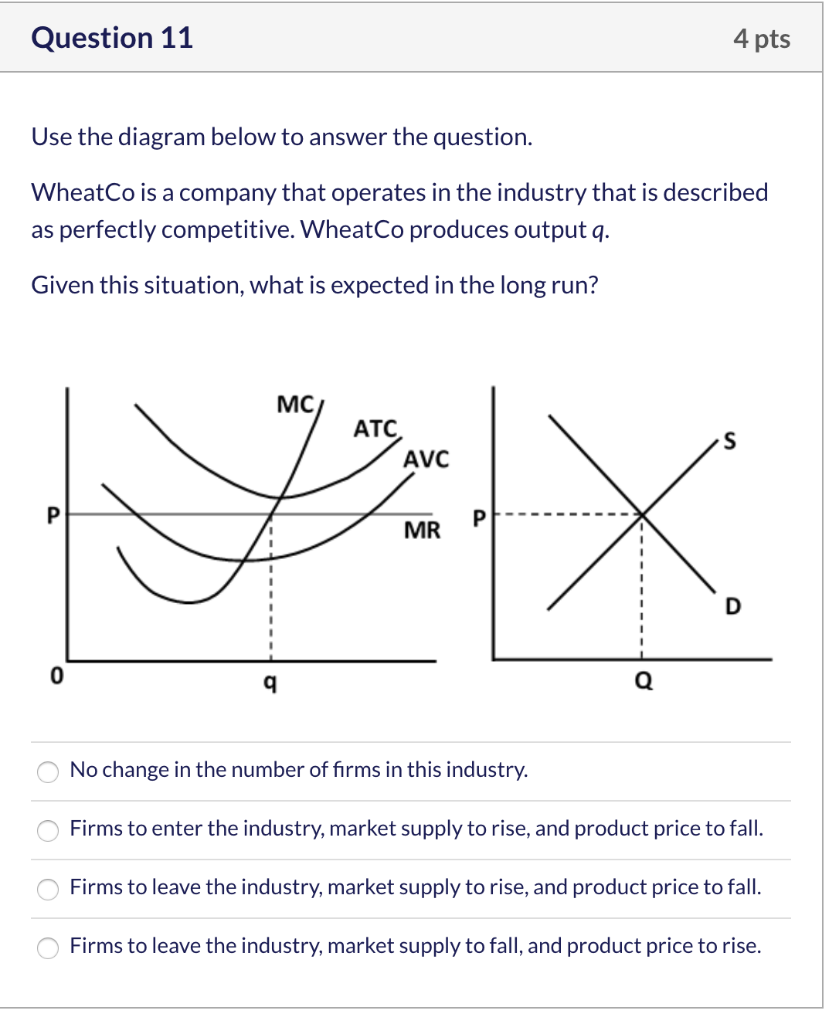
If this competitive firm produces output Q, it will. ... Refer to the diagram. Line (1) reflects the long-run supply curve for: an increasing-cost industry. ... Refer to the diagrams, which pertain to a purely competitive firm producing output q and the industry in which it operates. Which of the following is correct? If the competitive firm depicted in this diagram produces output Q, it will. earn a normal profit. Marginal cost is _____. (TVC+TFC)/Q. The diagram shows the average total cost curve for a purely competitive firm. At the long-run equilibrium level of output, this firm's total revenue ... Refer to the provided graph for a purely competitive firm ...
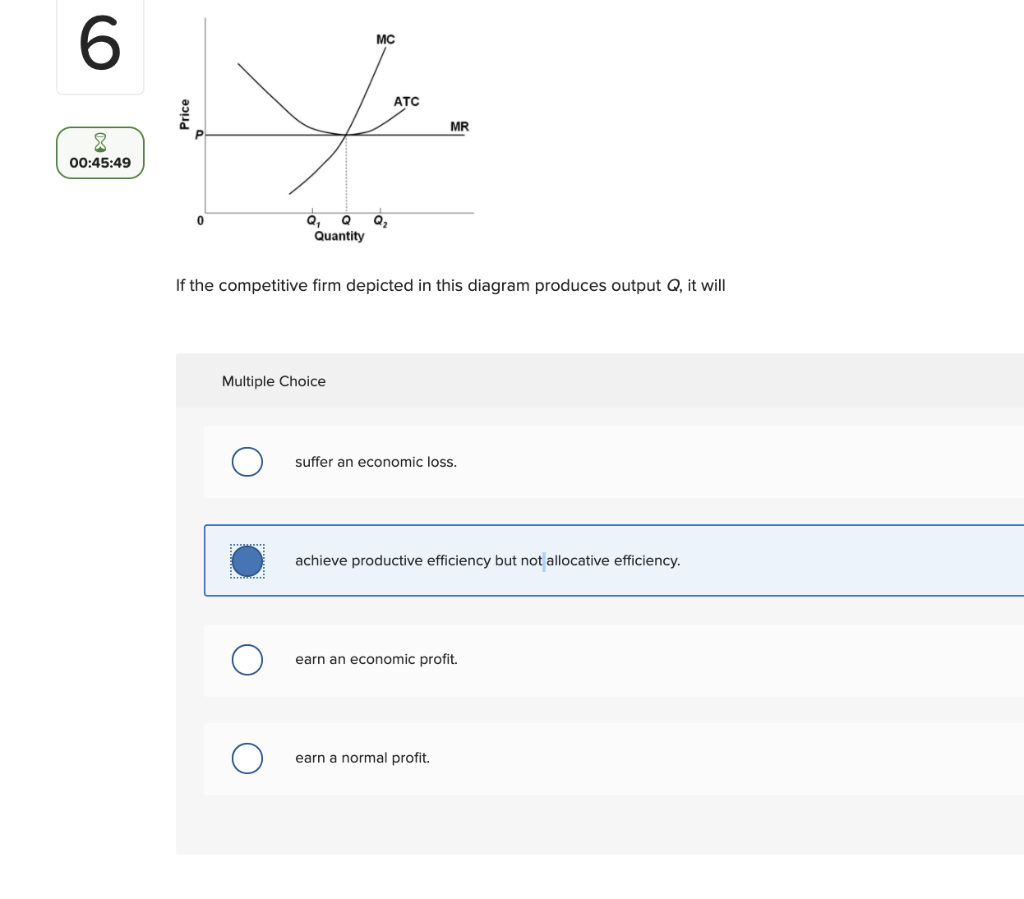
Award: 1.00 point If the competitive firm depicted in this diagram produces output Q, it will suffer an economic loss. earn a normal profit. earn an economic profit. achieve productive efficiency but not allocative efficiency.

If the competitive firm depicted in this diagram produces output q, it will
If the competitive firm depicted in this diagram produces output Q, it will suffer an economic loss. earn a normal profit. earn an economic profit. achieve productive efficiency but not allocative efficiency. earn a normal profit. If the industry depicted in this graph were a pure monopoly, the product price would be lower than $8. $8. $14. $16. If the competitive firm depicted in this diagram produces output Q, it will earn a normal profit. Technological advance improves productivity in a purely competitive industry. This change will result in a shift down of the individual firm's MC curve, causing the market (industry) supply curve to shift to the right. Refer to the above diagram. If this competitive firm produces output Q, it will: a. suffer an economic loss. b. earn a normal profit. c. earn an economic profit. d. achieve productive efficiency, but not allocative efficiency.
If the competitive firm depicted in this diagram produces output q, it will. In the competitive firm, the firm sets… View the full answer Transcribed image text : 6 MC ATC Price MR 00:45:49 Q, Q Quantity If the competitive firm depicted in this diagram produces output Q, it will Multiple Choice suffer an economic loss. achieve productive efficiency but not allocative efficiency. earn an economic profit. The second term, (∂P/∂Q)Q, is equal to area A in the diagram. This area represents the change in price given a small change in quantity (∂P/∂Q), multiplied by the quantity (Q). For a competitive firm, (∂P/∂Q) = 0, since the competitive firm is a price taker. For a competitive firm, AE = ME, as shown in the left of Figure 3.17. A monopolistically competitive firm sets a price higher than marginal cost because demand is higher than marginal revenue. Also, in the long run it produces a quantity where average total cost isn’t minimized, so it has excess capacity. Finally, firm entry and exit leads to firms earning zero economic profits. 假装都会了 If the competitive firm depicted in this diagram produces output Q, it will. ... If a purely competitive firm is producing at the MR = MC output level and earning an economic profit, then. new firms will enter this market. If the long-run supply curve is upward sloping, it indicates that resource prices fall when.
The rule for a profit-maximizing perfectly competitive firm is to produce the level of output where Price= MR = MC, so the raspberry farmer will produce a quantity of 90, which is labeled as e in Figure 4 (a). Remember that the area of a rectangle is equal to its base multiplied by its height. Refer to the above diagram. If this competitive firm produces output Q, it will: a. suffer an economic loss. b. earn a normal profit. c. earn an economic profit. d. achieve productive efficiency, but not allocative efficiency. If the competitive firm depicted in this diagram produces output Q, it will earn a normal profit. Technological advance improves productivity in a purely competitive industry. This change will result in a shift down of the individual firm's MC curve, causing the market (industry) supply curve to shift to the right. If the competitive firm depicted in this diagram produces output Q, it will suffer an economic loss. earn a normal profit. earn an economic profit. achieve productive efficiency but not allocative efficiency. earn a normal profit. If the industry depicted in this graph were a pure monopoly, the product price would be lower than $8. $8. $14. $16.



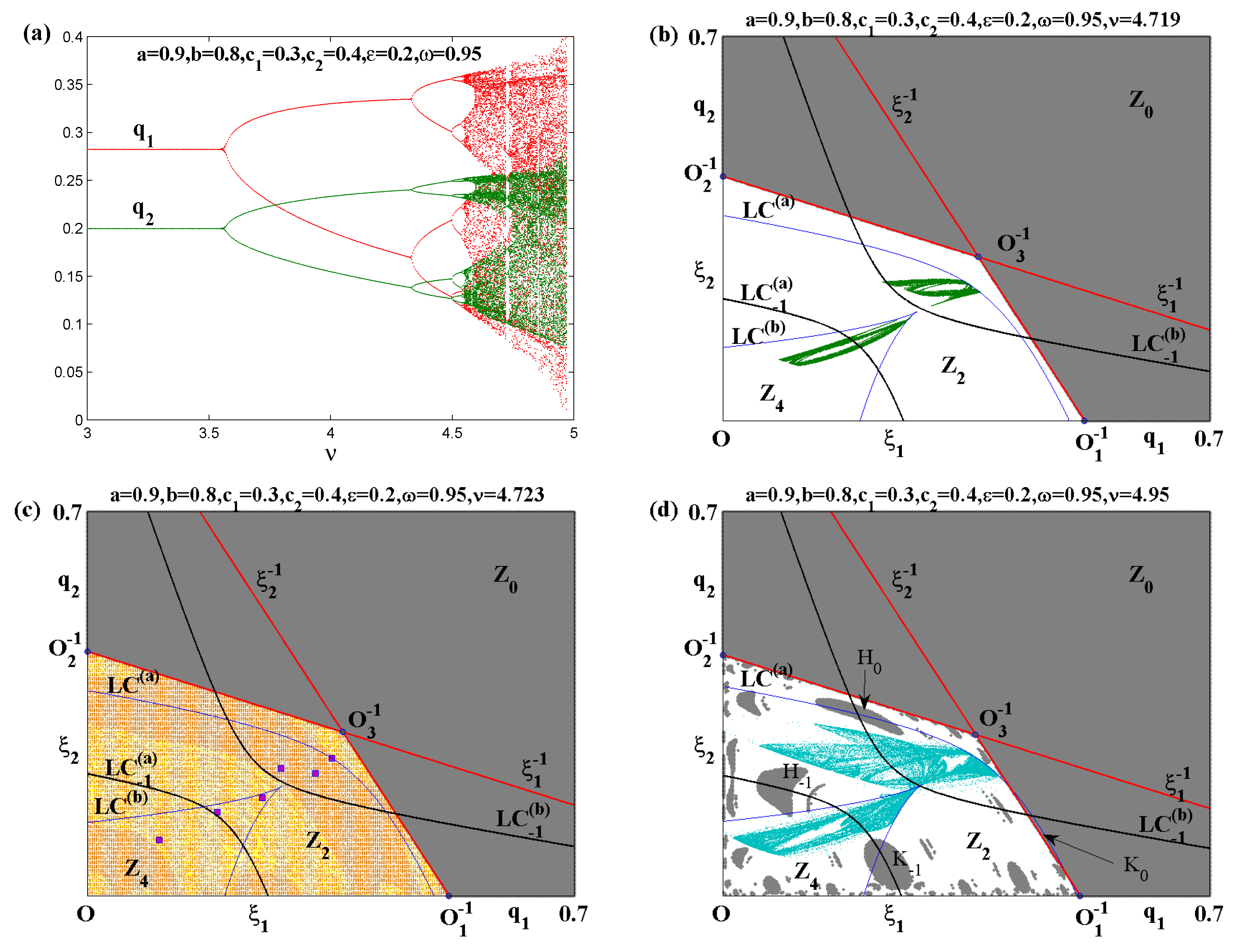



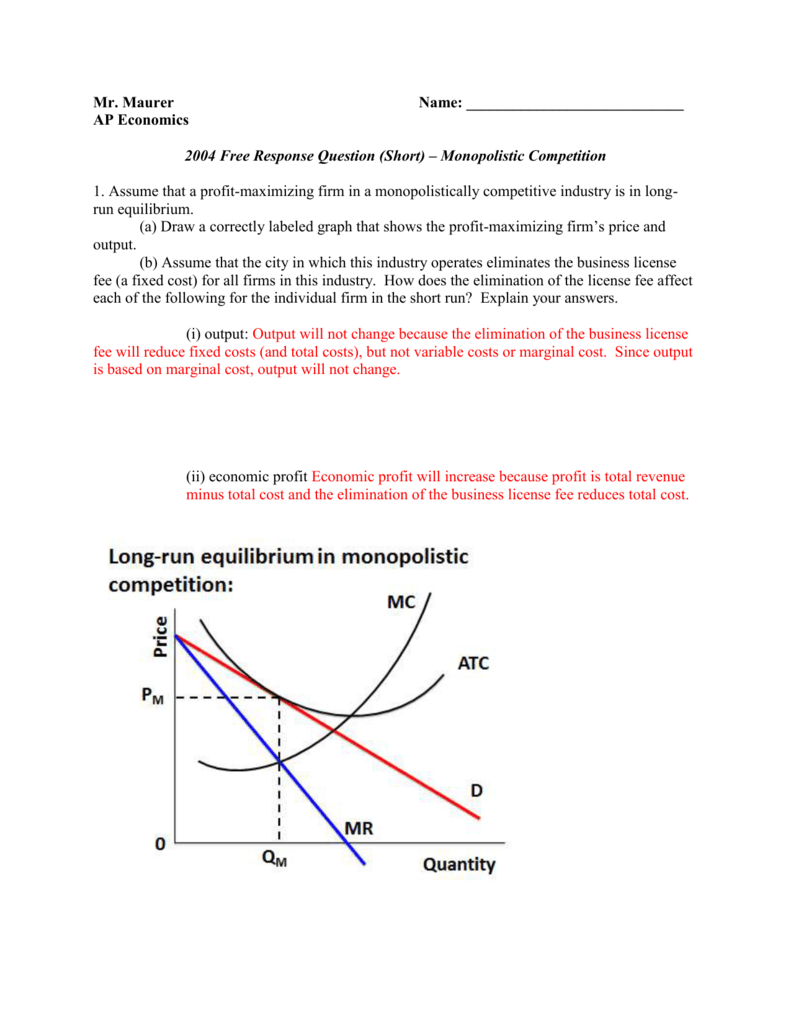













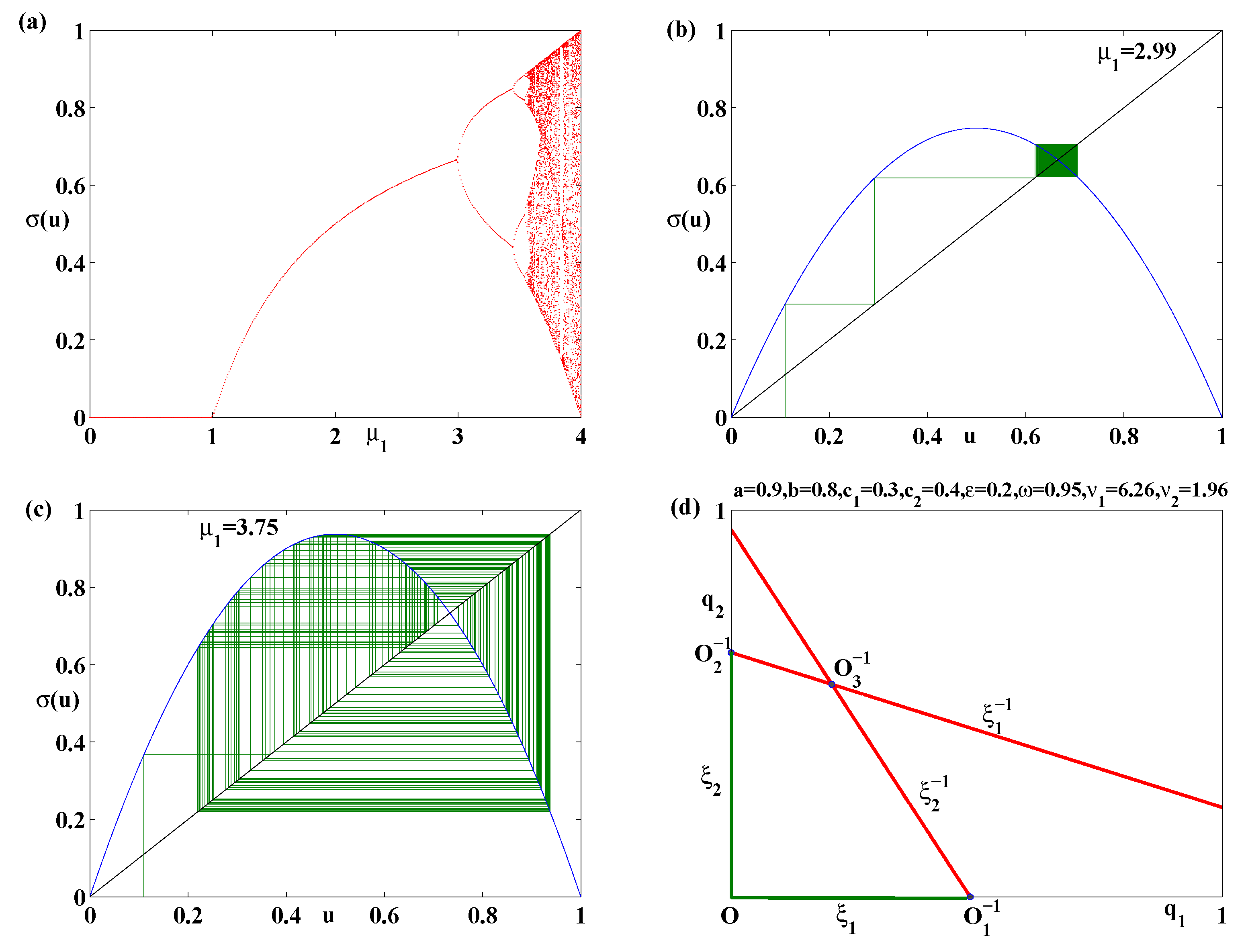



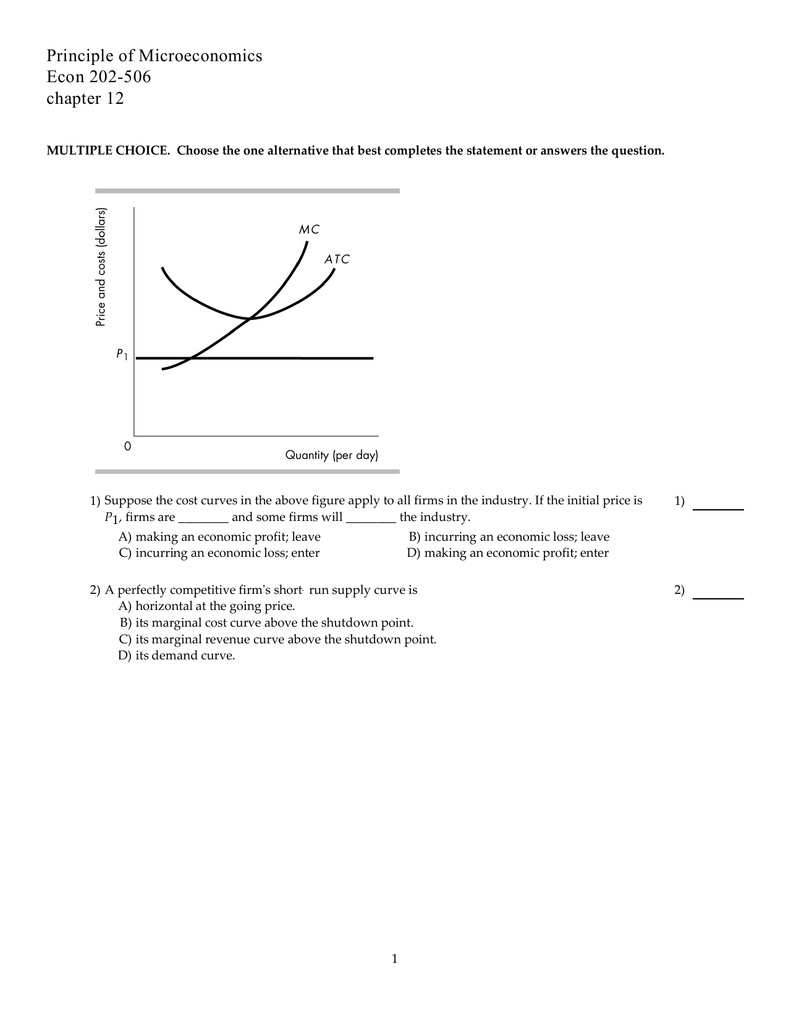



0 Response to "41 if the competitive firm depicted in this diagram produces output q, it will"
Post a Comment