41 draw and label an energy level diagram for hydrogen
Draw a neat labelled energy level diagram of the Hydrogen atom. Medium. An energy level diagram. shows whether a reaction is exothermic. or endothermic. It shows the energy in the reactants. and products, and the difference in energy between them.
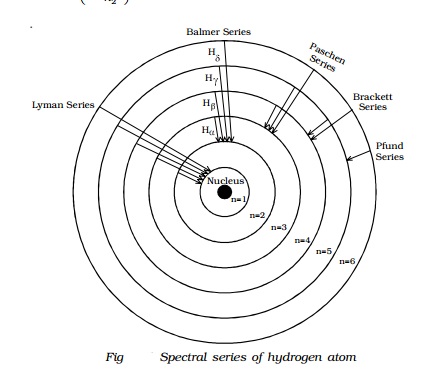
Draw a Neat, Labelled Energy Level Diagram for H Atom Showing the Transitions. Explain the Series of Spectral Lines for H Atom, Whose Fixed Inner Orbit Numbers Are 3 and 4 Respectively.

Draw and label an energy level diagram for hydrogen
Below is a blank energy level diagram which helps you depict electrons for any specific atom. At energy level 2, there are both s and p orbitals. The 2s has lower energy when compared to 2p. The three dashes in 2p subshells represent the same energy. 4s has lower energy when compared to 3d. Therefore, the order of energy level is as follows: s ... 3:05 (Triple only) draw and explain energy level diagrams to represent exothermic and endothermic reactions The symbol ΔH is used to represent the change in heat (or enthalpy change) of a reaction. ΔH is measured in kJ/mol (kilojoules per mole). Hydrogen Spectrum - Wavelength, Diagram, Hydrogen Emission Spectrum. Hydrogen Spectrum introduction. We all know that electrons in an atom or a molecule absorb energy and get excited, they jump from a lower energy level to a higher energy level, and they emit radiation when they come back to their original states.
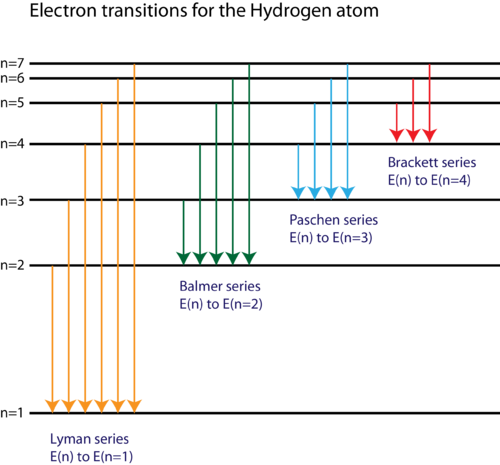
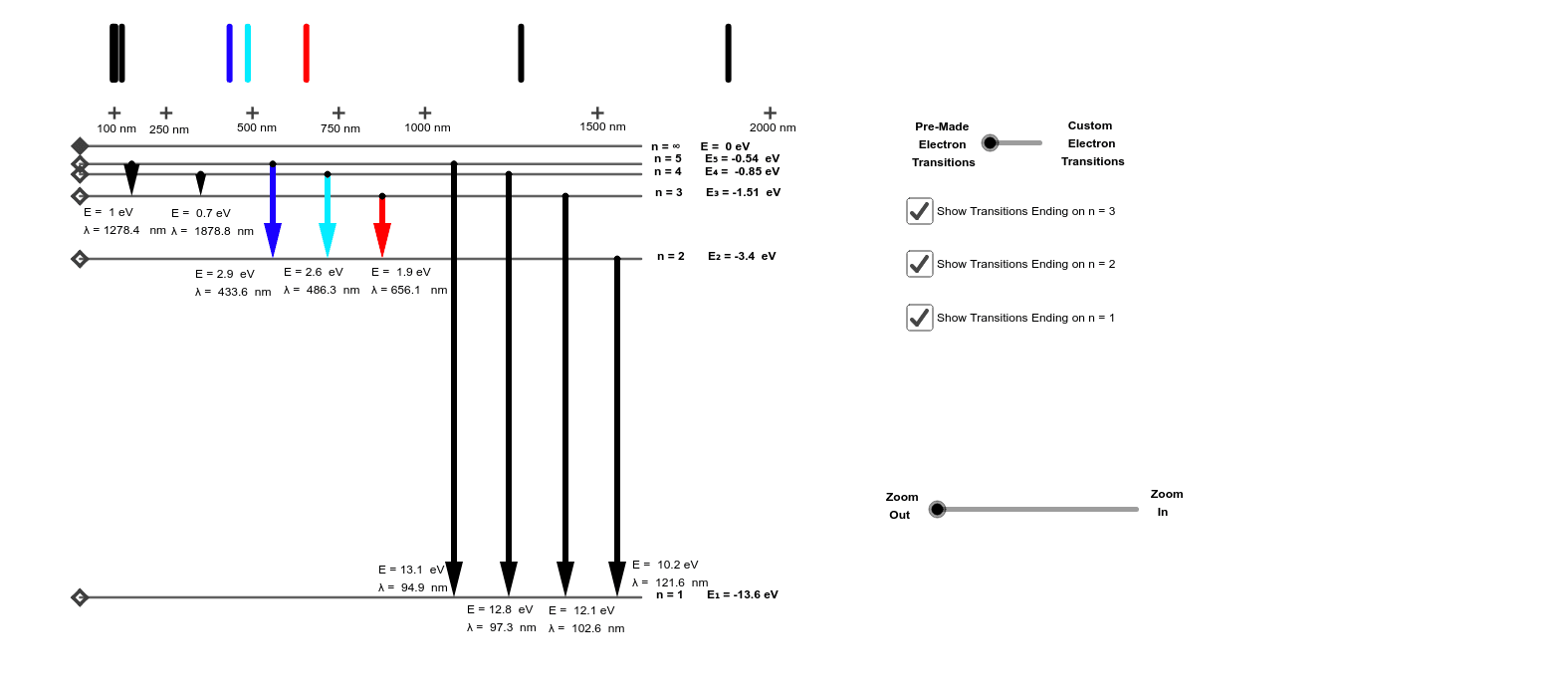
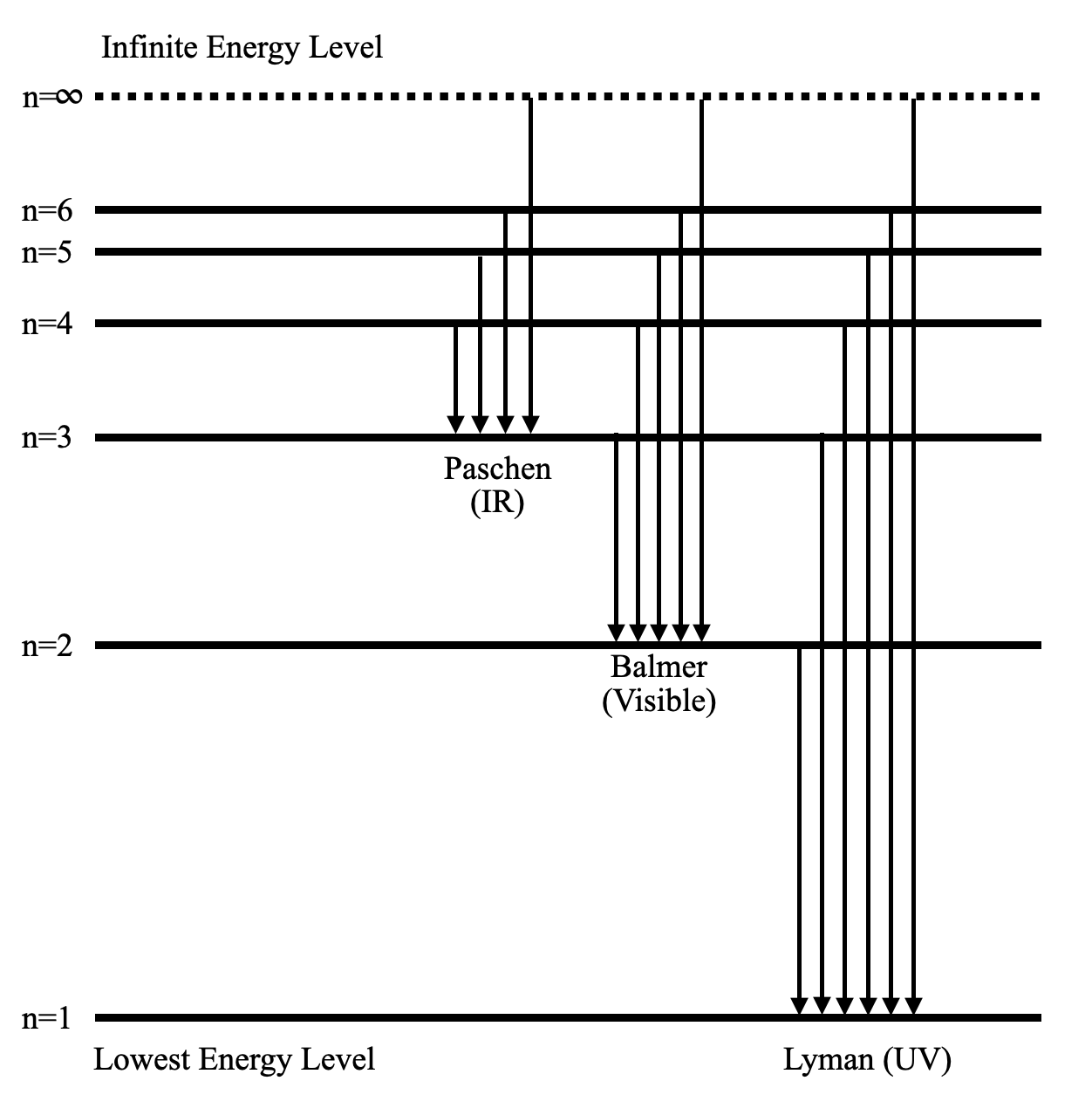
Draw and label an energy level diagram for hydrogen. 4. Construct an energy level diagram to scale for the allowed energies of the electron in the hydrogen atom. Use the results from question 1 above. On the energy level diagram: a. Draw and label the n = 1 and n = 6 energy levels. Give the value of n The ionization energy of an atom is the energy required to remove the electron completely from the atom. (transition from ground state n = 0 to infinity n = ∞ ). For hydrogen, the ionization energy = 13.6eV. When an excited electron returns to a lower level, it loses an exact amount of energy by emitting a photon. Sketch and label an energy level diagram for hydrogen, and draw the transitions corresponding to the first four lines in the Balmer series (nf = 2). Question: 1. In this lab you will use several visible lines emitted from hydrogen gas, a.k.a. the Balmer series. Sketch and label an energy level diagram for hydrogen, and draw the transitions corresponding to the first four lines in the Balmer series (n = 2). Calculate the change in energy (AE) for the first four lines of the Balmer series.
Molecular Orbital Energy Level Diagrams: Hydrogen and Helium "Count and Sort" Algorithm for Building Molecular Orbital Energy Level Diagrams . 1. Write the electron configuration for each atom , and count the total number of valence electrons. If you're working with an ion, adjust the valence electron count according to the charge. 2. Vol. 1, Hydrogen I - Phosphorus XV Author: xejyj Published Date: 20.11.2021 Leave a Comment on Atomic levels and grotrian diagrams. Atomic energy levels and Grotrian diagrams. the fine structure constant and the rest energy of the electron. The fine structure constant is given by α ≡ e2 ~c ≃ 1 137, (2.1.4) and the rest energy of the electron is mc2. Then, e2 a 0 = me4 ~2 = mα2~2c2 ~2 = α2 mc2. (2.1.5) This states that the energy scale of hydrogen bound states is a factor of α2 smaller than So, those are electrons falling from the higher energy levels down to the 2nd energy level. So, let's go ahead and draw them on our diagram here. So, let's say an electron fell from the 4th energy level down to the 2nd. Alright, so, that energy difference, if you do the calculations, that turns out to be the blue-green line in your line spectrum.
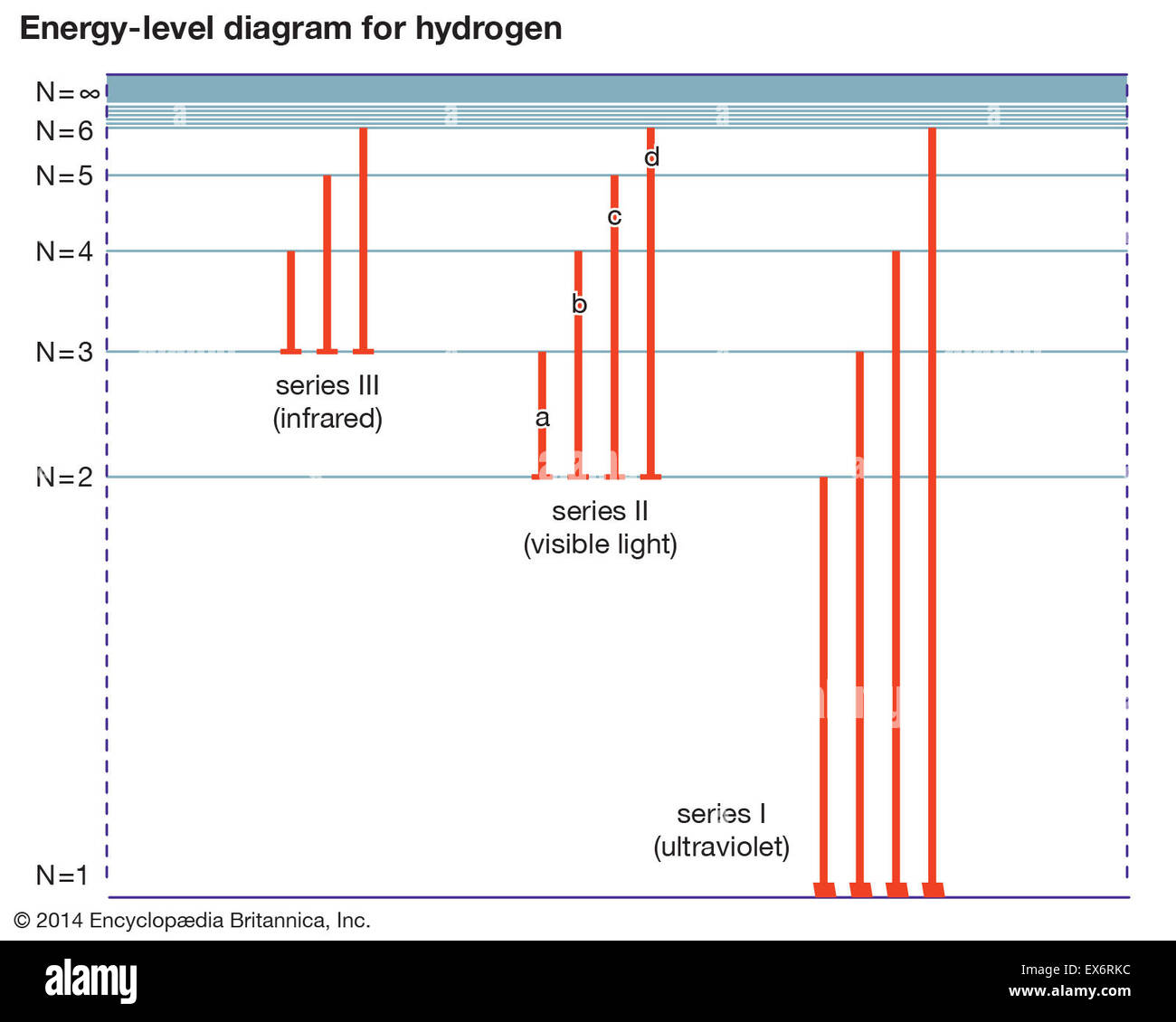
figures. (d) Draw an energy level diagram for hydrogen, and . draw vertical arrows to indicate each of these three electron transitions on the diagram. Label your lines "a", "b", and "c". Refer to lecture 5 notes for examples of energy level . diagrams. (a) E = 2.04 x 10-18. J (b) E = 2.08 x 10-19. J (c) E = 4.09 x 10-19. J (d) 2 ... Energy levels of the molecule LCAO: Energy Level Splitting and the Energy Matrix Element Bonding Anti-bonding Energy level diagram going from two isolated atoms to the molecule: 2:E1s 1:EA 1:EB 2Vss The two 1s orbitals on each Hydrogen atom combine to generate two molecular orbitals - the bonding orbital and the anti-bonding orbital - with ... Draw and label an energy level diagram for the hydrogen atom. In your diagram show how the series of lines in the ultraviolet and visible regions of its emission spectrum are produced, clearly labelling each series. showing y-axis labelled as energy/E / labelling at least two energy levels; showing a minimum of four energy levels/lines with convergence; showing jumps to n = 1 for ultraviolet ... Atomic Physics 1. Draw and label an energy level diagram for hydrogen using the Bohr Model. On it, show all the transitions by which an electron in the n 4 state could emit a photon.
Bohr Diagrams 1) Draw a nucleus with the number of protons and neutrons inside. 2) Carbon is in the 2nd period, so it has two energy levels, or shells. 3) Draw the shells around the nucleus. 6p 6n. Bohr Diagrams 1) Add the electrons. 2) Carbon has 6 electrons. 3) The first shell can only hold 2 electrons. 6p 6n.
3.3.1a - Bohr Diagram. Let's take a look at how to draw Bohr diagrams: For a hydrogen atom, H, the one electron goes into the first energy level. Draw a circle and label it with the symbol of the nucleus, H. Write the number of protons for the nucleus, 1p +. Draw an arc to represent the first energy level.

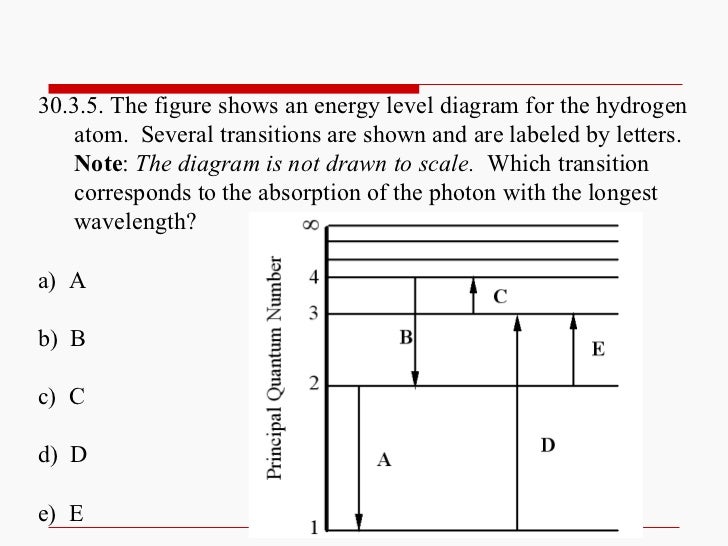
The Figure Shows An Energy Level Diagram For The Hydrogen Atom Several Transition Are Marked As I Ii Iii The Diagram Is Only Indicative And Not To Scale Img Src Https D10lpgp6xz60nq Cloudfront Net Physics Images
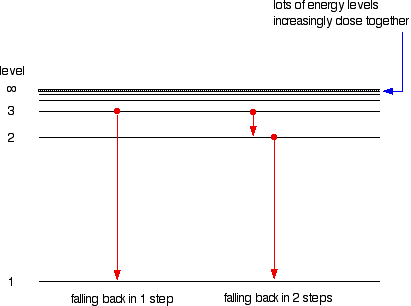
Hydrogen molecules are first broken up into hydrogen atoms (hence the atomic hydrogen emission spectrum) and electrons are then promoted into higher energy levels. Suppose a particular electron was excited into the third energy level. This would tend to lose energy again by falling back down to a lower level. It could do this in two different ways.
Energy level diagram for Molecular orbitals. ... Bond order value of 1 means that two hydrogen atoms are connected by a single bond. Greater value of bond order for H 2 molecule than H 2 + ion shows that two H 2 molecule is more stable than H 2 +. Bond length of H 2 is smaller than that of H 2 + ion.
The molecular orbital energy-level diagram, which is a diagram that shows the relative energies of molecular orbitals, for the H 2 molecule is shown in Figure 13. On either side of the central ladder are shown the energies of the 1 s orbitals of atoms A and B, and the central two-rung ladder shows the energies of the bonding and antibonding ...
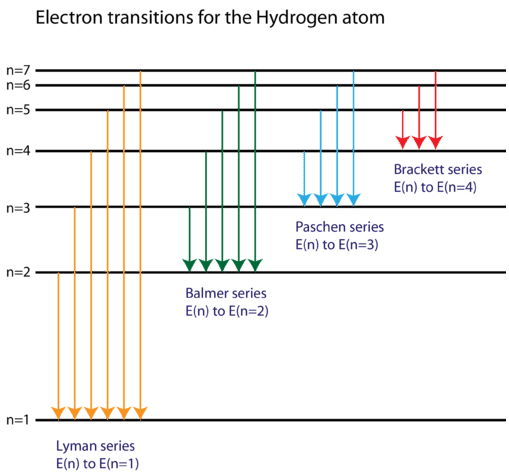
Energy level diagrams and the hydrogen atom. It's often helpful to draw a diagram showing the energy levels for the particular element you're interested in. The diagram for hydrogen is shown above. The n = 1 state is known as the ground state, while higher n states are known as excited states. If the electron in the atom makes a transition from ...
Answer. Step 1: The chemical equation for the complete combustion of methane is: CH4 (g) + 2O2 (g) → CO2 (g) + 2H2O (l) Step 2: Combustion reactions are always exothermic (Δ H is negative) so the reactants should be drawn higher in energy than the products. Step 3: Draw the curve in the energy level diagram clearly showing the transition state.

Using Bohr S Postulates Obtain The Expression For The Total Energy Of The Electron In The Stationary States Of The Hydrogen Atom Hence Draw The Energy Level Diagram Showing How The Line Spectra
2. Draw and label an energy level diagram for the hydrogen atom. In your diagram show how the series of lines in the ultraviolet and visible regions of its emission spectrum are produced, clearly labelling each series. (Total 4 marks) 3. Describe the emission spectrum of hydrogen. Outline how this spectrum is related to the energy levels in the ...
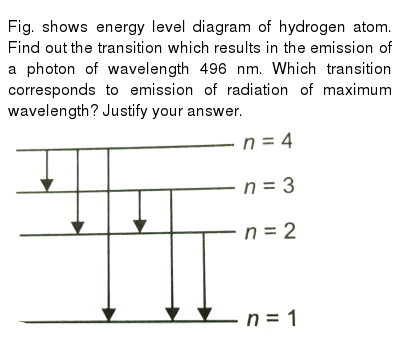
Fig Shows Energy Level Diagram Of Hydrogen Atom Find Out The Transition Which Results In The Emission Of A Photon Of Wavelength 496 Nm Which Transition Corresponds To Emission Of Radiation Of
Draw the first energy level. Draw the electrons in the energy levels according to the rules below. Keep track of how many electrons are put in each level and the number of electrons left to use. A Bohr diagram is a simplified visual representation of an atom that was developed by Danish physicist Niels Bohr in 1913.
(ii) Draw a diagram to show the electron transitions between energy levels in a hydrogen atom that are responsible for the two series of lines in the ultraviolet and visible regions of the spectrum. Label your diagram to show three transitions for each series.
MO Diagram for HF The AO energies suggest that the 1s orbital of hydrogen interacts mostly with a 2p orbital of fluorine. The F 2s is nonbonding. H-F nb σ σ* Energy H -13.6 eV 1s F -18.6 eV -40.2 eV 2s 2p So H-F has one σ bond and three lone electron pairs on fluorine
Hydrogen Spectrum - Wavelength, Diagram, Hydrogen Emission Spectrum. Hydrogen Spectrum introduction. We all know that electrons in an atom or a molecule absorb energy and get excited, they jump from a lower energy level to a higher energy level, and they emit radiation when they come back to their original states.
3:05 (Triple only) draw and explain energy level diagrams to represent exothermic and endothermic reactions The symbol ΔH is used to represent the change in heat (or enthalpy change) of a reaction. ΔH is measured in kJ/mol (kilojoules per mole).
Below is a blank energy level diagram which helps you depict electrons for any specific atom. At energy level 2, there are both s and p orbitals. The 2s has lower energy when compared to 2p. The three dashes in 2p subshells represent the same energy. 4s has lower energy when compared to 3d. Therefore, the order of energy level is as follows: s ...

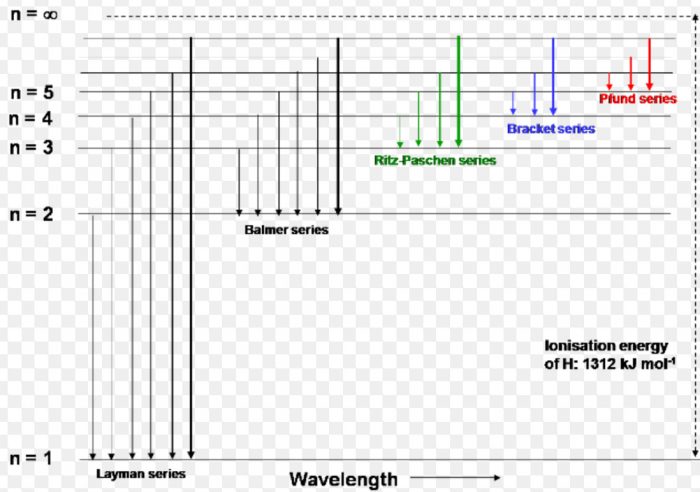
5 10 Draw Energy Level Diagram For Hydrogen Atom Showing At Least Four Lowest Energy Levels Show The Transitions Responsible For Emission Of Balmer Series 0 28 0 38 0 54 086 4 Energy Ev 1 5 1 3 W W Visible Visible 3 5 2 Balmer Series

Draw A Neat Labelled Energy Level Diagram For H Atom Showing The Transitions Explain The Series Of Spectral Lines For H Atom Whose Fixed Inner Orbit Numbers Are 3 And 4 Respectively

Draw A Neat Labelled Diagram Showing Energy Levels And Transition Between Them For The Hydrogen Atoms Physics Shaalaa Com

Draw Energy Level Diagram For Hydrogen Atom Showing At Least Four Lowest Energy Levels Show The Transitions Responsible For Physics Atoms 12318727 Meritnation Com

















0 Response to "41 draw and label an energy level diagram for hydrogen"
Post a Comment